Appium+Python+pytest自动化测试框架的实战
菜鸟一枚,写的不好勿喷,大家一起学习
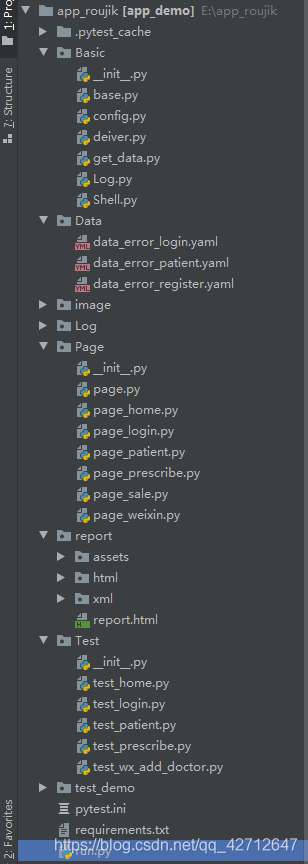
先简单介绍一下目录,再贴一些代码,代码里有注释
Basic目录下写的是一些公共的方法,Data目录下写的是测试数据,image存的是测试失败截图,Log日志文件,Page测试的定位元素,report测试报告,Test测试用例,pytest.ini是pytest启动配置文件,requirements.txt需要安装的py模块,run.py运行文件
Basic/base.py
里面封装了 一些方法,元素的点击,输入,查找,还有一些自己需要的公共方法也封装在里面,如果你们有别的需要可以自己封装调用
# coding=utf-8
import random
import allure
import pymysql
import time
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from Basic import Log
import os
log = Log.MyLog()
class Base(object):
def __init__(self, driver):
self.driver = driver
# 自定义一个元素查找方法
def find_element(self, feature,timeout=5, poll=1.0):
# feature = By.XPATH,"//*[@text='显示']"
"""
依据用户传入的元素信息特征,然后返回当前用户想要查找元素
:param feature: 元组类型,包含用户希望的查找方式,及该方式对应的值
:return: 返回当前用户查找的元素
"""
by = feature[0]
value = feature[1]
wait = WebDriverWait(self.driver, timeout, poll)
if by == By.XPATH:
# print( "说明了用户想要使用 xpath 路径的方式来获取元素" )
value = self.make_xpath(value)
return wait.until(lambda x: x.find_element(by,value))
def find_elements(self, feature):
wait = WebDriverWait(self.driver, 5, 1)
return wait.until(lambda x: x.find_elements(feature[0], feature[1]))
def click_element(self, loc):
'''
封装点击操作函数
'''
self.find_element(loc).click()
def input_text(self, loc, text):
'''
封装输入操作函数
'''
self.fm = self.find_element(loc)
self.fm.clear() # 需要先清空输入框,防止有默认内容
self.fm.send_keys(text)
# 自定义了一个可以自动帮我们拼接 xpath 路径的工具函数
def make_xpath(self, feature):
start_path = "//*["
end_path = "]"
res_path = ""
if isinstance(feature, str):
# 如果是字符串 我们不能直接上来就拆我们可以判断一下它是否是默认正确的 xpath 写法
if feature.startswith("//*["):
return feature
# 如果用户输入的是字符串,那么我们就拆成列表再次进行判断
split_list = feature.split(",")
if len(split_list) == 2:
# //*[contains(@text,'设')]
res_path = "%scontains(@%s,'%s')%s" % (start_path, split_list[0], split_list[1], end_path)
elif len(split_list) == 3:
# //[@text='设置']
res_path = "%s@%s='%s'%s" % (start_path, split_list[0], split_list[1], end_path)
else:
print("请按规则使用")
elif isinstance(feature, tuple):
for item in feature:
# 默认用户在元组当中定义的数据都是字符串
split_list2 = item.split(',')
if len(split_list2) == 2:
res_path += "contains(@%s,'%s') and " % (split_list2[0], split_list2[1])
elif len(split_list2) == 3:
res_path += "@%s='%s' and " % (split_list2[0], split_list2[1])
else:
print("请按规则使用")
andIndex = res_path.rfind(" and")
res_path = res_path[0:andIndex]
res_path = start_path + res_path + end_path
else:
print("请按规则使用")
return res_path
def assert_ele_in(self, text, element):
'''
封装断言操作函数
'''
try:
assert text in self.find_element(element).text
assert 0
except Exception:
assert 1
def get_assert_text(self, element):
ele = self.find_element(element, timeout=5, poll=0.1)
return ele.text
# 自定义一个获取 toast内容的方法
def get_toast_content(self, message):
tmp_feature = By.XPATH, "//*[contains(@text,'%s')]" % message
ele = self.find_element(tmp_feature)
return ele.text
# 自定义一个工具函数,可以接收用户传递的部分 toast 信息,然后返回一个布尔值,来告诉
# 用户,目标 toast 到底是否存在
def is_toast_exist(self, mes):
# 拿着用户传过来的 message 去判断一下包含该内容的 toast 到底是否存在。
try:
self.get_toast_content(mes)
return True
except Exception:
# 如果目标 toast 不存在那么就说明我们的实际结果和预期结果不一样
# 因此我们想要的是断言失败
return False
def get_mysql(self, table, value):
'''连接数据库'''
# 打开数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host='', port=, db=, user='', passwd='', charset='utf8')
# 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor
cursor = db.cursor()
try:
# 使用 execute() 方法执行 SQL 查询
cursor.execute(value)
db.commit()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
db.rollback()
# 使用 fetchone() 方法获取单条数据.
data = cursor.fetchone()
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
return data
def get_xpath(self, value):
'''封装获取xpath方法'''
text = By.XPATH, '//*[@text="%s"]' % value
return text
# 自定义一个获取当前设备尺寸的功能
def get_device_size(self):
x = self.driver.get_window_size()["width"]
y = self.driver.get_window_size()["height"]
return x, y
# 自定义一个功能,可以实现向左滑屏操作。
def swipe_left(self):
start_x = self.get_device_size()[0] * 0.9
start_y = self.get_device_size()[1] * 0.5
end_x = self.get_device_size()[0] * 0.4
end_y = self.get_device_size()[1] * 0.5
self.driver.swipe(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y)
# 自定义一个功能,可以实现向上滑屏操作。
def swipe_up(self):
start_x = self.get_device_size()[0] * 1/2
start_y = self.get_device_size()[1] * 1/2
end_x = self.get_device_size()[0] * 1/2
end_y = self.get_device_size()[1] * 1/7
self.driver.swipe(start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y, 500)
# 切换到微信
def switch_weixxin(self):
self.driver.start_activity("com.tencent.mm", ".ui.LauncherUI")
# 切换到医生端
def switch_doctor(self):
self.driver.start_activity("com.rjjk_doctor", ".MainActivity")
# 切换到销售端
def switch_sale(self):
self.driver.start_activity("com.rjjk_sales", ".MainActivity")
def switch_webview(self):
# 切换到webview
print(self.driver.contexts)
time.sleep(5)
self.driver.switch_to.context("WEBVIEW_com.tencent.mm:tools")
print("切换成功")
time.sleep(3)
# 自定义根据坐标定位
def taptest(self, a, b):
# 设定系数,控件在当前手机的坐标位置除以当前手机的最大坐标就是相对的系数了
# 获取当前手机屏幕大小X,Y
X = self.driver.get_window_size()['width']
Y = self.driver.get_window_size()['height']
# 屏幕坐标乘以系数即为用户要点击位置的具体坐标
self.driver.tap([(a * X, b * Y)])
# 自定义截图函数
def take_screenShot(self):
'''
测试失败截图,并把截图展示到allure报告中
'''
tm = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime(time.time()))
self.driver.get_screenshot_as_file(
os.getcwd() + os.sep + "image/%s.png" % tm)
allure.attach.file(os.getcwd() + os.sep + "image/%s.png" %
tm, attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.PNG)
# 自定义随机生成11位手机号
def create_phone(self):
# 第二位数字
second = [3, 4, 5, 7, 8][random.randint(0, 4)]
# 第三位数字
third = {
3: random.randint(0, 9),
4: [5, 7, 9][random.randint(0, 2)],
5: [i for i in range(10) if i != 4][random.randint(0, 8)],
7: [i for i in range(10) if i not in [4, 9]][random.randint(0, 7)],
8: random.randint(0, 9),
}[second]
# 最后八位数字
suffix = random.randint(9999999, 100000000)
# 拼接手机号
return "1{}{}{}".format(second, third, suffix)
Basic/deiver.py
APP启动的前置条件,一个是普通的app,一个是微信公众号,配置微信公众号自动化测试和一般的APP是有点区别的,微信需要切换webview才能定位到公众号
from appium import webdriver
def init_driver():
desired_caps = {}
# 手机 系统信息
desired_caps['platformName'] = 'Android'
desired_caps['platformVersion'] = '9'
# 设备号
desired_caps['deviceName'] = 'emulator-5554'
# 包名
desired_caps['appPackage'] = ''
# 启动名
desired_caps['appActivity'] = ''
desired_caps['automationName'] = 'Uiautomator2'
# 允许输入中文
desired_caps['unicodeKeyboard'] = True
desired_caps['resetKeyboard'] = True
desired_caps['autoGrantPermissions'] = True
desired_caps['noReset'] = False
# 手机驱动对象
driver = webdriver.Remote("http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub", desired_caps)
return driver
def driver_weixin():
desired_caps = {}
# 手机 系统信息
desired_caps['platformName'] = 'Android'
desired_caps['platformVersion'] = '9'
# 设备号
desired_caps['deviceName'] = ''
# 包名
desired_caps['appPackage'] = 'com.tencent.mm'
# 启动名
desired_caps['appActivity'] = '.ui.LauncherUI'
# desired_caps['automationName'] = 'Uiautomator2'
# 允许输入中文
desired_caps['unicodeKeyboard'] = True
desired_caps['resetKeyboard'] = True
desired_caps['noReset'] = True
# desired_caps["newCommandTimeout"] = 30
# desired_caps['fullReset'] = 'false'
# desired_caps['newCommandTimeout'] = 10
# desired_caps['recreateChromeDriverSessions'] = True
desired_caps['chromeOptions'] = {'androidProcess': 'com.tencent.mm:tools'}
# 手机驱动对象
driver = webdriver.Remote("http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub", desired_caps)
return driver
Basic/get_data.py
这是获取测试数据的方法
import os
import yaml
def getData(funcname, file):
PATH = os.getcwd() + os.sep
with open(PATH + 'Data/' + file + '.yaml', 'r', encoding="utf8") as f:
data = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
# 1 先将我们获取到的所有数据都存放在一个变量当中
tmpdata = data[funcname]
# 2 所以此时我们需要使用循环走进它的内心。
res_arr = list()
for value in tmpdata.values():
tmp_arr = list()
for j in value.values():
tmp_arr.append(j)
res_arr.append(tmp_arr)
return res_arr
Basic/Log.py
日志文件,不多介绍
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
封装log方法
"""
import logging
import os
import time
LEVELS = {
'debug': logging.DEBUG,
'info': logging.INFO,
'warning': logging.WARNING,
'error': logging.ERROR,
'critical': logging.CRITICAL
}
logger = logging.getLogger()
level = 'default'
def create_file(filename):
path = filename[0:filename.rfind('/')]
if not os.path.isdir(path):
os.makedirs(path)
if not os.path.isfile(filename):
fd = open(filename, mode='w', encoding='utf-8')
fd.close()
else:
pass
def set_handler(levels):
if levels == 'error':
logger.addHandler(MyLog.err_handler)
logger.addHandler(MyLog.handler)
def remove_handler(levels):
if levels == 'error':
logger.removeHandler(MyLog.err_handler)
logger.removeHandler(MyLog.handler)
def get_current_time():
return time.strftime(MyLog.date, time.localtime(time.time()))
class MyLog:
path = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
log_file = path+'/Log/log.log'
err_file = path+'/Log/err.log'
logger.setLevel(LEVELS.get(level, logging.NOTSET))
create_file(log_file)
create_file(err_file)
date = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'
handler = logging.FileHandler(log_file, encoding='utf-8')
err_handler = logging.FileHandler(err_file, encoding='utf-8')
@staticmethod
def debug(log_meg):
set_handler('debug')
logger.debug("[DEBUG " + get_current_time() + "]" + log_meg)
remove_handler('debug')
@staticmethod
def info(log_meg):
set_handler('info')
logger.info("[INFO " + get_current_time() + "]" + log_meg)
remove_handler('info')
@staticmethod
def warning(log_meg):
set_handler('warning')
logger.warning("[WARNING " + get_current_time() + "]" + log_meg)
remove_handler('warning')
@staticmethod
def error(log_meg):
set_handler('error')
logger.error("[ERROR " + get_current_time() + "]" + log_meg)
remove_handler('error')
@staticmethod
def critical(log_meg):
set_handler('critical')
logger.error("[CRITICAL " + get_current_time() + "]" + log_meg)
remove_handler('critical')
if __name__ == "__main__":
MyLog.debug("This is debug message")
MyLog.info("This is info message")
MyLog.warning("This is warning message")
MyLog.error("This is error")
MyLog.critical("This is critical message")
Basic/Shell.py
执行shell语句方法
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2018/8/1 下午2:54
# @Author : WangJuan
# @File : Shell.py
"""
封装执行shell语句方法
"""
import subprocess
class Shell:
@staticmethod
def invoke(cmd):
output, errors = subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE).communicate()
o = output.decode("utf-8")
return o
Page/page.py
class Page:
def __init__(self, driver):
self.driver = driver
@property
def initloginpage(self):
return Login_Page(self.driver)
Test/test_login.py
登陆的测试用,我贴一条使用数据文件的用例
class Test_login:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("args", getData("test_login_error", 'data_error_login'))
def test_error_login(self, args):
"""错误登陆"""
self.page.initloginpage.input_user(args[0])
self.page.initloginpage.input_pwd(args[1])
self.page.initloginpage.click_login()
toast_status = self.page.initloginpage.is_toast_exist(args[2])
if toast_status == False:
self.page.initpatientpage.take_screenShot()
assert False
pytest.ini
pytest配置文件,注释的是启动失败重试3次,因为appium会因为一些不可控的原因失败,所有正式运行脚本的时候需要加上这个
[pytest] ;addopts = -s --html=report/report.html --reruns 3 addopts = -s --html=report/report.html testpaths = ./Test python_files = test_*.py python_classes = Test* python_functions = test_add_prescription_list requirements.txt 框架中需要的患教,直接pip install -r requirements.txt 安装就可以了,可能会失败,多试几次 ```python adbutils==0.3.4 allure-pytest==2.7.0 allure-python-commons==2.7.0 Appium-Python-Client==0.46 atomicwrites==1.3.0 attrs==19.1.0 certifi==2019.6.16 chardet==3.0.4 colorama==0.4.1 coverage==4.5.3 decorator==4.4.0 deprecation==2.0.6 docopt==0.6.2 enum34==1.1.6 facebook-wda==0.3.4 fire==0.1.3 humanize==0.5.1 idna==2.8 importlib-metadata==0.18 logzero==1.5.0 lxml==4.3.4 more-itertools==7.1.0 namedlist==1.7 packaging==19.0 Pillow==6.1.0 pluggy==0.12.0 progress==1.5 py==1.8.0 PyMySQL==0.9.3 pyparsing==2.4.0 pytest==5.0.0 pytest-cov==2.7.1 pytest-html==1.21.1 pytest-metadata==1.8.0 pytest-repeat==0.8.0 pytest-rerunfailures==7.0 PyYAML==5.1.1 requests==2.22.0 retry==0.9.2 selenium==3.141.0 six==1.12.0 tornado==6.0.3 uiautomator2==0.3.3 urllib3==1.25.3 wcwidth==0.1.7 weditor==0.2.3 whichcraft==0.6.0 zipp==0.5.1
到此这篇关于Appium+Python+pytest自动化测试框架的实战的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Appium Python pytest自动化测试内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

如何在Python 中使用 join() 函数把列表拼接成一个字符串
这篇文章主要介绍了如何在Python 中使用 join() 函数把列表拼接成一个字符串,文章围绕 join() 函数的相关资料展开详细内容,需要的小伙伴可以参考一下,希望对你有帮助2022-03-03
Pytorch 的损失函数Loss function使用详解
今天小编就为大家分享一篇Pytorch 的损失函数Loss function使用详解,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。一起跟随小编过来看看吧2020-01-01
python django使用haystack:全文检索的框架(实例讲解)
下面小编就为大家带来一篇python django使用haystack:全文检索的框架(实例讲解)。小编觉得挺不错的,现在就分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧2017-09-09
Pytorch中Softmax与LogSigmoid的对比分析
这篇文章主要介绍了Pytorch中Softmax与LogSigmoid的对比分析,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教2021-06-06












最新评论