C#各种异常处理方式总结
更新时间:2022年08月27日 11:20:58 作者:Darren Ji
这篇文章介绍了C#各种异常的处理方式,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细。对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下
.NET的异常处理机制用来发现、处理运行时错误。如果开发人员没有提供异常的处理机制,就默认采用.NET的机制。
通常使用try...catch...finally捕获异常。
try
{
//有可能发生异常
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
//处理异常
}
finally
{
//清理
}- 如果没有异常发生,就直接到finally语句块中。
- finally语句块是必须执行的
- 这里的catch和finally语句块是可选的。try语句块后面可以跟1个或多个catch语句块,try语句块后面可以直接跟finally语句块。
- Exception是所有异常的基类
使用.NET默认异常处理机制捕获异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 0;
int result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
使用try...catch手动捕获异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{
result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");
}
catch (DivideByZeroException exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("出现异常");
}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
使用try...catch...finally手动捕获异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{
result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");
}
catch (DivideByZeroException exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("出现异常");
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("放行吧,肯定会执行到我这里的~~");
}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
可见,finally语句块中的内容一定会被执行。
使用try...多个catch...finally手动捕获异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{
result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");
}
catch (DivideByZeroException exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("不能被0除的异常");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("异常");
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("放行吧,肯定会执行到我这里的~~");
}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
可见,只要有一个catch语句块捕获到异常,其它catch语句块不执行。
使用try...catch(不带括号,不带参数)手动捕获异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 0;
int result = 0;
try
{
result = 100/a;
Console.WriteLine("这里不会执行");
}
catch
{
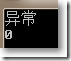
Console.WriteLine("异常");
}
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
通过以上方法,可以捕获任何异常。
try...catch手动捕获抛出的异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
throw new DivideByZeroException("除数不能为零");
}
catch (DivideByZeroException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("异常");
}
Console.WriteLine("最后想说的");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
抛出异常本身并没有显示。
较高层次上下文捕获较低抛出的异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculate c = new Calculate();
try
{
c.Divide();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("捕获异常");
}
Console.WriteLine("最后想说的");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Calculate
{
public void Divide()
{
try
{
int a = 0;
int result = 100/a;
}
catch (DivideByZeroException e)
{
throw;
}
}
}
在Calculate内部抛出的异常,被更高层次的客户端捕获。
自定义异常
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
throw new MyException("i am exception");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("捕获到自定义异常了~~");
}
Console.WriteLine("最后想说的");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class MyException : Exception
{
public MyException(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine("这是我自定义的异常:" + str);
}
}
总结:
- .NET异常处理并不是标准的try...catch...finally,可以是很灵活的。
- 尽量在较低层次抛异常,在较高层次捕获异常。
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对脚本之家的支持。如果你想了解更多相关内容请查看下面相关链接
相关文章

Unity的Console的控制类LogEntries深入解析与实用案例
这篇文章主要为大家介绍了Unity的Console的控制类LogEntries深入解析与实用案例,有需要的朋友可以借鉴参考下,希望能够有所帮助,祝大家多多进步,早日升职加薪2023-07-07
深入Unix时间戳与C# DateTime时间类型互换的详解
本篇文章是对Unix时间戳与C# DateTime时间类型互换进行了详细的分析介绍,需要的朋友参考下2013-06-06












最新评论