ASP.NET Core Middleware的实现方法详解
概念
ASP.NET Core Middleware是在应用程序处理管道pipeline中用于处理请求和操作响应的组件。
每个组件:
- 在pipeline中判断是否将请求传递给下一个组件
- 在处理管道的下个组件执行之前和之后执行一些工作, HttpContxt对象能跨域请求、响应的执行周期
特性和行为
ASP.NET Core处理管道由一系列请求委托组成,一环接一环的被调用, 下面给出自己绘制的Middleware pipeline流程图:
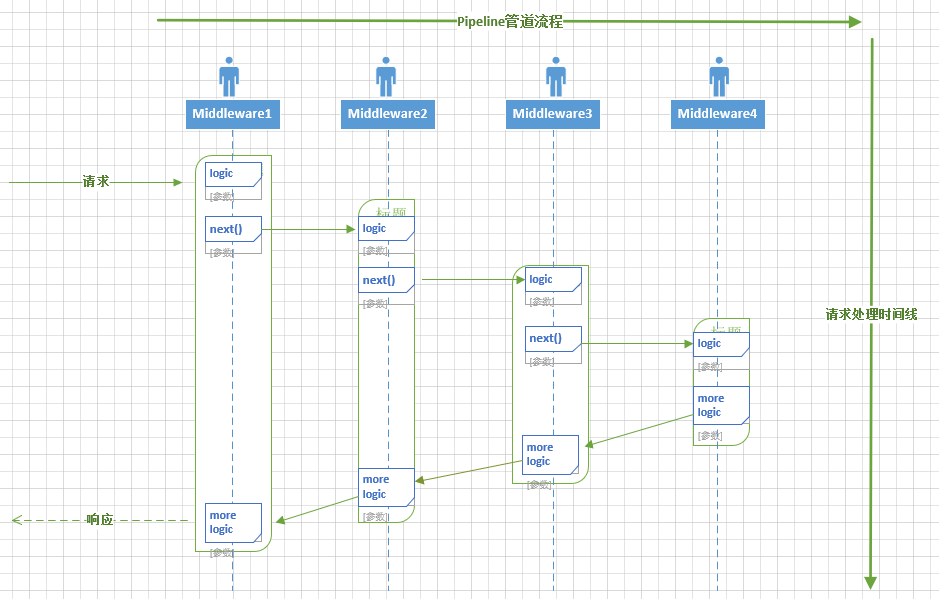
从上图可以看出,请求自进入处理管道,经历了四个中间件,每个中间件都包含后续紧邻中间件 执行委托(next)的引用,同时每个中间件在交棒之前和交棒之后可以自行决定参与一些Http请求和响应的逻辑处理。
每个中间件还可以决定不将请求转发给下一个委托,这称为请求管道的短路(短路是有必要的,某些专有中间件比如 StaticFileMiddleware 可以在完成功能之后,避免请求被转发到其他动态处理过程)。
源码实现
观察一个标准的中间件代码的写法和用法:
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Alyio.AspNetCore.ApiMessages;
using Gridsum.WebDissector.Common;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
namespace Gridsum.WebDissector
{
sealed class AuthorizationMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next; // 下一个中间件执行委托的引用
public AuthorizationMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public Task Invoke(HttpContext context) // 贯穿始终的HttpContext对象
{
if (context.Request.Path.Value.StartsWith("/api/"))
{
return _next(context);
}
if (context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated && context.User().DisallowBrowseWebsite)
{
throw new ForbiddenMessage("You are not allow to browse the website.");
}
return _next(context);
}
}
}
public static IApplicationBuilder UserAuthorization(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
return app.UseMiddleware<AuthorizationMiddleware>();
}
// 启用该中间件,也就是注册该中间件
app.UserAuthorization();
标准的中间件使用方式是如此简单明了,带着几个问题探究一下源码实现
(1).中间件传参是怎样完成的: app.UseMiddleware<Authorization>(AuthOption); 我们传参的时候,为什么能自动注入中间件构造函数非第1个参数
(2).编写中间件的时候,为什么必须要定义特定的 Invoke/InvokeAsync 函数?
(3).设定中间件的顺序很重要,中间件的嵌套顺序是怎么确定的 ?
思考以上标准中间件的行为: 输入下一个中间件的执行委托Next, 定义当前中间件的执行委托Invoke/InvokeAsync;
每个中间件完成了 Func<RequestDelegate,RequestDelegate>这样的行为;
通过参数next与下一个中间件的执行委托Invoke/InvokeAsync 建立"链式"关系。
public delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext context);
//-----------------节选自 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder.UseMiddlewareExtensions------------------
/// <summary>
/// Adds a middleware type to the application's request pipeline.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TMiddleware">The middleware type.</typeparam>
/// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param>
/// <param name="args">The arguments to pass to the middleware type instance's constructor.</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</returns>
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware<TMiddleware>(this IApplicationBuilder app, params object[] args)
{
return app.UseMiddleware(typeof(TMiddleware), args);
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds a middleware type to the application's request pipeline.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param>
/// <param name="middleware">The middleware type.</param>
/// <param name="args">The arguments to pass to the middleware type instance's constructor.</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</returns>
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder app, Type middleware, params object[] args)
{
if (typeof(IMiddleware).GetTypeInfo().IsAssignableFrom(middleware.GetTypeInfo()))
{
// IMiddleware doesn't support passing args directly since it's
// activated from the container
if (args.Length > 0)
{
throw new NotSupportedException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareExplicitArgumentsNotSupported(typeof(IMiddleware)));
}
return UseMiddlewareInterface(app, middleware);
}
var applicationServices = app.ApplicationServices;
return app.Use(next =>
{
var methods = middleware.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public); // 执行委托名称被限制为Invoke/InvokeAsync
var invokeMethods = methods.Where(m =>
string.Equals(m.Name, InvokeMethodName, StringComparison.Ordinal)
|| string.Equals(m.Name, InvokeAsyncMethodName, StringComparison.Ordinal)
).ToArray();
if (invokeMethods.Length > 1)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddleMutlipleInvokes(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName));
}
if (invokeMethods.Length == 0)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoInvokeMethod(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, middleware));
}
var methodInfo = invokeMethods[0];
if (!typeof(Task).IsAssignableFrom(methodInfo.ReturnType))
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNonTaskReturnType(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, nameof(Task)));
}
var parameters = methodInfo.GetParameters();
if (parameters.Length == 0 || parameters[0].ParameterType != typeof(HttpContext))
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoParameters(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, nameof(HttpContext)));
}
var ctorArgs = new object[args.Length + 1];
ctorArgs[0] = next;
Array.Copy(args, 0, ctorArgs, 1, args.Length); // 通过反射形成中间件实例的时候,构造函数第一个参数被指定为 下一个中间件的执行委托 var instance = ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(app.ApplicationServices, middleware, ctorArgs);
if (parameters.Length == 1)
{
return (RequestDelegate)methodInfo.CreateDelegate(typeof(RequestDelegate), instance);
}
// 当前执行委托除了可指定HttpContext参数以外, 还可以注入更多的依赖参数
var factory = Compile<object>(methodInfo, parameters);
return context =>
{
var serviceProvider = context.RequestServices ?? applicationServices;
if (serviceProvider == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareIServiceProviderNotAvailable(nameof(IServiceProvider)));
}
return factory(instance, context, serviceProvider);
};
});
}
//-------------------节选自 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder.Internal.ApplicationBuilder-------------------
private readonly IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components = new List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>();
publicIApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate,RequestDelegate>middleware)
{
this._components.Add(middleware);
return this;
}
public RequestDelegate Build()
{
RequestDelegate app = context =>
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 404;
return Task.CompletedTask;
};
foreach (var component in _components.Reverse())
{
app = component(app);
}
return app;
}
通过以上代码我们可以看出:
- 注册中间件的过程实际上,是给一个
Type= List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>的容器依次添加元素的过程; - 容器中每个元素对应每个中间件的行为委托
Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>, 这个行为委托包含2个关键行为:输入下一个中间件的执行委托next:RequestDelegate, 完成当前中间件的Invoke函数: RequestDelegate; - 通过build方法完成前后中间件的链式传值关系
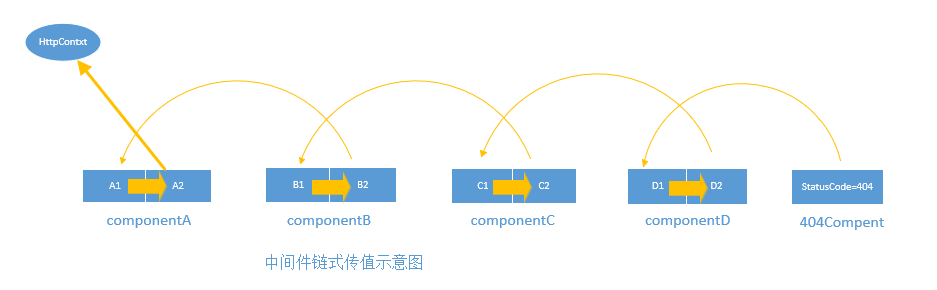
分析源码:回答上面的问题:
- 使用反射构造中间件的时候,第一个参数Array[0] 是下一个中间件的执行委托
- 当前中间件执行委托 函数名称被限制为: Invoke/InvokeAsync, 函数支持传入除HttpContext之外的参数
- 按照代码顺序添加进入 _components容器, 通过后一个中间件的执行委托 -----(指向)----> 前一个中间件的输入执行委托建立链式关系。
附:非标准中间件的用法
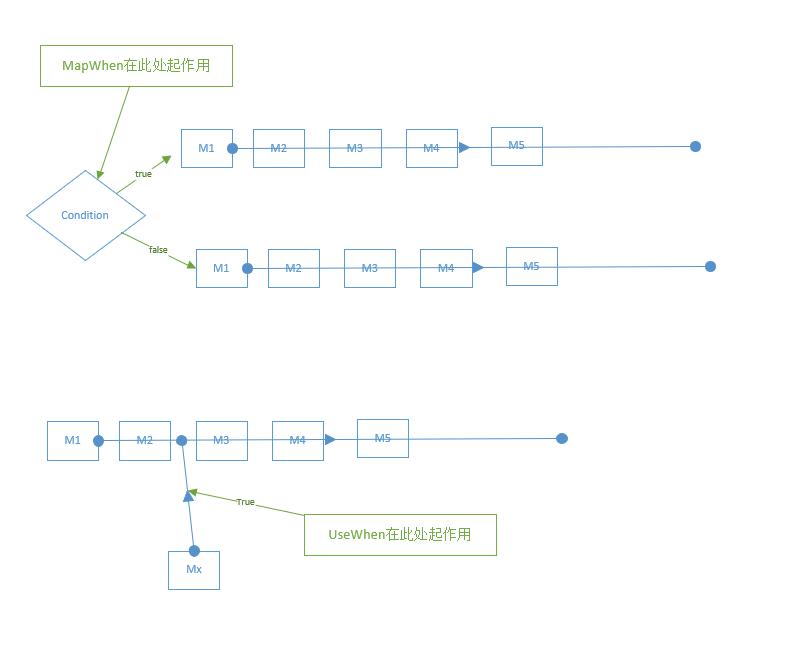
短路中间件、 分叉中间件
整个处理管道的形成,存在一些管道分叉或者临时插入中间件的行为,一些重要方法可供使用
- Use方法是一个注册中间件的简便写法
- Run方法是一个约定,一些中间件使用Run方法来完成管道的结尾
- Map扩展方法:请求满足指定路径,将会执行分叉管道,强调满足 path
- MapWhen方法:HttpContext满足条件,将会执行分叉管道:
- UseWhen方法:选择性的注入中间件
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对脚本之家的支持。
- 详解ASP.NET Core中间件Middleware
- 理解ASP.NET Core 中间件(Middleware)
- 探究ASP.NET Core Middleware实现方法
- ASP.NET Core应用错误处理之StatusCodePagesMiddleware中间件针对响应码呈现错误页面
- ASP.NET Core应用错误处理之ExceptionHandlerMiddleware中间件呈现“定制化错误页面”
- ASP.NET Core应用错误处理之DeveloperExceptionPageMiddleware中间件呈现“开发者异常页面”
- 利用Asp.Net Core的MiddleWare思想如何处理复杂业务流程详解
- ASP.NET Core使用Middleware设置有条件允许访问路由
相关文章

asp.net页面与页面之间传参数值方法(post传值和get传值)
这篇文章主要介绍了asp.net页面与页面之间传参数值方法,说明了post传值和get传值的使用方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2014-02-02
关于服务器或虚拟主机不支持 AjaxPro 的问题终极解决方法
asp.net的网站,访问时提示不支持 AjaxPro,那就因为误删的映射导致,可以通过下面的方法解决2012-03-03
.Net创建Excel文件(插入数据、修改格式、生成图表)的方法
2012-01-01












最新评论