Android入门教程之Fragment的具体使用详解
Fragment 的简单用法
Fragment 是一种可以嵌入在 Activity 当中的 UI 片段,它能让程序更加合理和充分地利用大屏幕的空间,因此在平板上应用非常广泛
在一个 Activity 中添加两个 Fragment,并让两个 Fragment 平分 Activity 的空间,首先新建一个左侧 Fragment 的布局 left_fragment.xml,这个布局只放置了一个按钮
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="Button" />
</LinearLayout>
然后新建一个右侧 Fragment 的布局 right_fragment.xml,将背景色设置成绿色,并放置一个 TextView 用于显示一段文本
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#00ff00"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:text="This is right fragment" />
</LinearLayout>
接着新建一个 LeftFragment 类,并让它继承自 Fragment,注意这里要使用 AndroidX 库中的 Fragment,将刚刚定义的两个布局动态加载进来
class LeftFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.left_fragment, container, false)
}
}
class RightFragment : Fragment() {
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.right_fragment, container, false)
}
}
接下来修改 activity_main.xml 中的代码,使用 <fragment> 标签在布局中添加 Fragment
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/leftFrag"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/rightFrag"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest.RightFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
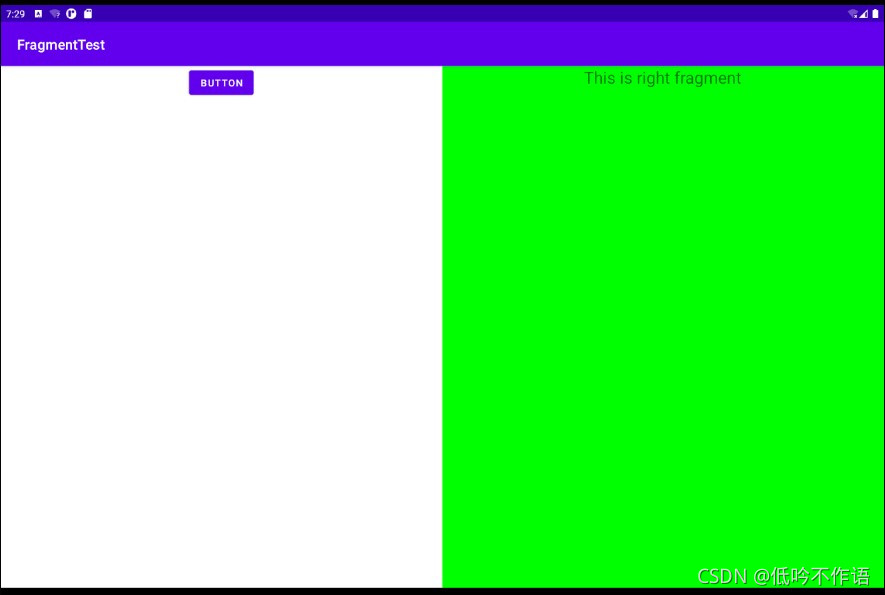
动态加载 Fragment
Fragment 真正强大之处在于,它可以在程序运行时根据具体情况来动态添加 Fragment,使得程序界面更加多样化
修改 activity_main.xml 的代码,使用 FrameLayout 布局,所有的空间都会默认摆放在布局的左上角,由于这里仅需要在布局里放入一个 Fragment,不需要任何定位,因此适合使用 FragLayout
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/leftFrag"
android:name="com.example.fragmenttest.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/rightLayout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
修改 MainActivity 中的代码,实现动态添加 Fragment 的功能,给左侧 Fragment 的按钮注册一个点击事件,会动态加载右侧 Fragment
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
button.setOnClickListener {
replaceFragment(RightFragment())
}
}
private fun replaceFragment(fragment: Fragment) {
val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager
val transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction()
transaction.replace(R.id.rightLayout, fragment)
transaction.commit()
}
}
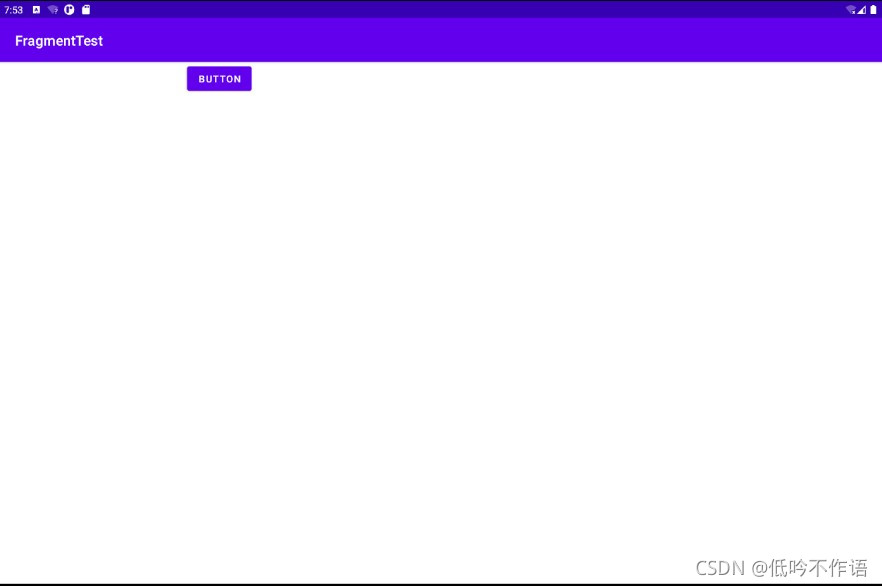
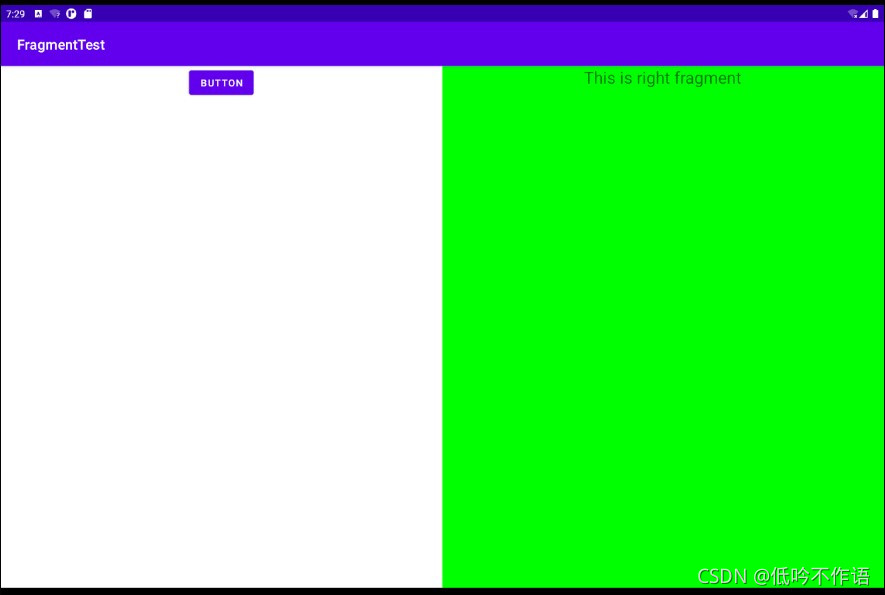
Fragment 实现返回栈
在上一节,通过点击按钮加载一个 Fragment 之后,按下 Back 键程序就会直接退出,如果我们希望实现类似返回栈的效果,按下 Back 键可以返回
FragmentTransaction 中提供了一个 addToBackStack() 方法,可以用于将一个事务添加到返回栈中,修改 MainActivity 中的代码
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
button.setOnClickListener {
replaceFragment(RightFragment())
}
}
private fun replaceFragment(fragment: Fragment) {
val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager
val transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction()
transaction.replace(R.id.rightLayout, fragment)
transaction.addToBackStack(null)
transaction.commit()
}
}
我们在事务提交之前调用了 FragmentTransaction 的 addToBackStack() 方法,它可以接收一个名字用于描述返回栈的状态,一般传入 null 即可。现在重新运行程序,点击按钮加载右侧 Fragment,然后按下 Back 键,程序不会立刻退出,而是返回上一状态
Fragment 和 Activity 之间的交互
为了方便 Fragment 和 Activity 之间进行交互,FragmentManager 提供了一个类似于 findViewById() 的方法,专门用于从布局文件中获取 Fragment 的实例
supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.leftFrag) as LeftFragment
那么在 Fragment 中又该怎么调用 Activity 里的方法呢?在每个 Fragment 中都可以通过调用 getActivity() 方法来得到和当前 Fragment 相关联的 Activity 实例
if (activity != null) {
val mainActivity = activity as MainActivity
}
不同的 Fragment 之间也可以通信,基本思路是:首先在一个 Fragment 中得到与它相关联的 Activity,然后再通过这个 Activity 去获取另外一个 Fragment 实例,就实现了不同的 Fragment 之间的通信了
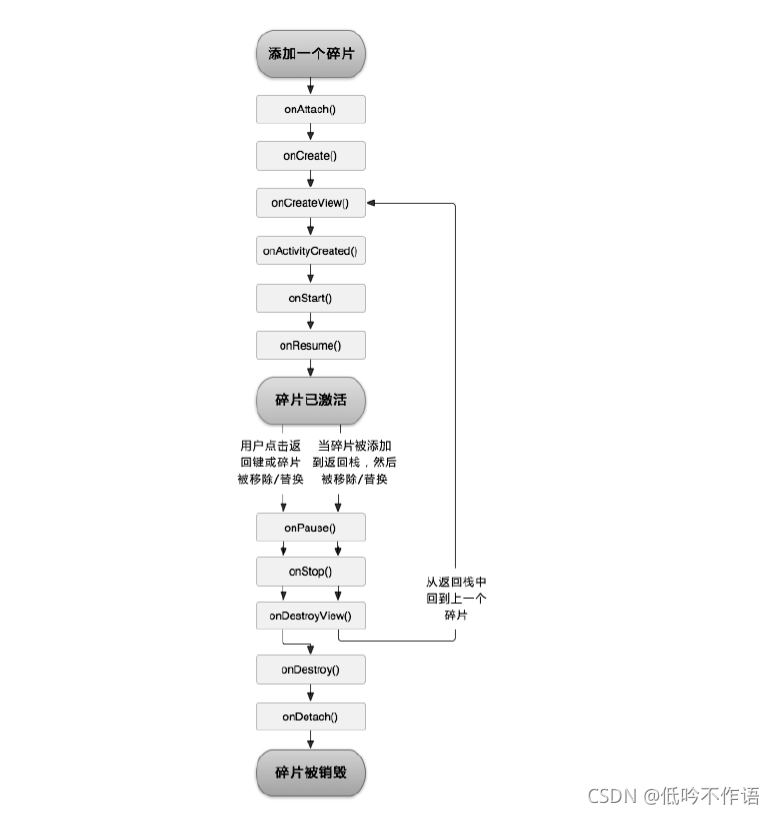
Fragment 生命周期
和 Activity 一样,Fragment 也有自己的生命周期,并且大体一致,只不过在一些细小的地方会有部分区别:
- 运行状态
当一个 Fragment 所关联的 Activity 正处于运行状态,该 Fragment 也处于运行状态
- 暂停状态
当一个 Activity 进入暂停状态(由于另一个未占满的 Activity 被添加到了栈顶),与它相关联的 Fragment 就会进入暂停状态
- 停止状态
当一个 Activity 进入停止状态,与它相关联的 Fragment 就会进入停止状态,或者通过调用 FragmentTransaction 的 remove()、replace() 方法将 Fragment 从 Activity 中移除,但在事务提交前调用了 addToBackStack() 方法,也会进入停止状态
- 销毁状态
当 Activity 被销毁时,与它相关联的 Fragment 就会进入销毁状态,或者通过调用 FragmentTransaction 的 remove()、replace() 方法将 Fragment 从 Activity 中移除,但在事务提交前没有调用了 addToBackStack() 方法,也会进入销毁状态
Fragment 完整的生命周期可参考下图
到此这篇关于Android入门教程之Fragment的具体使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android Fragment内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

Android App中使用Gallery制作幻灯片播放效果
这篇文章主要介绍了Android App中使用Gallery制作幻灯片播放效果,相册应用中的轮播功能也与本文中例子的原理类似,需要的朋友可以参考下2016-04-04
Android编程中TextView字体属性设置方法(大小、字体、下划线、背景色)
这篇文章主要介绍了Android编程中TextView字体属性设置方法,包括大小、字体、下划线、背景色等设置技巧,具有一定参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2015-10-10
Android12四大组件之Activity生命周期变化详解
虽然说我们天天都在使用Activity,但是你真的对Activity的生命机制完全了解了吗?Activity的生命周期方法只有七个,但是其实那只是默认的情况。也就是说在其他情况下,Activity的生命周期可能不会是按照我们以前所知道的流程,本章着重讲解Activity的生命周期变化2022-07-07












最新评论