kotlin android extensions 插件实现示例详解
前言
kotlin-android-extensions 插件是 Kotlin 官方提供的一个编译器插件,用于替换 findViewById 模板代码,降低开发成本
虽然 kotlin-android-extensions 现在已经过时了,但比起其他替换 findViewById 的方案,比如第三方的 ButterKnife 与官方现在推荐的 ViewBinding
kotlin-android-extensions 还是有着一个明显的优点的:极其简洁的 API,KAE 方案比起其他方案写起来更加简便,这是怎么实现的呢?我们一起来看下
原理浅析
当我们接入KAE后就可以通过以下方式直接获取 View
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
viewToShowText.text = "Hello"
}
}
而它的原理也很简单,KAE插件将上面这段代码转换成了如下代码
public final class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private HashMap _$_findViewCache;
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.setContentView(1300023);
TextView var10000 = (TextView)this._$_findCachedViewById(id.textView);
var10000.setText((CharSequence)"Hello");
}
public View _$_findCachedViewById(int var1) {
if (this._$_findViewCache == null) {
this._$_findViewCache = new HashMap();
}
View var2 = (View)this._$_findViewCache.get(var1);
if (var2 == null) {
var2 = this.findViewById(var1);
this._$_findViewCache.put(var1, var2);
}
return var2;
}
public void _$_clearFindViewByIdCache() {
if (this._$_findViewCache != null) {
this._$_findViewCache.clear();
}
}
}
可以看到,实际上 KAE 插件会帮我们生成一个 _$_findCachedViewById()函数,在这个函数中首先会尝试从一个 HashMap 中获取传入的资源 id 参数所对应的控件实例缓存,如果还没有缓存的话,就调用findViewById()函数来查找控件实例,并写入 HashMap 缓存当中。这样当下次再获取相同控件实例的话,就可以直接从 HashMap 缓存中获取了。
当然KAE也帮我们生成了_$_clearFindViewByIdCache()函数,不过在 Activity 中没有调用,在 Fragment 的 onDestroyView 方法中会被调用到
总体结构
在了解了KAE插件的简单原理后,我们一步一步来看一下它是怎么实现的,首先来看一下总体结构
KAE插件可以分为 Gradle 插件,编译器插件,IDE 插件三部分,如下图所示
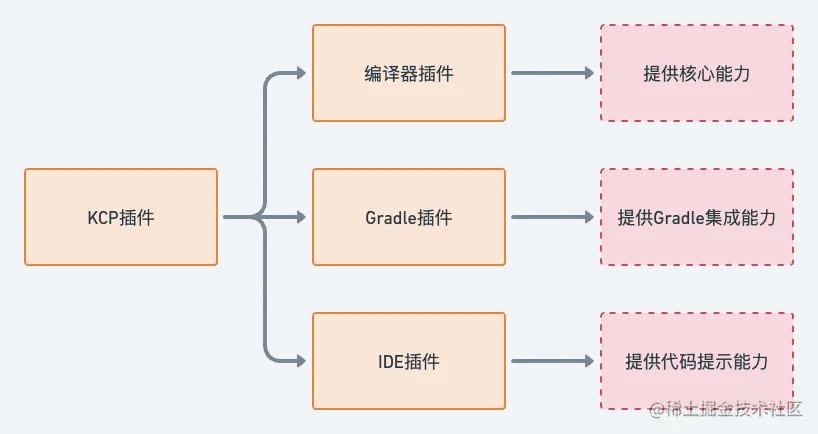
我们今天只分析 Gradle 插件与编译器插件的源码,它们的具体结构如下:
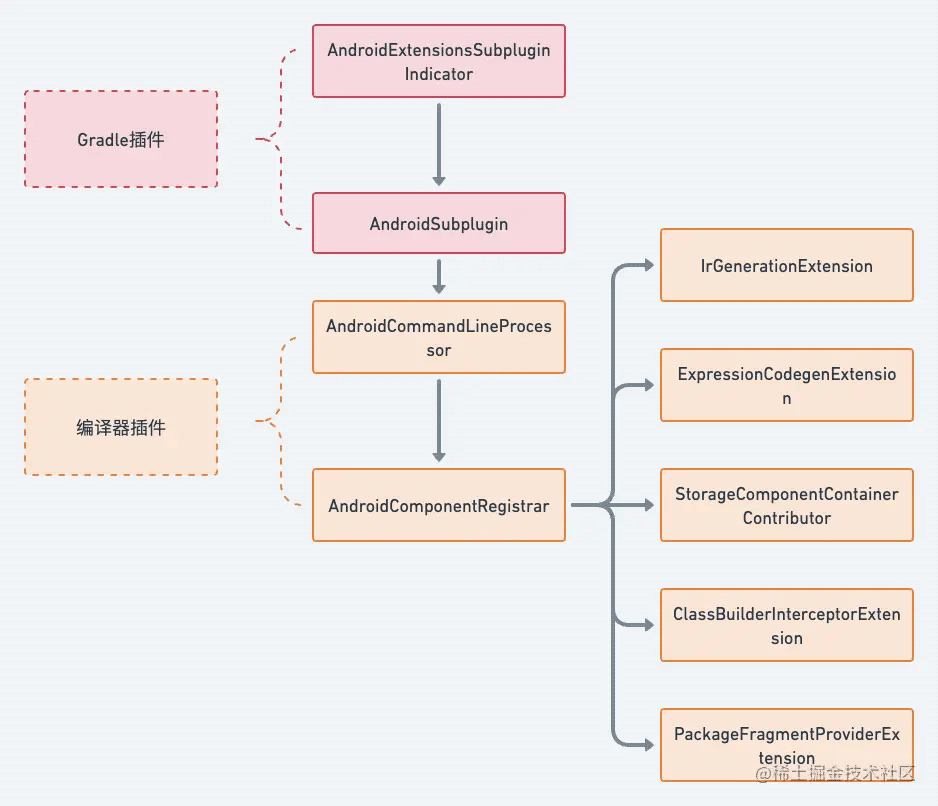
AndroidExtensionsSubpluginIndicator是KAE插件的入口AndroidSubplugin用于配置传递给编译器插件的参数AndroidCommandLineProcessor用于接收编译器插件的参数AndroidComponentRegistrar用于注册如图的各种Extension
源码分析
插件入口
当我们查看 kotlin-gradle-plugin 的源码,可以看到 kotlin-android-extensions.properties 文件,这就是插件的入口
implementation-class=org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.internal.AndroidExtensionsSubpluginIndicator
接下来我们看一下入口类做了什么工作
class AndroidExtensionsSubpluginIndicator @Inject internal constructor(private val registry: ToolingModelBuilderRegistry) :
Plugin<Project> {
override fun apply(project: Project) {
project.extensions.create("androidExtensions", AndroidExtensionsExtension::class.java)
addAndroidExtensionsRuntime(project)
project.plugins.apply(AndroidSubplugin::class.java)
}
private fun addAndroidExtensionsRuntime(project: Project) {
project.configurations.all { configuration ->
val name = configuration.name
if (name != "implementation") return@all
configuration.dependencies.add(
project.dependencies.create(
"org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-android-extensions-runtime:$kotlinPluginVersion"
)
)
}
}
}
open class AndroidExtensionsExtension {
open var isExperimental: Boolean = false
open var features: Set<String> = AndroidExtensionsFeature.values().mapTo(mutableSetOf()) { it.featureName }
open var defaultCacheImplementation: CacheImplementation = CacheImplementation.HASH_MAP
}
AndroidExtensionsSubpluginIndicator中主要做了这么几件事
- 创建
androidExtensions配置,可以看出其中可以配置是否开启实验特性,启用的feature(因为插件中包含views与parcelize两个功能),viewId缓存的具体实现(是hashMap还是sparseArray) - 自动添加
kotlin-android-extensions-runtime依赖,这样就不必在接入了插件之后,再手动添加依赖了,这种写法可以学习一下 - 配置
AndroidSubplugin插件,开始配置给编译器插件的传参
配置编译器插件传参
class AndroidSubplugin : KotlinCompilerPluginSupportPlugin {
// 1. 是否开启编译器插件
override fun isApplicable(kotlinCompilation: KotlinCompilation<*>): Boolean {
if (kotlinCompilation !is KotlinJvmAndroidCompilation)
return false
// ...
return true
}
// 2. 传递给编译器插件的参数
override fun applyToCompilation(
kotlinCompilation: KotlinCompilation<*>
): Provider<List<SubpluginOption>> {
//...
val pluginOptions = arrayListOf<SubpluginOption>()
pluginOptions += SubpluginOption("features",
AndroidExtensionsFeature.parseFeatures(androidExtensionsExtension.features).joinToString(",") { it.featureName })
fun addVariant(sourceSet: AndroidSourceSet) {
val optionValue = lazy {
sourceSet.name + ';' + sourceSet.res.srcDirs.joinToString(";") { it.absolutePath }
}
pluginOptions += CompositeSubpluginOption(
"variant", optionValue, listOf(
SubpluginOption("sourceSetName", sourceSet.name),
//use the INTERNAL option kind since the resources are tracked as sources (see below)
FilesSubpluginOption("resDirs", project.files(Callable { sourceSet.res.srcDirs }))
)
)
kotlinCompilation.compileKotlinTaskProvider.configure {
it.androidLayoutResourceFiles.from(
sourceSet.res.sourceDirectoryTrees.layoutDirectories
)
}
}
addVariant(mainSourceSet)
androidExtension.productFlavors.configureEach { flavor ->
androidExtension.sourceSets.findByName(flavor.name)?.let {
addVariant(it)
}
}
return project.provider { wrapPluginOptions(pluginOptions, "configuration") }
}
// 3. 定义编译器插件的唯一 id,需要与后面编译器插件中定义的 pluginId 保持一致
override fun getCompilerPluginId() = "org.jetbrains.kotlin.android"
// 4. 定义编译器插件的 `Maven` 坐标信息,便于编译器下载它
override fun getPluginArtifact(): SubpluginArtifact =
JetBrainsSubpluginArtifact(artifactId = "kotlin-android-extensions")
}
主要也是重写以上4个函数,各自的功能在文中都有注释,其中主要需要注意applyToCompilation方法,我们传递了features,variant等参数给编译器插件
variant的主要作用是为不同 buildType,productFlavor目录的 layout 文件生成不同的包名
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.* import kotlinx.android.synthetic.debug.activity_debug.* import kotlinx.android.synthetic.demo.activity_demo.*
比如如上代码,activity_debug文件放在debug目录下,而activiyt_demo文件则放在demo这个flavor目录下,这种情况下它们的包名是不同的
编译器插件接收参数
class AndroidCommandLineProcessor : CommandLineProcessor {
override val pluginId: String = ANDROID_COMPILER_PLUGIN_ID
override val pluginOptions: Collection<AbstractCliOption>
= listOf(VARIANT_OPTION, PACKAGE_OPTION, EXPERIMENTAL_OPTION, DEFAULT_CACHE_IMPL_OPTION, CONFIGURATION, FEATURES_OPTION)
override fun processOption(option: AbstractCliOption, value: String, configuration: CompilerConfiguration) {
when (option) {
VARIANT_OPTION -> configuration.appendList(AndroidConfigurationKeys.VARIANT, value)
PACKAGE_OPTION -> configuration.put(AndroidConfigurationKeys.PACKAGE, value)
EXPERIMENTAL_OPTION -> configuration.put(AndroidConfigurationKeys.EXPERIMENTAL, value)
DEFAULT_CACHE_IMPL_OPTION -> configuration.put(AndroidConfigurationKeys.DEFAULT_CACHE_IMPL, value)
else -> throw CliOptionProcessingException("Unknown option: ${option.optionName}")
}
}
}
这段代码很简单,主要是解析variant,包名,是否开启试验特性,缓存实现方式这几个参数
注册各种Extension
接下来到了编译器插件的核心部分,通过注册各种Extension的方式修改编译器的产物
class AndroidComponentRegistrar : ComponentRegistrar {
companion object {
fun registerViewExtensions(configuration: CompilerConfiguration, isExperimental: Boolean, project: MockProject) {
ExpressionCodegenExtension.registerExtension(project,
CliAndroidExtensionsExpressionCodegenExtension(isExperimental, globalCacheImpl))
IrGenerationExtension.registerExtension(project,
CliAndroidIrExtension(isExperimental, globalCacheImpl))
StorageComponentContainerContributor.registerExtension(project,
AndroidExtensionPropertiesComponentContainerContributor())
ClassBuilderInterceptorExtension.registerExtension(project,
CliAndroidOnDestroyClassBuilderInterceptorExtension(globalCacheImpl))
PackageFragmentProviderExtension.registerExtension(project,
CliAndroidPackageFragmentProviderExtension(isExperimental))
}
}
override fun registerProjectComponents(project: MockProject, configuration: CompilerConfiguration) {
if (AndroidExtensionsFeature.VIEWS in features) {
registerViewExtensions(configuration, isExperimental, project)
}
}
}
可以看出,主要就是在开启了AndroidExtensionsFeature.VIEWS特性时,注册了5个Extension,接下来我们来看下这5个Extension都做了什么
IrGenerationExtension
IrGenerationExtension是KAE插件的核心部分,在生成 IR 时回调,我们可以在这个时候修改与添加 IR,KAE插件生成的_findCachedViewById方法都是在这个时候生成的,具体实现如下:
private class AndroidIrTransformer(val extension: AndroidIrExtension, val pluginContext: IrPluginContext) :
IrElementTransformerVoidWithContext() {
override fun visitClassNew(declaration: IrClass): IrStatement {
if ((containerOptions.cache ?: extension.getGlobalCacheImpl(declaration)).hasCache) {
val cacheField = declaration.getCacheField()
declaration.declarations += cacheField // 添加_$_findViewCache属性
declaration.declarations += declaration.getClearCacheFun() // 添加_$_clearFindViewByIdCache方法
declaration.declarations += declaration.getCachedFindViewByIdFun() // 添加_$_findCachedViewById方法
}
return super.visitClassNew(declaration)
}
override fun visitCall(expression: IrCall): IrExpression {
val result = if (expression.type.classifierOrNull?.isFragment == true) {
// this.get[Support]FragmentManager().findFragmentById(R$id.<name>)
createMethod(fragmentManager.child("findFragmentById"), createClass(fragment).defaultType.makeNullable()) {
addValueParameter("id", pluginContext.irBuiltIns.intType)
}.callWithRanges(expression).apply {
// ...
}
} else if (containerHasCache) {
// this._$_findCachedViewById(R$id.<name>)
receiverClass.owner.getCachedFindViewByIdFun().callWithRanges(expression).apply {
dispatchReceiver = receiver
putValueArgument(0, resourceId)
}
} else {
// this.findViewById(R$id.<name>)
irBuilder(currentScope!!.scope.scopeOwnerSymbol, expression).irFindViewById(receiver, resourceId, containerType)
}
return with(expression) { IrTypeOperatorCallImpl(startOffset, endOffset, type, IrTypeOperator.CAST, type, result) }
}
}
如上所示,主要做了两件事:
- 在
visitClassNew方法中给对应的类(比如 Activity 或者 Fragment )添加了_$_findViewCache属性,以及_$_clearFindViewByIdCache与_$_findCachedViewById方法 - 在
visitCall方法中,将viewId替换为相应的表达式,比如this._$_findCachedViewById(R$id.<name>)或者this.findViewById(R$id.<name>)
可以看出,其实KAE插件的大部分功能都是通过IrGenerationExtension实现的
ExpressionCodegenExtension
ExpressionCodegenExtension的作用其实与IrGenerationExtension基本一致,都是用来生成_$_clearFindViewByIdCache等代码的
主要区别在于,IrGenerationExtension在使用IR后端时回调,生成的是IR。
而ExpressionCodegenExtension在使用 JVM 非IR后端时回调,生成的是字节码
在 Kotlin 1.5 之后,JVM 后端已经默认开启 IR,可以认为这两个 Extension 就是新老版本的两种实现
StorageComponentContainerContributor
StorageComponentContainerContributor的主要作用是检查调用是否正确
class AndroidExtensionPropertiesCallChecker : CallChecker {
override fun check(resolvedCall: ResolvedCall<*>, reportOn: PsiElement, context: CallCheckerContext) {
// ...
with(context.trace) {
checkUnresolvedWidgetType(reportOn, androidSyntheticProperty)
checkDeprecated(reportOn, containingPackage)
checkPartiallyDefinedResource(resolvedCall, androidSyntheticProperty, context)
}
}
}
如上,主要做了是否有无法解析的返回类型等检查
ClassBuilderInterceptorExtension
ClassBuilderInterceptorExtension的主要作用是在onDestroyView方法中调用_$_clearFindViewByIdCache方法,清除KAE缓存
private class AndroidOnDestroyCollectorClassBuilder(
private val delegate: ClassBuilder,
private val hasCache: Boolean
) : DelegatingClassBuilder() {
override fun newMethod(
origin: JvmDeclarationOrigin,
access: Int,
name: String,
desc: String,
signature: String?,
exceptions: Array<out String>?
): MethodVisitor {
val mv = super.newMethod(origin, access, name, desc, signature, exceptions)
if (!hasCache || name != ON_DESTROY_METHOD_NAME || desc != "()V") return mv
hasOnDestroy = true
return object : MethodVisitor(Opcodes.API_VERSION, mv) {
override fun visitInsn(opcode: Int) {
if (opcode == Opcodes.RETURN) {
visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0)
visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKEVIRTUAL, currentClassName, CLEAR_CACHE_METHOD_NAME, "()V", false)
}
super.visitInsn(opcode)
}
}
}
}
可以看出,只有在 Fragment 的onDestroyView方法中添加了 clear 方法,这是因为 Fragment 的生命周期与其根 View 生命周期可能并不一致,而 Activity 的 onDestroy 中是没有也没必要添加的
PackageFragmentProviderExtension
PackageFragmentProviderExtension的主要作用是注册各种包名,以及该包名下的各种提示
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.* import kotlinx.android.synthetic.debug.activity_debug.* import kotlinx.android.synthetic.demo.activity_demo.*
比如我们在 IDE 中引入上面的代码,就可以引入 xml 文件中定义的各个 id 了,这就是通过这个Extension实现的
总结
本文主要从原理浅析,总体架构,源码分析等角度分析了 kotlin-android-extensions 插件到底是怎么实现的
相比其它方案,KAE使用起来可以说是非常简洁优雅了,可以看出 Kotlin 编译器插件真的可以打造出极简的 API,因此虽然KAE已经过时了,但还是有必要学习一下的
以上就是kotlin android extensions 插件实现示例详解的详细内容,更多关于kotlin android extensions 插件的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
相关文章

Android Studio gradle 编译提示‘default not found’ 解决办法
这篇文章主要介绍了Android Studio gradle 编译提示‘default not found’ 解决办法的相关资料,需要的朋友可以参考下2016-12-12












最新评论