Vue 响应式系统依赖收集过程原理解析
背景
在 Vue 的初始化阶段,_init 方法执行的时候,会执行 initState(vm) ,它的定义在 src/core/instance/state.js 中。在初始化 data 和 props option 时我们注意 initProps 和 initData 方法中都调用了 observe 方法。通过 observe (value),就可以将数据变成响应式。
export function initState (vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm)
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}initProps
if (value === undefined) { observe(value); }initData
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
目标
- 理解 Vue 数据响应式原理,了解响应式原理依赖收集的过程
- 了解在什么阶段会触发依赖收集
源码解读
入口函数:observe
observe 方法定义在 src/core/observer/index.js 中。如果是一个非 VNode 的对象类型的数据,它会尝试给这个值去创建一个 observer 实例,如果创建成功,返回新的 observer。或者如果 ob 已经存在了,就会直接返回一个现有的 observer。
/**
* 尝试给这个值去创建一个 observer 实例,如果创建成功,返回新的 observer
* 或者如果值已经有了,返回一个现有的 observer
* @param {*} value
* @param {boolean} asRootData
* @returns Observer | void
*/
export function observe (value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
let ob: Observer | void
// 如果 value 已经有 observer,就返回现有的 observer
// 否则如果不是服务器渲染,value是数组或者对象,value 是可扩展的,value 不是 vue 实例,就创建一个新的 observer
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__
} else if (
shouldObserve &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
ob = new Observer(value)
}
// 如果是根组件,vmCount 不为0
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++
}
return ob
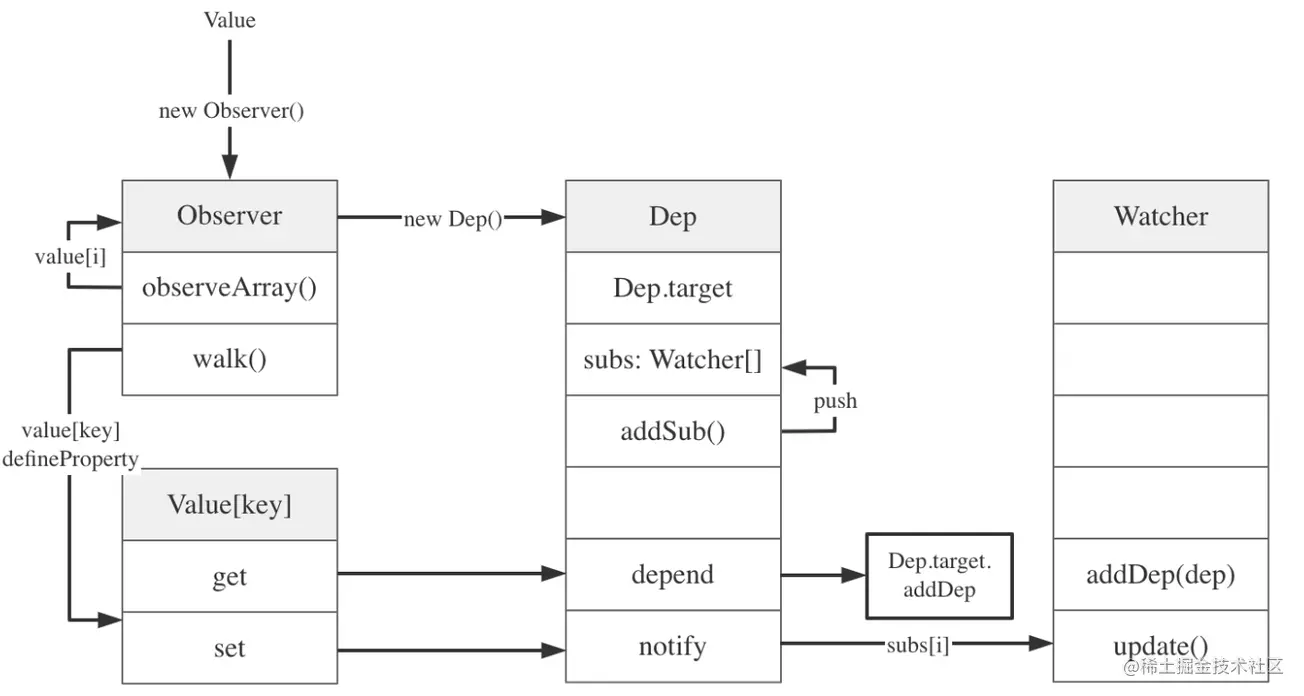
}通过 new Observer(value) 可以给 value 创建一个 observer 实例,那么 Observer 类的定义和作用是什么?在同一个文件下可以看到 class Observer 是如何定义的。
class Observer
Observer 方法定义在 src/core/observer/index.js 中。在它的构造函数中,首先实例化 Dep 对象(主要用来存放它的 watcher列表),接着通过执行 def 函数把自身实例添加到数据对象 value 的 ob 属性上,所以存在 ob 属性意味着已经被观察过。最后判断 value 为数组的情况下,会数组项遍历,给数组的每一项创建一个 observe 实例;如果是对象,那么遍历所有的属性,通过Object.defineProperty修改getter/setters。
/**
* Observer 类和每个响应式对象关联。
* observer 会转化对象的属性值的 getter/setters 方法收集依赖和派发更新。
*/
export class Observer {
value: any;
dep: Dep;
vmCount: number; // number of vms that have this object as root $data
constructor(value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep() // 存放 Observer 的 watcher 列表
this.vmCount = 0
def(value, '__ob__', this) // __ob__ 指向自身 observe 实例,存在 __ob__ 属性意味着已经被观察过
// 如果是数组
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
// hasProto = '__proto__' in {} 判断对象是否存在 __proto__ 属性
if (hasProto) {
// 如果有 __proto__,就将 value.__proto__ 指向 arrayMethods
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods)
} else {
// 否则,就遍历 arrayMethods,将值复制到 value 上
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
}
this.observeArray(value) // 数组项遍历,给数组的每一项创建一个 observe 实例
} else {
this.walk(value) // 遍历所有的属性,修改 getter/setters
}
}
// 遍历所有的属性,修改 getter/setters,这个方法只有在 value 是object时调用
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}
// 数组项遍历,给数组的每一项创建一个 observe 实例
observeArray (items: Array<any>) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}我们来看看对于数组和对象, Observe 分别做了什么处理。
Observe 如何处理数组
首先,对于 value 为数组而言,由于 proto 不是标准属性,有些浏览器不支持,比如 IE6-10,Opera10.1,所以需要根据对象是否存在 proto 属性区分在原型链上添加方法, protoAugment 和 copyAugment 都是在目标对象上添加属性值。
/**
* 将 target.__proto__ 指向 src
* 拦截原型链__proto__,来增强目标对象或数组
* @param {*} target
* @param {Object} src
*/
function protoAugment (target, src: Object) {
/* eslint-disable no-proto */
target.__proto__ = src
/* eslint-enable no-proto */
}
/**
* 遍历 key 属性值列表,将 src 中的 key 属性值逐一定义到 target 的属性中
* 通过定义隐藏属性,来增强目标对象或数组
* @param {Object} target
* @param {Object} src
* @param {Array<string>} keys
*/
/* istanbul ignore next */
function copyAugment (target: Object, src: Object, keys: Array<string>) {
for (let i = 0, l = keys.length; i < l; i++) {
const key = keys[i]
def(target, key, src[key]) // // 为 target 定义 key 和值
}
}在原型链上添加的属性方法 arrayMethods 在 src/core/observer/array.js 可以找到他的定义。实际上 arrayMethods 就是 push pop shift unshift splice sort reverse 七个个方法。这么做的目的是因为要通过 proto 操作数据的原型链,覆盖数组默认的七个原型方法,以实现数组响应式。
Observe 如何处理对象
其次,对于对象而言,会去遍历对象的每个 key,调用 defineReactive(obj, keys[i]) 方法。它会为 obj[key] 创建一个依赖类 dep(会帮这个key 定义一个 id 和 subs(watcher 订阅者列表) 方便依赖收集)然后再利用 Object.defineProperty 对对象的 get 和 set 方法做了处理。get 拦截对 obj[key] 的读取操作,set 拦截对 obj[key] 的写操作。
/**
* 在对象上定义一个响应式的属性。
* @param {Object} obj
* @param {string} key
* @param {*} val
* @param {*} customSetter
* @param {*} shallow
* @returns
*/
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
const dep = new Dep() // 为 Object 的 key 创建一个依赖类,会帮这个key 定义一个 id 和 subs(watcher 订阅者列表)
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key)
// 获取 obj[key] 的属性描述符,发现它是不可配置对象的话直接 return
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get
const setter = property && property.set
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
// 对 obj[key] 进行观察,保证对象中的所有 key 都被观察
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
// 旧的 obj[key]
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
// 如果新老值一样,则直接 return,不跟新更不触发响应式更新过程
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
// setter 不存在说明该属性是一个只读属性,直接 return
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) return
// 设置新值
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
// 对新值进行观察,让新值也是响应式的
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify() // 通知依赖的观察者更新
}
})
}可以看到,defineReactive(obj, keys[i]) 中对对象做了处理,不论嵌套的多深,都会 observe(value) 继续观察,在设置了新的值后,也会重新对新值进行观察,让新值也是响应式的。
上面的代码中,在 Observer 类构造函数执行时创建了一个 new Dep(),之后在定义对象的响应式属性时,也为 Object 的 key 创建一个依赖类 const dep = new Dep(),然后在 set 数据值会触发 dep.notify()。那么 Dep 的作用是什么呢?
class Dep
Dep 类的定义在 src/core/observer/dep.js 下。它的构造函数中定义了 id 和一个用于储存订阅这个 dep 的 watcher 的数组 subs[]。
/**
* 一个 dep 对应一个 object.key,每次 key 更新时调用 dep.notify(),
* dep 下的 subs 存放 Watcher 列表,可以调用 dep.notify() 触发 watcher.update() 使 Watcher 列表更新。
*/
export default class Dep {
static target: ?Watcher; // Dep 类的静态属性,可以使用 Dep.target 访问,内容是 Watcher
id: number;
subs: Array<Watcher>; // Watcher 组成的订阅列表
constructor() {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = [] // watcher 订阅者列表
}
// 向订阅者列表中添加一个订阅者 Watcher
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
// 从订阅者列表中删掉一个 Watcher
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
// 让全局唯一的 watcher 添加当前的依赖
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
// 通知订阅者列表触发更新
notify () {
// 用 slice() 方法拷贝一个 subs,不影响 this.subs
const subs = this.subs.slice()
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
// 如果不是运行异步,Watcher 列表不会在调度器中排序,我们需要去对他们进行排序以确保他们按顺序正确的调度
subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
}
// 依次触发 Watcher.update()
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
}Dep.target
这里的 Dep.target 就是一个 watcher实例,在依赖收集时会调用 watcher.addDep(this) 向观察者中添加自己这个依赖。 Dep.notify() 会通知这个依赖的观察者们依次触发 Watcher.update()。
Dep.target 是当前正在执行的 watcher,同一时间只会有一个 watcher 在执行。
Dep.target = null
const targetStack = []
// 在需要进行依赖收集的时候调用,设置 Dep.target = watcher
export function pushTarget (target: ?Watcher) {
targetStack.push(target)
Dep.target = target
}
// 依赖收集结束调用,设置 Dep.target 为对堆栈中前一个 watcher
export function popTarget () {
targetStack.pop()
Dep.target = targetStack[targetStack.length - 1]
}
class Watcher
Watcher类定义在 src/core/observer/watcher.js 中。一个组件渲染时创建一个 watcher。
或者一个表达式创建一个 Watcher ,当表达式发生改变时触发调度。
Watcher 的原型方法中和依赖收集相关的方法有 get() addDep() cleanupDep()等。在 watcher 的构造函数中会调用它的原型方法 get(),它将 Dep.target 指向当前 watcher。
/**
* Watcher 解析一个表达式,收集依赖,当表达式发生改变时触发调度。Watcher 类用于 $watch() api 和指令。
*/
export default class Watcher {
vm: Component;
expression: string;
cb: Function;
id: number;
deep: boolean;
user: boolean;
lazy: boolean;
sync: boolean;
dirty: boolean;
active: boolean;
deps: Array<Dep>; // deps 表示上一次添加的 Dep 实例数组
newDeps: Array<Dep>; // newDeps 表示新添加的 Dep 实例数组
depIds: SimpleSet;
newDepIds: SimpleSet;
before: ?Function;
getter: Function;
value: any;
constructor( // 类实例化时传入的参数会用作构造函数的参数
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: Function,
options?: ?Object,
isRenderWatcher?: boolean
) {
this.vm = vm
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this
}
vm._watchers.push(this)
// options
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep
this.user = !!options.user
this.lazy = !!options.lazy
this.sync = !!options.sync
this.before = options.before
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false
}
this.cb = cb
this.id = ++uid // uid for batching
this.active = true
this.dirty = this.lazy // for lazy watchers
this.deps = []
this.newDeps = []
this.depIds = new Set()
this.newDepIds = new Set()
this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
? expOrFn.toString()
: ''
// parse expression for getter
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn)
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = noop
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Failed watching path: "${expOrFn}" ` +
'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' +
'For full control, use a function instead.',
vm
)
}
}
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get()
}
// 一些原型方法
// 以下是定义在 watcher 类原型对象上的方法,用 Watcher.prototype.get() 访问
/**
* Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies.
*/
get () {
// 将 Dep.target 指向当前 watcher
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
// 让 vm 调用 this.getter,并传入 vm 作为参数
// this.getter = expOrFn
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// 如果需要监听对象内部值的变化,那么调用 traverse 方法
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value) // 递归遍历 value 的每个属性, 确保每个属性都被监听
}
// 当前 vm 的数据依赖收集已经完成,恢复 Dep.target
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}
/**
* Add a dependency to this directive.
* 添加一个依赖:如果dep数组中没有dep.id,那么触发 dep 订阅当前 watcher
*/
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
/**
* Clean up for dependency collection.
* 清除依赖收集
*/
cleanupDeps () {
// 先保持 deps 和 newDepIds数量相同
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
const dep = this.deps[i]
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
dep.removeSub(this) // 如果当前 dep 中没有 newDepIds,就移除它的订阅者列表
}
}
// 更新 depIds、deps 为当前的 deps,然后清除 newDepIds 和 newDeps
let tmp = this.depIds
this.depIds = this.newDepIds
this.newDepIds = tmp
this.newDepIds.clear()
tmp = this.deps
this.deps = this.newDeps
this.newDeps = tmp
this.newDeps.length = 0
}
/**
* Subscriber interface.
* Will be called when a dependency changes.
*/
// 订阅者接口,当依赖改变时将会被调用
update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
/**
* Scheduler job interface.
* Will be called by the scheduler.
*/
// 调度器工作接口,将会被调度器调用
run () {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
const info = `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`
invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info)
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}
/**
* Evaluate the value of the watcher.
* This only gets called for lazy watchers.
*/
evaluate () {
this.value = this.get()
this.dirty = false
}
/**
* Depend on all deps collected by this watcher.
*/
depend () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
/**
* Remove self from all dependencies' subscriber list.
* 从所有依赖项的订阅者列表中删除 self
*/
teardown () {
if (this.active) {
// remove self from vm's watcher list
// this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it
// if the vm is being destroyed.
// 如果组件不是正在被销毁
if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
remove(this.vm._watchers, this) // 从数组中删除一个项目。
}
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].removeSub(this)
}
this.active = false
}
}
}上面的流程是在 Vue 初始化时对数据做的处理,调用创建了 observe 实例和 dep 实例。但是并没有提到 watcher 实例是在什么时候创建的。我们先来看看一些使用 Watcher 的地方。
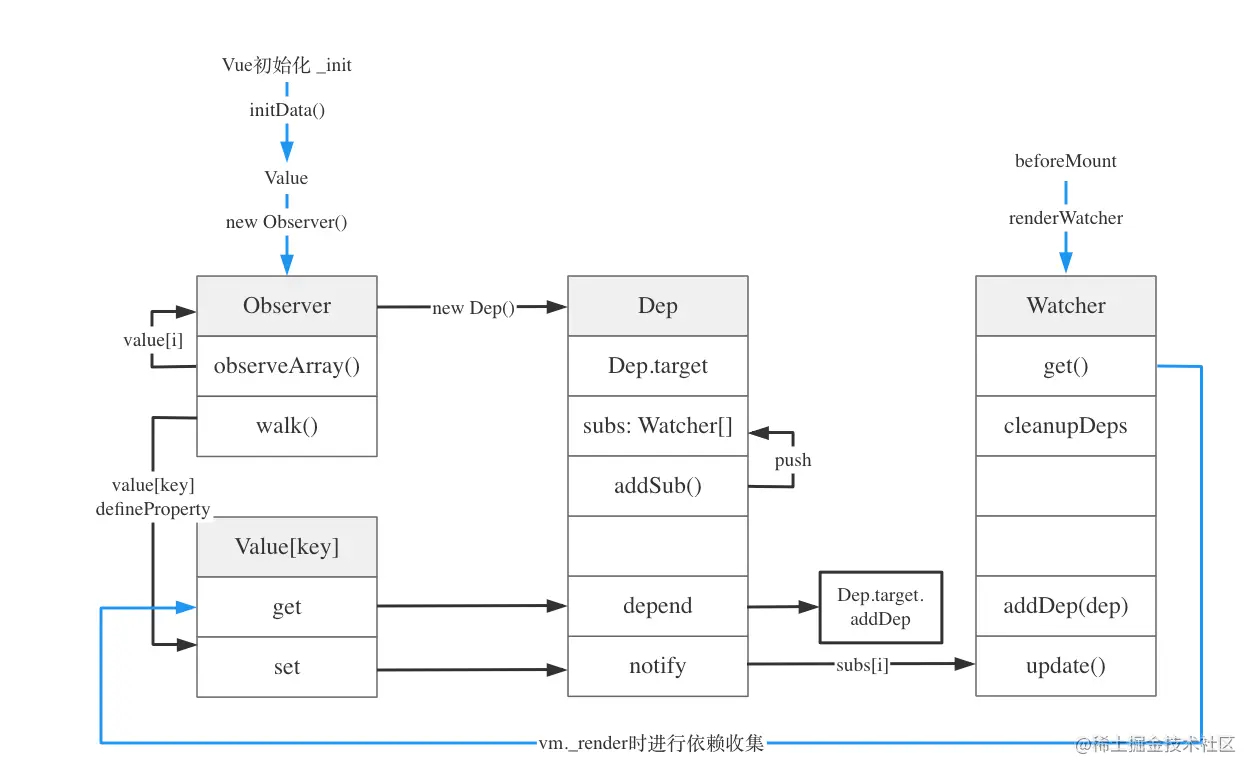
Watcher 的应用
- beforeMount
在 beforeMount 生命周期时,会通过 new Watcher 生成一个渲染 Watcher,它会在页面渲染的过程中访问每个数据对象的 getter 属性,从而进行依赖的收集。 - initComputed()
遍历 computed 中的每个 key,向 computed watcher 列表中新增一个 watcher 实例。 - initWatch()
遍历 watch 中的每一个 key,调用 vm.$watch 创建一个 watcher 实例。
何时触发依赖收集?
在 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 中可以看到,在 beforeMount 阶段实例化了一个 render watcher,并传入一个 updateComponent 的 expOrFn 方法。之后 watcher 调用它的 this.get()。\
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)在 get() 中先调用了 pushTarget(this) 将 Dep.target 指向当前的渲染 watcher。然后调用了 this.getter.call(vm, vm),实际上意味着执行了 vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)。vm._render() 返回了一个 vnode,vm._update完成页面更新。在这个过程中会对 vm 上的数据访问,这个时候就触发了数据对象的 getter。
// this.getter = expOrFn = updateComponent() value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
数据的 getter 中触发 dep.depend() 进行依赖收集。
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},当依赖收集完成后会popTarget(),恢复 Dep.target() = null。最后清空这些依赖。
popTarget() this.cleanupDeps()
数据变化时,如何进行更新?
数据更新时,会执行setter,首先会对这个新值 newVal observe(newVal),再调用这个属性的 dep.notify() 通知它的订阅者们进行更新。
总结
- Vue 初始化时就会通过 Object.defineProperty 拦截属性的 getter 和 setter ,为对象的每个值创建一个 dep 并用 Dep.addSub() 来存储该属性值的 watcher 列表。
- 触发依赖收集的阶段是在 beforeMount 时,它会为组件创建一个渲染 Watcher,在执行 render 的过程中就会触发对象的 getter 方法,通过dep.depend()将订阅者收集起来。通俗的来说,渲染的时候会先解析模板,由于模板中有使用到 data 中的数据,所以会触发 get 操作,从将渲染的 Watcher 对象搜集起来,以便在 set 的时候批量更新。
参考资料
到此这篇关于Vue 响应式系统依赖收集过程分析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Vue 响应式系统依赖收集内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

vue 使用iView组件中的Table实现定时自动滚动效果
要在css中设置table的高度,使数据过多时出现滚动条,将纵向设置为overflow-y: auto;横向设置隐藏 overflow-x: hidden,接下来通过本文介绍vue使用iView组件中的Table实现定时自动滚动效果,需要的朋友可以参考下2024-05-05
Vue使用ElemenUI对table的指定列进行合算的方法
这篇文章主要介绍了Vue使用ElemenUI对table的指定列进行合算的方法,本文结合实例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,需要的朋友可以参考下2023-03-03












最新评论