如何利用python写GUI及生成.exe可执行文件
一.GUI(Graphical User Interface(图形用户接口))
1.导入需要用到的包
import tkinter as tk import tkinter.messagebox import copy import os
2.获取文件夹中所有图片
def get_picture(dirs):
'''获得所有图片'''
picture_list = []
for dir, dir_abs, files in os.walk(dirs):
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.png'): # 注意检查分析数据格式
picture_list.append(os.path.join(dir, file))
return picture_list
3.定义一个类windows
class Window:
button_list = []
object_list = []
pictures = get_picture("F:\\pic\\class-1\\classresnet\\data\\dangerous")
file = pictures[0]
is_show = True
index = 0
image_file = ''
4.创建窗口和frame
def __init__(self):
'''创建窗口和frame'''
self.window = tk.Tk()
self.window.title('护目镜安全检测')
self.window.geometry('600x400')
self.frame = tk.Frame(self.window)
self.frame.pack()
self.frame_l = tk.Frame(self.frame)
self.frame_r = tk.Frame(self.frame)
self.frame_l.pack(side='left')
self.frame_r.pack(side='right')
self.frame_ll = tk.Frame(self.frame_r)
self.frame_rr = tk.Frame(self.frame_r)
self.frame_ll.pack(side='left')
self.frame_rr.pack(side='right')
5.定义需要用到的函数(下一页、上一页等按钮要用到的)
def next_picture(self):
'''下一张图片'''
self.index = self.pictures.index(self.file)
self.index += 1
if self.index < len(self.pictures):
self.checkout_button()
self.file = self.pictures[self.index]
self.create_canvas(self.file)
else:
self.index = len(self.pictures) - 1
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '已近是最后一张了')
def checkout_button(self):
'''判断列表中是否只有button对象'''
object_list_copy = copy.copy(self.object_list)
for ob in self.object_list:
if ob in self.button_list:
pass
else:
b = object_list_copy.pop(self.object_list.index(ob))
b.destroy()
self.object_list = object_list_copy
def pre_picture(self):
'''上一页'''
self.index = self.pictures.index(self.file)
self.index -= 1
if self.index >= 0:
self.checkout_button()
self.file = self.pictures[self.index]
self.create_canvas(self.file)
else:
self.index = 0
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '已经是第一张了')
def show_picture(self):
'''展示图片和翻页按钮'''
self.file = self.pictures[0]
if self.is_show:
self.is_show = False
self.create_canvas(self.file)
button1 = tk.Button(self.frame_ll, text='上一张', font=('Arial', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='orange',
command=self.pre_picture, relief='ridge', )
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(self.frame_rr, text='下一张', font=('Arial', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='orange',
command=self.next_picture, relief='ridge', )
button2.pack()
self.button_list.append(button1)
self.button_list.append(button2)
self.object_list.extend(self.button_list)
else:
self.is_show = True
while self.object_list:
o = self.object_list.pop()
o.destroy()
6.创建按钮、画布,调用主程序
def new_button(self):
'''创建展示按钮'''"开始检测和显示结果可在此处新添加tk.button"
tk.Button(self.frame_l, text='开始读取', font=('Arial Black', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='green',
command=self.show_picture, relief='ridge').pack()
# tk.Button(self.frame_l, text='开始检测', font=('Arial Black', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='blue',command=classresnet, relief='ridge').pack()
def create_canvas(self, file):
'''用画布展示图片'''
self.image_file = tk.PhotoImage(file=file)
canvas = tk.Canvas(self.frame_r, height=500, width=600, bg='gray')
canvas.create_image(1, 1, anchor='nw', image=self.image_file)
canvas.pack()
self.object_list.append(canvas)
def run(self):
'''主程序调用'''
self.window.mainloop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
w = Window()
w.new_button()
w.run()
效果展示

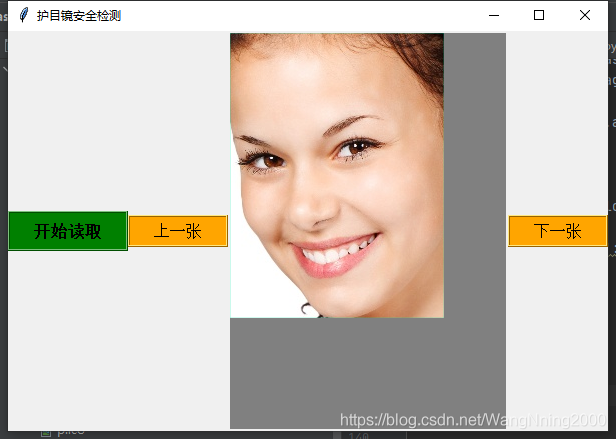
完整代码
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.messagebox
import copy
import os
# from glob2 import glob
# import main
"""Graphical User Interface(图形用户接口)"""
def get_picture(dirs):
'''获得所有图片'''
picture_list = []
for dir, dir_abs, files in os.walk(dirs):
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.png'): # 注意检查分析数据格式
picture_list.append(os.path.join(dir, file))
return picture_list
class Window:
button_list = []
object_list = []
# for pngfile in glob("F:\\pic\\class-1\\classresnet\\datas\\*.png"):
# main.image_demo()
# output_dir = "F:\\pic\\class-1\\classresnet\\data\\try" # 保存截取的图像目录
# print('图片获取完成 。。。!')
#
# main.classresnet()
pictures = get_picture("F:\\pic\\class-1\\classresnet\\data\\dangerous")
file = pictures[0]
is_show = True
index = 0
image_file = ''
def __init__(self):
'''创建窗口和frame'''
self.window = tk.Tk()
self.window.title('护目镜安全检测')
self.window.geometry('600x400')
self.frame = tk.Frame(self.window)
self.frame.pack()
self.frame_l = tk.Frame(self.frame)
self.frame_r = tk.Frame(self.frame)
self.frame_l.pack(side='left')
self.frame_r.pack(side='right')
self.frame_ll = tk.Frame(self.frame_r)
self.frame_rr = tk.Frame(self.frame_r)
self.frame_ll.pack(side='left')
self.frame_rr.pack(side='right')
def next_picture(self):
'''下一张图片'''
self.index = self.pictures.index(self.file)
self.index += 1
if self.index < len(self.pictures):
self.checkout_button()
self.file = self.pictures[self.index]
self.create_canvas(self.file)
else:
self.index = len(self.pictures) - 1
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '已近是最后一张了')
def checkout_button(self):
'''判断列表中是否只有button对象'''
object_list_copy = copy.copy(self.object_list)
for ob in self.object_list:
if ob in self.button_list:
pass
else:
b = object_list_copy.pop(self.object_list.index(ob))
b.destroy()
self.object_list = object_list_copy
def pre_picture(self):
'''上一页'''
self.index = self.pictures.index(self.file)
self.index -= 1
if self.index >= 0:
self.checkout_button()
self.file = self.pictures[self.index]
self.create_canvas(self.file)
else:
self.index = 0
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo('提示', '已经是第一张了')
def show_picture(self):
'''展示图片和翻页按钮'''
self.file = self.pictures[0]
if self.is_show:
self.is_show = False
self.create_canvas(self.file)
button1 = tk.Button(self.frame_ll, text='上一张', font=('Arial', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='orange',
command=self.pre_picture, relief='ridge', )
button1.pack()
button2 = tk.Button(self.frame_rr, text='下一张', font=('Arial', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='orange',
command=self.next_picture, relief='ridge', )
button2.pack()
self.button_list.append(button1)
self.button_list.append(button2)
self.object_list.extend(self.button_list)
else:
self.is_show = True
while self.object_list:
o = self.object_list.pop()
o.destroy()
# def code_button(self):
# tk.Button(self.frame_l, text='开始检测', font=('Arial Black', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='blue',
# command=main.classresnet, relief='ridge').pack()
def new_button(self):
'''创建展示按钮'''"开始检测和显示结果可在此处新添加tk.button"
tk.Button(self.frame_l, text='开始读取', font=('Arial Black', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='green',
command=self.show_picture, relief='ridge').pack()
# tk.Button(self.frame_l, text='开始检测', font=('Arial Black', 12), width=10, height=1, bg='blue',command=classresnet, relief='ridge').pack()
def create_canvas(self, file):
'''用画布展示图片'''
self.image_file = tk.PhotoImage(file=file)
canvas = tk.Canvas(self.frame_r, height=500, width=600, bg='gray')
canvas.create_image(1, 1, anchor='nw', image=self.image_file)
canvas.pack()
self.object_list.append(canvas)
def run(self):
'''主程序调用'''
self.window.mainloop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
w = Window()
w.new_button()
w.run()
二.生成exe文件
在windows下,可以使用pyinstaller打包python程序为exe可执行程序。
1.安装pyinstaller
在cmd命令行窗口运行以下命令安装pyinstaller
pip install pyinstaller
2.打包python程序
在python程序所在目录,执行以下命令
pyinstaller -F xxx.py -w
注:如果不加-w,生成的exe文件会同时出现命令行窗口
3.运行exe文件
打包完成后,在对应目录会出现build和dist文件夹,exe文件就出现在dist文件夹,直接运行即可。
4.常用命令参数
(1) -F 指定打包后只生成一个exe格式的文件(dist文件只有一个exe格式的文件T1)
pyinstaller -F T1.py
(2) -i 改变生成程序的icon图标
pyinstaller -F -i ./my.ico T1.py
(3) -n NAME,–name=NAME 设置产生文件的名字(mypy)
pyinstaller -F -n mypy -i ./my.ico T1.py
效果展示

执行exe应用
因为是exe应用,是可执行文件了,所以直接双击运行即可,运行效果如下图所示:

总结
到此这篇关于如何利用python写GUI及生成.exe可执行文件的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python写GUI及生成.exe内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

Pytorch中的图像增广transforms类和预处理方法
这篇文章主要介绍了Pytorch中的图像增广和预处理方法(transforms类),本文通过实例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2023-04-04
python GUI库图形界面开发之PyQt5窗口背景与不规则窗口实例
这篇文章主要介绍了python GUI库图形界面开发之PyQt5窗口背景与不规则窗口实例,需要的朋友可以参考下2020-02-02
Python中的__new__与__init__魔术方法理解笔记
这篇文章主要介绍了Python中的__new__与__init__魔术方法理解笔记,需要的朋友可以参考下2014-11-11
ubuntu安装sublime3并配置python3环境的方法
这篇文章主要介绍了ubuntu安装sublime3并配置python3环境的方法,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧2018-03-03












最新评论