php并发加锁问题分析与设计代码实例讲解
在工作项目中,会遇到一些php并发访问去修改一个数据问题,如果这个数据不加锁,就会造成数据的错误。下面我将分析一个财务支付锁的问题。希望对大家有所帮助。
1 没有应用锁机制
1.1 财务支付简化版本代码
<!--?php
/**
* pay.php
*
* 支付没有应用锁
*
* Copy right (c) 2016
*
* modification history:
* --------------------
* 2018/9/10, by CleverCode, Create
*
*/
//用户支付
function pay($userId,$money)
{
if(false == is_int($userId) || false == is_int($money))
{
return false;
}
//取出总额
$total = getUserLeftMoney($userId);
//花费大于剩余
if($money --> $total)
{
return false;
}
//余额
$left = $total - $money;
//更新余额
return setUserLeftMoney($userId,$left);
}
//取出用户的余额
function getUserLeftMoney($userId)
{
if(false == is_int($userId))
{
return 0;
}
$sql = "select account form user_account where userid = ${userId}";
//$mysql = new mysql();//mysql数据库
return $mysql->query($sql);
}
//更新用户余额
function setUserLeftMoney($userId,$money)
{
if(false == is_int($userId) || false == is_int($money))
{
return false;
}
$sql = "update user_account set account = ${money} where userid = ${userId}";
//$mysql = new mysql();//mysql数据库
return $mysql->execute($sql);
}
?>
1.2 问题分析
如果有两个操作人(p和m),都用用户编号100账户,分别在pc和手机端同时登陆,100账户总余额有1000,p操作人花200,m操作人花300。并发过程如下。
p操作人:
取出用户的余额1000。
支付后剩余 800 = 1000 - 200。
更新后账户余额800。
m操作人:
取出用户余额1000。
支付后剩余700 = 1000 - 300。
支付后账户余额700。
两次支付后,账户的余额居然还有700,应该的情况是花费了500,账户余额500才对。造成这个现象的根本原因,是并发的时候,p和m同时操作取到的余额数据都是1000。
2 加锁设计
锁的操作一般只有两步,一 获取锁(getLock);二是释放锁(releaseLock)。但现实锁的方式有很多种,可以是文件方式实现;sql实现;Memcache实现;根据这种场景我们考虑使用策略模式。
2.1 类图设计如下
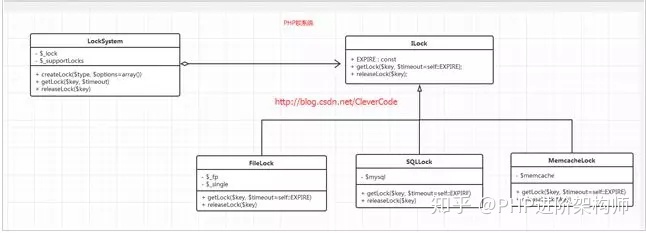
2.2 php源码设计如下
LockSystem.php
<!--?php
/**
* LockSystem.php
*
* php锁机制
*
* Copy right (c) 2018
*
* modification history:
* --------------------
* 2018/9/10, by CleverCode, Create
*
*/
class LockSystem
{
const LOCK_TYPE_DB = 'SQLLock';
const LOCK_TYPE_FILE = 'FileLock';
const LOCK_TYPE_MEMCACHE = 'MemcacheLock';
private $_lock = null;
private static $_supportLocks = array('FileLock', 'SQLLock', 'MemcacheLock');
public function __construct($type, $options = array())
{
if(false == empty($type))
{
$this--->createLock($type, $options);
}
}
public function createLock($type, $options=array())
{
if (false == in_array($type, self::$_supportLocks))
{
throw new Exception("not support lock of ${type}");
}
$this->_lock = new $type($options);
}
public function getLock($key, $timeout = ILock::EXPIRE)
{
if (false == $this->_lock instanceof ILock)
{
throw new Exception('false == $this->_lock instanceof ILock');
}
$this->_lock->getLock($key, $timeout);
}
public function releaseLock($key)
{
if (false == $this->_lock instanceof ILock)
{
throw new Exception('false == $this->_lock instanceof ILock');
}
$this->_lock->releaseLock($key);
}
}
interface ILock
{
const EXPIRE = 5;
public function getLock($key, $timeout=self::EXPIRE);
public function releaseLock($key);
}
class FileLock implements ILock
{
private $_fp;
private $_single;
public function __construct($options)
{
if (isset($options['path']) && is_dir($options['path']))
{
$this->_lockPath = $options['path'].'/';
}
else
{
$this->_lockPath = '/tmp/';
}
$this->_single = isset($options['single'])?$options['single']:false;
}
public function getLock($key, $timeout=self::EXPIRE)
{
$startTime = Timer::getTimeStamp();
$file = md5(__FILE__.$key);
$this->fp = fopen($this->_lockPath.$file.'.lock', "w+");
if (true || $this->_single)
{
$op = LOCK_EX + LOCK_NB;
}
else
{
$op = LOCK_EX;
}
if (false == flock($this->fp, $op, $a))
{
throw new Exception('failed');
}
return true;
}
public function releaseLock($key)
{
flock($this->fp, LOCK_UN);
fclose($this->fp);
}
}
class SQLLock implements ILock
{
public function __construct($options)
{
$this->_db = new mysql();
}
public function getLock($key, $timeout=self::EXPIRE)
{
$sql = "SELECT GET_LOCK('".$key."', '".$timeout."')";
$res = $this->_db->query($sql);
return $res;
}
public function releaseLock($key)
{
$sql = "SELECT RELEASE_LOCK('".$key."')";
return $this->_db->query($sql);
}
}
class MemcacheLock implements ILock
{
public function __construct($options)
{
$this->memcache = new Memcache();
}
public function getLock($key, $timeout=self::EXPIRE)
{
$waitime = 20000;
$totalWaitime = 0;
$time = $timeout*1000000;
while ($totalWaitime < $time && false == $this->memcache->add($key, 1, $timeout))
{
usleep($waitime);
$totalWaitime += $waitime;
}
if ($totalWaitime >= $time)
throw new Exception('can not get lock for waiting '.$timeout.'s.');
}
public function releaseLock($key)
{
$this->memcache->delete($key);
}
}
3 应用锁机制
3.1 支付系统应用锁
<!--?php
/**
* pay.php
*
* 支付应用锁
*
* Copy right (c) 2018
*
* modification history:
* --------------------
* 2018/9/10, by CleverCode, Create
*
*/
//用户支付
function pay($userId,$money)
{
if(false == is_int($userId) || false == is_int($money))
{
return false;
}
try
{
//创建锁(推荐使用MemcacheLock)
$lockSystem = new LockSystem(LockSystem::LOCK_TYPE_MEMCACHE);
//获取锁
$lockKey = 'pay'.$userId;
$lockSystem--->getLock($lockKey,8);
//取出总额
$total = getUserLeftMoney($userId);
//花费大于剩余
if($money > $total)
{
$ret = false;
}
else
{
//余额
$left = $total - $money;
//更新余额
$ret = setUserLeftMoney($userId,$left);
}
//释放锁
$lockSystem->releaseLock($lockKey);
}
catch (Exception $e)
{
//释放锁
$lockSystem->releaseLock($lockKey);
}
}
//取出用户的余额
function getUserLeftMoney($userId)
{
if(false == is_int($userId))
{
return 0;
}
$sql = "select account form user_account where userid = ${userId}";
//$mysql = new mysql();//mysql数据库
return $mysql->query($sql);
}
//更新用户余额
function setUserLeftMoney($userId,$money)
{
if(false == is_int($userId) || false == is_int($money))
{
return false;
}
$sql = "update user_account set account = ${money} where userid = ${userId}";
//$mysql = new mysql();//mysql数据库
return $mysql->execute($sql);
}
?>
3.2 锁分析
p操作人:
获取锁:pay100
取出用户的余额1000。
支付后剩余 800 = 1000 - 200。
更新后账户余额800。
释放锁:pay100
m操作人:
1、等待锁:pay100
2、获取锁:pay100
3、获取余额:800
3、支付后剩余500 = 800 - 300。
5、支付后账户余额500。
6、释放锁:pay100
两次支付后,余额500。非常完美了解决了并发造成的临界区资源的访问问题。
到此这篇关于php并发加锁问题分析与设计代码实例讲解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关php并发加锁问题分析与设计内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

Laravel学习教程之request validation的编写
这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于Laravel学习教程之request validation编写的相关资料,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧。2017-10-10












最新评论