Python WEB应用部署的实现方法
本文介绍了Python WEB应用部署的实现方法,分享给大家,具体如下:

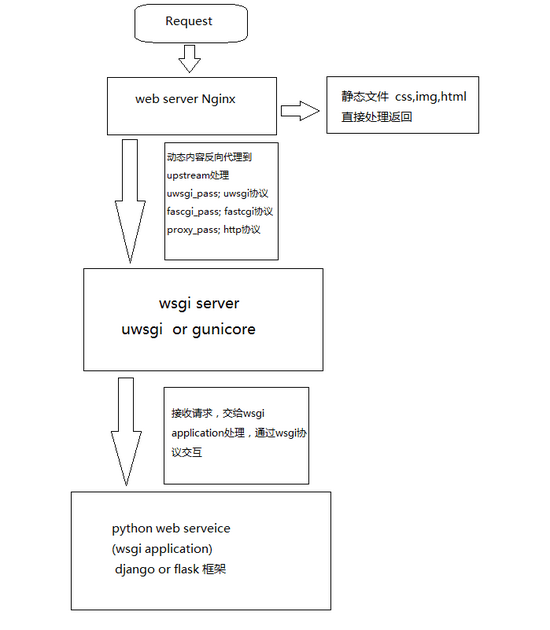
使用Apache模块mod_wsgi运行Python WSGI应用
Flask应用是基于WSGI规范的,所以它可以运行在任何一个支持WSGI协议的Web应用服务器中,最常用的就是 Apache+mod_wsgi 的方式
Apache主配置文件是/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
其他配置文件存储在/etc/httpd/conf.d/目录
安装mod_wsgi
安装httpd-devel
$ yum install httpd-devel $ rpm -ql httpd-devel
安装mod__wsgi
$ yum install mod_wsgi
安装完成之后, mod_wsgi.so 会在Apache的modules目录中
在 httpd.conf 文件中添加以下内容
LoadModule wsgi_module modules/mod_wsgi.so
重启Apache来启用配置
$ sudo service httpd restart
测试mod_wsgi
在Apache的DocumentRoot根目录下创建一个文件 test.wsgi
def application(environ, start_response):
status = '200 OK'
output = 'Hello World!'
response_headers = [('Content-type', 'text/plain'),
('Content-Length', str(len(output)))]
start_response(status, response_headers)
return [output]
这里的函数 application 即为WSGI应用对象,它返回的值就是该应用收到请求后的响应。
然后,再打开Apache的配置文件httpd.conf,在其最后加上URL路径映射:
WSGIScriptAlias /test /var/www/html/test.wsgi
测试 curl http://localhost/test

使用Python虚拟环境
virtualenv 是一个创建隔绝的Python环境的工具。virtualenv创建一个包含所有必要的可执行文件以及 pip 库的文件夹,用来使用Python工程所需的包。
配置app.wsgi
activate_this = '/var/www/html/py3env/bin/activate_this.py' execfile(activate_this, dict(__file__=activate_this)) from flask import Flask application = Flask(__name__) import sys sys.path.insert(0, '/var/www/flask_test') from app import app as application
我们的虚拟环境在目录 /var/www/html 下,你可以在其 /bin 子目录中找到启用脚本 activate_this.py 。在WSGI应用的一开始执行它即可。
apache配置文件
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/html/app.wsgi <Directory /var/www/html> Require all granted </Directory> </VirtualHost>!
参考
https://www.jb51.net/article/153875.htm
使用Nginx+uWSGI运行Python WSGI应用
uWSGI是一个Web应用服务器,它具有应用服务器,代理,进程管理及应用监控等功能。虽然uWSGI本身就可以直接用来当Web服务器,但一般建议将其作为应用服务器配合Nginx一起使用,这样可以更好的发挥Nginx在Web端的强大功能。
安装uWSGI
$ pip install uwsgi
创建 server.py
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello World!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
创建 uwsgi 配置文件 uwsgi.ini
[uwsgi] http=0.0.0.0:8080 #指定项目执行的端口号 chdir=/var/www/html/# 项目目录 wsgi-file=/var/www/html/server.py # 项目启动文件目录 callable=app #指定应用对象,WSGI标准是"application" master=true #主进程(监控其他进程状态,如果有进程死了,则重启) touch-reload=/var/www/html/ #监听的文件路径,当要监听的文件路径下的文件发生变化的时候自动重新加载服务器。 daemonize=uwsgi.log #日志文件 stats = 127.0.0.1:9090 #在指定的地址上,开启状态服务 vacuum = True # 当服务器退出的时候自动清理环境, # 多进程&多线程 processes = 6 threads = 2
启动
uwsgi --ini uwsgi.ini # 启动 uwsgi --reload uwsgi.pid # 重启 uwsgi --stop uwsgi.pid # 关闭

配置Nginx
将uWSGI的HTTP端口监听改为socket端口监听
socket=127.0.0.1:8080
修改nginx配置文件nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost 192.168.1.5;
#root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8080;
}
Nginx会将收到的所有请求都转发到 127.0.0.1:8080 端口上,即uWSGI服务器上。
这里有一个坑,由于Centos7 SElinux导致的权限问题,Nginx无法将请求转发到uWSGI,我直接把它关掉了。
vi /etc/selinux/config
把 SELINUX=enforcing 改成 SELINUX=disabled
重启nginx测试。

使用Python虚拟环境
[uwsgi] ... virtualenv=/home/Smi1e/virtualenv
部署多个应用

参考
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
相关文章

Python中列表遍历使用range和enumerate的区别讲解
这篇文章主要介绍了Python中列表遍历使用range和enumerate的区别,在Python编程语言中,遍历list有range和enumerate方法,本文结合示例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2022-12-12
django使用django-apscheduler 实现定时任务的例子
今天小编就为大家分享一篇django使用django-apscheduler 实现定时任务的例子,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。一起跟随小编过来看看吧2019-07-07












最新评论