Spring实现拥有者权限验证的方法示例
问题描述
在做权限验证的时候,我们经常会遇到这样的情况:教师拥有多个学生,但是在处理学生信息的时候,教师只能操作自己班级的学生。所以,我们要做的就是,当教师尝试处理别的班的学生的时候,抛出异常。
实体关系
用户1:1教师,教师m:n班级,班级1:n学生

实现思路
以findById为例。因为从整体上看,用户和学生是m:n的关系,所以在调用这个接口的时候,获取该学生的所有用户,然后跟当前登录用户进行对比,如果不在其中,抛出异常。
利用切面,我们可以在findById、update、delete方法上进行验证。
注解
我们会在方法上添加注解,以表示对该方法进行权限验证。
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 注解使用在方法上
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 运行时生效
public @interface AuthorityAnnotation {
/**
* 仓库名
*/
@Required
Class repository();
}
因为我们需要获取出学生,但是并不限于学生,所以就要将仓库repository作为一个参数传入。
实体
上面我们说过,需要获取学生中的用户,所以我们可以在实体中定义一个方法,获取所有有权限的用户:getBelongUsers()
但是,我们知道,学生和用户没用直接的关系,而且为了复用,在对其他实体进行验证的时候也能使用,可以考虑创建一个接口,让需要验证的实体去实现他。
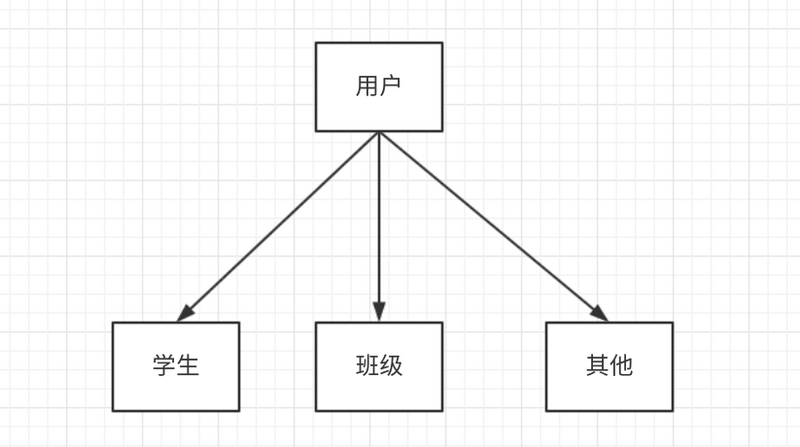
这样,我们可以在让每个实体都集成这个接口,然后形成链式调用,这样就解决了上面你的两个问题。
public interface BaseEntity {
List<User> getBelongToUsers();
}
教师:
@Entity
public class Teacher implements YunzhiEntity, BaseEntity {
...
@Override
public List<User> getBelongToUsers() {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(this.getUser());
return userList;
}
}
班级:
@Entity
public class Klass implements BaseEntity {
...
@Override
public List<User> getBelongToUsers() {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Teacher teacher: this.getTeacherList()) {
userList.addAll(teacher.getBelongToUsers());
}
return userList;
}
}
学生:
@Entity
public class Student implements BaseEntity {
...
@Override
public List<User> getBelongToUsers() {
return this.getKlass().getBelongToUsers();
}
}
切面
有了实体后,我们就可以建立切面实现验证功能了。
@Aspect
@Component
public class OwnerAuthorityAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OwnerAuthorityAspect.class.getName());
/**
* 使用注解,并第一个参数为id
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.yunzhiclub.alice.annotation.AuthorityAnnotation) && args(id,..) && @annotation(authorityAnnotation)")
public void doAccessCheck(Long id, AuthorityAnnotation authorityAnnotation) { }
@Before("doAccessCheck(id, authorityAnnotation)")
public void before(Long id, AuthorityAnnotation authorityAnnotation) {
}
首先,我们要获取到待操作对象。但是在获取对象之前,我们必须获取到repository。
这里我们利用applicationContext来获取仓库bean,然后再利用获取到的bean,生成repository对象。
@Aspect
@Component
public class OwnerAuthorityAspect implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext = null; // 初始化上下文
......
@Before("doAccessCheck(id, authorityAnnotation)")
public void before(Long id, AuthorityAnnotation authorityAnnotation) {
logger.debug("获取注解上的repository, 并通过applicationContext来获取bean");
Class<?> repositoryClass = authorityAnnotation.repository();
Object object = applicationContext.getBean(repositoryClass);
logger.debug("将Bean转换为CrudRepository");
CrudRepository<BaseEntity, Object> crudRepository = (CrudRepository<BaseEntity, Object>)object;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
该类实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,通过setApplicationContext函数获取到了applicationContext。
接下来,就是利用repository获取对象,然后获取他的所属用户,再与当前登录用户进行比较。
@Before("doAccessCheck(id, authorityAnnotation)")
public void before(Long id, AuthorityAnnotation authorityAnnotation) {
logger.debug("获取注解上的repository, 并通过applicationContext来获取bean");
Class<?> repositoryClass = authorityAnnotation.repository();
Object object = applicationContext.getBean(repositoryClass);
logger.debug("将Bean转换为CrudRepository");
CrudRepository<BaseEntity, Object> crudRepository = (CrudRepository<BaseEntity, Object>)object;
logger.debug("获取实体对象");
Optional<BaseEntity> baseEntityOptional = crudRepository.findById(id);
if(!baseEntityOptional.isPresent()) {
throw new RuntimeException("对不起,未找到相关的记录");
}
BaseEntity baseEntity = baseEntityOptional.get();
logger.debug("获取登录用户以及拥有者,并进行比对");
List<User> belongToTUsers = baseEntity.getBelongToUsers();
User currentLoginUser = userService.getCurrentLoginUser();
Boolean havePermission = false;
if (currentLoginUser != null && belongToTUsers.size() != 0) {
for (User user: belongToTUsers) {
if (user.getId().equals(currentLoginUser.getId())) {
havePermission = true;
break;
}
}
if (!havePermission) {
throw new RuntimeException("权限不允许");
}
}
}
使用
在控制器的方法上使用注解:@AuthorityAnnotation,传入repository。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
private final StudentService studentService; // 学生
@Autowired
public StudentController(StudentService studentService) {
this.studentService = studentService;
}
/**
* 通过id获取学生
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@AuthorityAnnotation(repository = StudentRepository.class)
@GetMapping("/{id}")
@JsonView(StudentJsonView.get.class)
public Student findById(@PathVariable Long id) {
return studentService.findById(id);
}
}
出现的问题
实现之后,进行单元测试的过程中出现了问题。
@Test
public void update() throws Exception {
logger.info("获取一个保存学生");
Student student = studentService.getOneSaveStudent();
Long id = student.getId();
logger.info("获取一个更新学生");
Student newStudent = studentService.getOneUnSaveStudent();
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(newStudent);
logger.info("发送更新请求");
this.mockMvc
.perform(put(baseUrl + "/" + id)
.cookie(this.cookie)
.content(jsonString)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
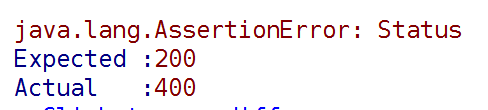
400的错误,说明参数错误,参数传的是实体,看下传了什么:

我们看到,这个字段并不是我们实体中的字段,但是为什么序列化的时候出现了这个字段呢?
原因是这样的,我们在实体中定义了一个getBelongToUsers函数,然后JSONobject在进行序列化的时候会根据实体中的getter方法,获取get后面的为key,也就是将belongToUsers看做了字段。
所以就出现了上面传实体字段多出的情况,从而引发了400的错误。
解决
我们不想JSONobject在序列化的时候处理getBelongToUsers,就需要声明一下,这里用到了注解:@JsonIgnore。这样在序列化的时候就会忽略它。
@Entity
public class Student implements BaseEntity {
......
@JsonIgnore
@Override
public List<User> getBelongToUsers() {
return this.getKlass().getBelongToUsers();
}
}
修改后的学生实体如上,其他实现了getBelongToUsers方法的,都需要做相同处理。
总结
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
相关文章

Java安全框架——Shiro的使用详解(附springboot整合Shiro的demo)
这篇文章主要介绍了Java安全框架——Shiro的使用详解,帮助大家更好的理解和学习使用Shiro,感兴趣的朋友可以了解下2021-04-04












最新评论