python 实现多线程的三种方法总结
1._thread.start_new_thread(了解)
import threading
import time
import _thread
def job():
print("这是一个需要执行的任务。。。。。")
print("当前线程的个数:", threading.active_count() )
print("当前线程的信息:", threading.current_thread())
time.sleep(100)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建多线程时, 需要制定该线程执行的任务
_thread.start_new_thread(job, ())
_thread.start_new_thread(job, ())
job()
2.threading.Thread
import threading
import time
def job():
print("这是一个需要执行的任务。。。。。")
print("当前线程的个数:", threading.active_count() )
time.sleep(1)
print("当前线程的信息:", threading.current_thread())
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建多线程时, 需要制定该线程执行的任务.name线程名字 target目标函数名
t1 = threading.Thread(target=job,name='job1')
t2 = threading.Thread(target=job,name='job2')
t1.start()
t2.start()
print(threading.active_count())
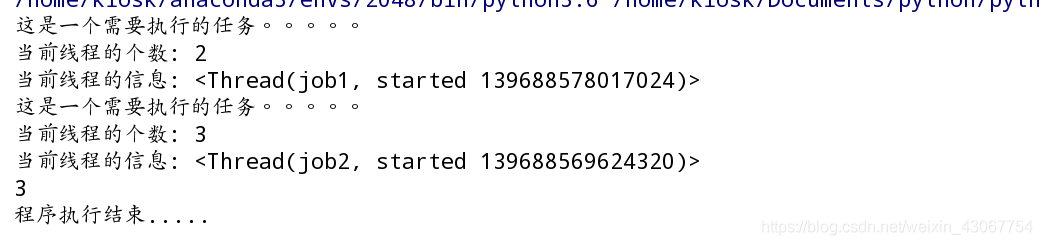
print("程序执行结束.....")
输出:
这是一个需要执行的任务。。。。。
当前线程的个数: 3
这是一个需要执行的任务。。。。。
3
程序执行结束.....
当前线程的个数: 3
当前线程的信息: <Thread(job1, started 140416648140544)>
当前线程的信息: <Thread(job2, started 140416639747840)>
出现的问题: 主线程执行结束, 但是子线程还在运行。
join()方法可以等待所有的子线程执行结束之后, 再执行主线程。
import threading
import time
def job():
print("这是一个需要执行的任务。。。。。")
print("当前线程的个数:", threading.active_count() )
print("当前线程的信息:", threading.current_thread())
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建多线程时, 需要制定该线程执行的任务.name线程名字 target目标函数名
t1 = threading.Thread(target=job,name='job1')
t2 = threading.Thread(target=job,name='job2')
t1.start()
t2.start()
print(threading.active_count())
# 出现的问题: 主线程执行结束, 但是子线程还在运行。
# 等待所有的子线程执行结束之后, 再执行主线程
t1.join()
t2.join()
print("程序执行结束.....")
之前写过一个简单爬虫的实验,现在希望获取十个ip的城市和国家
-不使用多线程
import time
from urllib.request import urlopen
# 记录时间的装饰器
def timeit(f):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
res = f(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
print("%s函数运行时间:%.2f" % (f.__name__, end_time - start_time))
return res
return wrapper
def get_addr(ip):
url = "http://ip-api.com/json/%s" % (ip)
urlObj = urlopen(url)
# 服务端返回的页面信息, 此处为字符串类型
pageContent = urlObj.read().decode('utf-8')
# 2. 处理Json数据
import json
# 解码: 将json数据格式解码为python可以识别的对象;
dict_data = json.loads(pageContent)
print("""
%s
所在城市: %s
所在国家: %s
""" % (ip, dict_data['city'], dict_data['country']))
@timeit
def main():
ips = ['12.13.14.%s' % (i + 1) for i in range(10)]
for ip in ips:
get_addr(ip)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()

时间需要138.91秒。
-使用多线程
import threading
import time
from urllib.request import urlopen
def timeit(f):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
res = f(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
print("%s函数运行时间:%.2f" % (f.__name__, end_time - start_time))
return res
return wrapper
def get_addr(ip):
url = "http://ip-api.com/json/%s" % (ip)
urlObj = urlopen(url)
# 服务端返回的页面信息, 此处为字符串类型
pageContent = urlObj.read().decode('utf-8')
# 2. 处理Json数据
import json
# 解码: 将json数据格式解码为python可以识别的对象;
dict_data = json.loads(pageContent)
print("""
%s
所在城市: %s
所在国家: %s
""" % (ip, dict_data['city'], dict_data['country']))
@timeit
def main():
ips = ['12.13.14.%s' % (i + 1) for i in range(10)]
threads = []
for ip in ips:
# 实例化10个对象,target=目标函数名,args=目标函数参数(元组格式)
t = threading.Thread(target=get_addr, args=(ip, ))
threads.append(t)
t.start()
# 等待所有子线程结束再运行主线程
[thread.join() for thread in threads]
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()


3.重写run方法
重写run方法, 实现多线程, 因为start方法执行时, 调用的是run方法;run方法里面编写的内容就是你要执行的任务;
import threading
import time
# 重写一个类,继承于threading.Thread
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, jobName):
super(MyThread, self).__init__()
self.jobName = jobName
# 重写run方法, 实现多线程, 因为start方法执行时, 调用的是run方法;
# run方法里面编写的内容就是你要执行的任务;
def run(self):
print("这是一个需要执行的任务%s。。。。。" %(self.jobName))
print("当前线程的个数:", threading.active_count() )
time.sleep(1)
print("当前线程的信息:", threading.current_thread())
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = MyThread("name1")
t2 = MyThread("name2")
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print("程序执行结束.....")
重写run方法实现刚才爬虫多线程案例
import threading
import time
from urllib.request import urlopen
def timeit(f):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
res = f(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
print("%s函数运行时间:%.2f" % (f.__name__, end_time - start_time))
return res
return wrapper
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, ip):
super(MyThread, self).__init__()
self.ip = ip
def run(self):
url = "http://ip-api.com/json/%s" % (self.ip)
urlObj = urlopen(url)
# 服务端返回的页面信息, 此处为字符串类型
pageContent = urlObj.read().decode('utf-8')
# 2. 处理Json数据
import json
# 解码: 将json数据格式解码为python可以识别的对象;
dict_data = json.loads(pageContent)
print("""
%s
所在城市: %s
所在国家: %s
""" % (self.ip, dict_data['city'], dict_data['country']))
@timeit
def main():
ips = ['12.13.14.%s' % (i + 1) for i in range(10)]
threads = []
for ip in ips:
# 实例化自己重写的类
t = MyThread(ip)
threads.append(t)
t.start()
[thread.join() for thread in threads]
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
相关文章

用Python中的__slots__缓存资源以节省内存开销的方法
这篇文章主要介绍了用Python中的__slots__通过缓存资源的方式以节省内存开销的方法,且示例代码非常简单,需要的朋友可以参考下2015-04-04
python3中datetime库,time库以及pandas中的时间函数区别与详解
这篇文章主要介绍了python3中datetime库,time库以及pandas中的时间函数区别与详解,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧2020-04-04












最新评论