基于spring boot 2和shiro实现身份验证案例
Shiro是一个功能强大且易于使用的Java安全框架,官网:https://shiro.apache.org/。
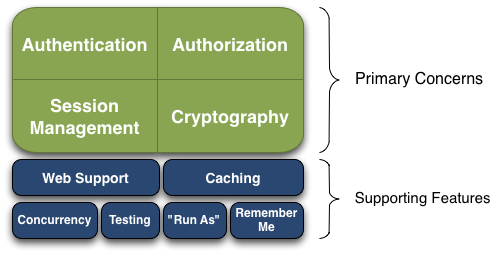
主要功能有身份验证、授权、加密和会话管理。
其它特性有Web支持、缓存、测试支持、允许一个用户用另一个用户的身份进行访问、记住我。
Shiro有三个核心组件:Subject,SecurityManager和 Realm。
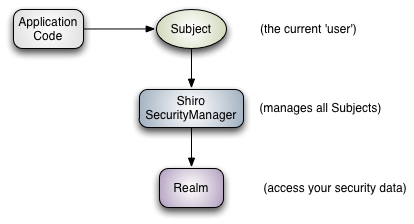
Subject:即当前操作“用户”,“用户”并不仅仅指人,也可以是第三方进程、后台帐户或其他类似事物。
SecurityManager:安全管理器,Shiro框架的核心,通过SecurityManager来管理所有Subject,并通过它来提供安全管理的各种服务。
Realm:域,充当了Shiro与应用安全数据间的“桥梁”或者“连接器”。也就是说,当对用户执行认证(登录)和授权(访问控制)验证时,Shiro会从应用配置的Realm中查找用户及其权限信息。当配置Shiro时,必须至少指定一个Realm,用于认证和(或)授权。
Spring Boot 中整合Shiro,根据引入的依赖包shiro-spring和shiro-spring-boot-web-starter(当前版本都是1.4.2)不同有两种不同方法。
方法一:引入依赖包shiro-spring
1、IDEA中创建一个新的SpringBoot项目,pom.xml引用的依赖包如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
2、创建Realm和配置shiro
(1)创建Realm
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
public class MyRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
/**权限信息,暂不实现*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
/**身份认证:验证用户输入的账号和密码是否正确。*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//获取用户输入的账号
String userName = (String) token.getPrincipal();
//验证用户admin和密码123456是否正确
if (!"admin".equals(userName)) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("账户不存在!");
}
SimpleAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(userName, "123456", getName());
return authenticationInfo;
//实际项目中,上面账号从数据库中获取用户对象,再判断是否存在
/*User user = userService.findByUserName(userName);
if (user == null) {
throw new UnknownAccountException("账户不存在!");
}
SimpleAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPassword(), getName());
return authenticationInfo;
*/
}
}
(2)配置Shiro
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;
import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
@Bean
MyRealm myRealm() {
return new MyRealm();
}
@Bean
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager() {
DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
manager.setRealm(myRealm());
return manager;
}
@Bean
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean() {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager());
//如果不设置默认会自动寻找Web工程根目录下的"/login.jsp"页面
bean.setLoginUrl("/login");
//登录成功后要跳转的链接
bean.setSuccessUrl("/index");
//未授权界面
bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/403");
//配置不会被拦截的链接
Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("/doLogin", "anon");
map.put("/**", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return bean;
}
}
3、控制器测试方法
package com.example.demo.controller;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
return "登录页面...";
}
@PostMapping("/doLogin")
public String doLogin(String userName, String password) {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(userName, password));
return "登录成功!";
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
return e.getMessage();
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
return "登陆失败,密码错误!";
}
}
//如果没有先登陆,访问会跳到/login
@GetMapping("/index")
public String index() {
return "index";
}
@GetMapping("/403")
public String unauthorizedRole(){
return "没有权限";
}
}
方法二:引入依赖包shiro-spring-boot-web-starter
1、pom.xml中删除shiro-spring,引入shiro-spring-boot-web-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
2、创建Realm和配置shiro
(1)创建Realm,代码和方法一的一样。
(2)配置Shiro
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.config.DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.config.ShiroFilterChainDefinition;
import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
@Bean
MyRealm myRealm() {
return new MyRealm();
}
@Bean
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager() {
DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
manager.setRealm(myRealm());
return manager;
}
@Bean
ShiroFilterChainDefinition shiroFilterChainDefinition() {
DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition definition = new DefaultShiroFilterChainDefinition();
definition.addPathDefinition("/doLogin", "anon");
definition.addPathDefinition("/**", "authc");
return definition;
}
}
(3)application.yml配置
shiro: unauthorizedUrl: /403 successUrl: /index loginUrl: /login
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
相关文章

Spring Boot2解决idea console 控制台输出乱码的问题
这篇文章主要介绍了Spring Boot2解决idea console 控制台输出乱码的问题,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教2021-07-07
IDEA设置生成带注释的getter和setter的图文教程
通常我们用idea默认生成的getter和setter方法是不带注释的,当然,我们同样可以设置idea像MyEclipse一样生成带有Javadoc的模板,具体设置方法,大家参考下本文2018-05-05












最新评论