Redis结合AOP与自定义注解实现分布式缓存流程详解
1、背景
项目中如果查询数据是直接到MySQL数据库中查询的话,会查磁盘走IO,效率会比较低,所以现在一般项目中都会使用缓存,目的就是提高查询数据的速度,将数据存入缓存中,也就是内存中,这样查询效率大大提高
分布式缓存方案
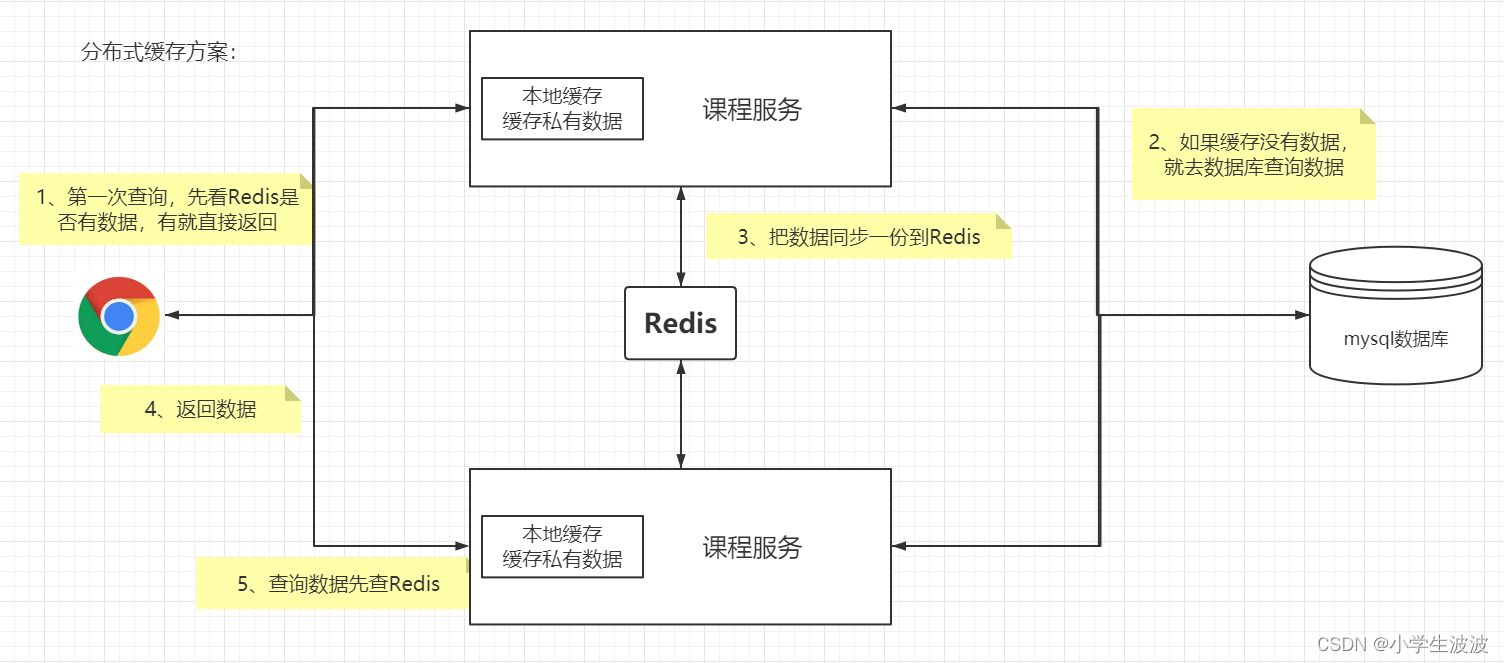
优点:
- 使用Redis作为共享缓存 ,解决缓存不同步问题
- Redis是独立的服务,缓存不用占应用本身的内存空间
什么样的数据适合放到缓存中呢?
同时满足下面两个条件的数据就适合放缓存:
- 经常要查询的数据
- 不经常改变的数据
接下来我们使用 AOP技术 来实现分布式缓存,这样做的好处是避免重复代码,极大减少了工作量
2、目标
我们希望分布式缓存能帮我们达到这样的目标:
- 对业务代码无侵入(或侵入性较小)
- 使用起来非常方便,最好是打一个注解就可以了,可插拔式的
- 对性能影响尽可能的小
- 要便于后期维护
3、方案
此处我们选择的方案就是:AOP+自定义注解+Redis
- 自定义一个注解,需要做缓存的接口打上这个注解即可
- 使用Spring AOP的环绕通知增强被自定义注解修饰的方法,把缓存的存储和删除都放这里统一处理
- 那么需要用到分布式锁的接口,只需要打一个注解即可,这样才够灵活优雅
4、实战编码
4.1、环境准备
首先我们需要一个简单的SpringBoot项目环境,这里我写了一个基础Demo版本,地址如下:
https://gitee.com/colinWu_java/spring-boot-base.git
大家可以先下载下来,本文就是基于这份主干代码进行修改的
4.2、pom依赖
pom.xml中需要新增以下依赖:
<!-- aop -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--jackson-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.10.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.11.1</version>
</dependency>4.3、自定义注解
添加缓存的注解
package org.wujiangbo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @desc 自定义注解:向缓存中添加数据
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyCache {
String cacheNames() default "";
String key() default "";
//缓存时间(单位:秒,默认是无限期)
int time() default -1;
}删除缓存注解:
package org.wujiangbo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @desc 自定义注解:从缓存中删除数据
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyCacheEvict {
String cacheNames() default "";
String key() default "";
}4.4、切面处理类
下面两个切面类实际上是可以写在一个类中的,但是为了方便理解和观看,我分开写了
package org.wujiangbo.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.wujiangbo.annotation.MyCache;
import org.wujiangbo.service.RedisService;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @desc 切面类,处理分布式缓存添加功能
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyCacheAop {
@Resource
private RedisService redisService;
/**
* 定义切点
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(myCache)")
public void pointCut(MyCache myCache){
}
/**
* 环绕通知
*/
@Around("pointCut(myCache)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, MyCache myCache) {
String cacheNames = myCache.cacheNames();
String key = myCache.key();
int time = myCache.time();
/**
* 思路:
* 1、拼装redis中存缓存的key值
* 2、看redis中是否存在该key
* 3、如果存在,直接取出来返回即可,不需要执行目标方法了
* 4、如果不存在,就执行目标方法,然后将缓存放一份到redis中
*/
String redisKey = new StringBuilder(cacheNames).append(":").append(key).toString();
String methodPath = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object result ;
if (redisService.exists(redisKey)){
log.info("访问接口:[{}],直接从缓存获取数据", methodPath);
return redisService.getCacheObject(redisKey);
}
try {
//执行接口
result = joinPoint.proceed();
//接口返回结果存Redis
redisService.setCacheObject(redisKey, result, time, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
log.info("访问接口:[{}],返回值存入缓存成功", methodPath);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("发生异常:{}", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
}
还有一个:
package org.wujiangbo.aop;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.wujiangbo.annotation.MyCacheEvict;
import org.wujiangbo.service.RedisService;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @desc 切面类,处理分布式缓存删除功能
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyCacheEvictAop {
@Resource
private RedisService redisService;
/**
* 定义切点
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(myCache)")
public void pointCut(MyCacheEvict myCache){
}
/**
* 环绕通知
*/
@Around("pointCut(myCache)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, MyCacheEvict myCache) {
String cacheNames = myCache.cacheNames();
String key = myCache.key();
/**
* 思路:
* 1、拼装redis中存缓存的key值
* 2、删除缓存
* 3、执行目标接口业务代码
* 4、再删除缓存
*/
String redisKey = new StringBuilder(cacheNames).append(":").append(key).toString();
String methodPath = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object result ;
//删除缓存
redisService.deleteObject(redisKey);
try {
//执行接口
result = joinPoint.proceed();
//删除缓存
redisService.deleteObject(redisKey);
log.info("访问接口:[{}],缓存删除成功", methodPath);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("发生异常:{}", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return result;
}
}4.5、工具类
Redis的工具类:
package org.wujiangbo.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.BoundSetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @desc Redis工具类
*/
@Component //交给Spring来管理 的自定义组件
public class RedisService {
@Autowired
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 查看key是否存在
*/
public boolean exists(String key)
{
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
/**
* 清空Redis所有缓存数据
*/
public void clearAllRedisData()
{
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys("*");
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
}
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
* @param timeout 时间
* @param timeUnit 时间颗粒度
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value, final Integer timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit)
{
if(timeout == -1){
//永久有效
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
else{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeout, timeUnit);
}
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout)
{
return expire(key, timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout, final TimeUnit unit)
{
return redisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit);
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象。
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> T getCacheObject(final String key)
{
ValueOperations<String, T> operation = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
return operation.get(key);
}
/**
* 删除单个对象
*
* @param key
*/
public boolean deleteObject(final String key)
{
if(exists(key)){
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
return true;
}
/**
* 删除集合对象
*
* @param collection 多个对象
* @return
*/
public long deleteObject(final Collection collection)
{
return redisTemplate.delete(collection);
}
/**
* 缓存List数据
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param dataList 待缓存的List数据
* @return 缓存的对象
*/
public <T> long setCacheList(final String key, final List<T> dataList)
{
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, dataList);
return count == null ? 0 : count;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的list对象
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> List<T> getCacheList(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, 0, -1);
}
/**
* 缓存Set
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @param dataSet 缓存的数据
* @return 缓存数据的对象
*/
public <T> BoundSetOperations<String, T> setCacheSet(final String key, final Set<T> dataSet)
{
BoundSetOperations<String, T> setOperation = redisTemplate.boundSetOps(key);
Iterator<T> it = dataSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
setOperation.add(it.next());
}
return setOperation;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的set
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Set<T> getCacheSet(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
}
/**
* 缓存Map
*
* @param key
* @param dataMap
*/
public <T> void setCacheMap(final String key, final Map<String, T> dataMap)
{
if (dataMap != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, dataMap);
}
}
/**
* 获得缓存的Map
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Map<String, T> getCacheMap(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
}
/**
* 往Hash中存入数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @param value 值
*/
public <T> void setCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hKey, value);
}
/**
* 获取Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @return Hash中的对象
*/
public <T> T getCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey)
{
HashOperations<String, String, T> opsForHash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return opsForHash.get(key, hKey);
}
/**
* 获取多个Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKeys Hash键集合
* @return Hash对象集合
*/
public <T> List<T> getMultiCacheMapValue(final String key, final Collection<Object> hKeys)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, hKeys);
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象列表
*
* @param pattern 字符串前缀
* @return 对象列表
*/
public Collection<String> keys(final String pattern)
{
return redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
}
}4.6、配置类
package org.wujiangbo.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonTypeInfo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.jsontype.impl.LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @desc redis配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisSerializableConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Resource
private RedisConnectionFactory factory;
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate()
{
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
mapper.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY);
serializer.setObjectMapper(mapper);
// 使用StringRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的key值
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
// Hash的key也采用StringRedisSerializer的序列化方式
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
@Bean
public DefaultRedisScript<Long> limitScript()
{
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptText(limitScriptText());
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
return redisScript;
}
/**
* 限流脚本
*/
private String limitScriptText()
{
return "local key = KEYS[1]\n" +
"local count = tonumber(ARGV[1])\n" +
"local time = tonumber(ARGV[2])\n" +
"local current = redis.call('get', key);\n" +
"if current and tonumber(current) > count then\n" +
" return tonumber(current);\n" +
"end\n" +
"current = redis.call('incr', key)\n" +
"if tonumber(current) == 1 then\n" +
" redis.call('expire', key, time)\n" +
"end\n" +
"return tonumber(current);";
}
}FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer类:
package org.wujiangbo.config;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JavaType;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.type.TypeFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.SerializationException;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* @desc Redis使用FastJson序列化
*/
public class FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer<T> implements RedisSerializer<T>
{
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private Class<T> clazz;
static
{
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
}
public FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer(Class<T> clazz)
{
super();
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public byte[] serialize(T t) throws SerializationException
{
if (t == null)
{
return new byte[0];
}
return JSON.toJSONString(t, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName).getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET);
}
@Override
public T deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws SerializationException
{
if (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0)
{
return null;
}
String str = new String(bytes, DEFAULT_CHARSET);
return JSON.parseObject(str, clazz);
}
public void setObjectMapper(ObjectMapper objectMapper)
{
Assert.notNull(objectMapper, "'objectMapper' must not be null");
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
}
protected JavaType getJavaType(Class<?> clazz)
{
return TypeFactory.defaultInstance().constructType(clazz);
}
}4.7、yml配置
server:
port: 8001
undertow:
# 设置IO线程数, 它主要执行非阻塞的任务,它们会负责多个连接, 默认设置每个CPU核心一个线程
# 不要设置过大,如果过大,启动项目会报错:打开文件数过多(CPU有几核,就填写几)
io-threads: 6
# 阻塞任务线程池, 当执行类似servlet请求阻塞IO操作, undertow会从这个线程池中取得线程
# 它的值设置取决于系统线程执行任务的阻塞系数,默认值是:io-threads * 8
worker-threads: 48
# 以下的配置会影响buffer,这些buffer会用于服务器连接的IO操作,有点类似netty的池化内存管理
# 每块buffer的空间大小,越小的空间被利用越充分,不要设置太大,以免影响其他应用,合适即可
buffer-size: 1024
# 每个区分配的buffer数量 , 所以pool的大小是buffer-size * buffers-per-region
buffers-per-region: 1024
# 是否分配的直接内存(NIO直接分配的堆外内存)
direct-buffers: true
spring:
#配置数据库链接信息
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test1?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
application:
name: springboot #服务名
#redis配置
redis:
# 数据库索引
database: 0
# 地址
host: 127.0.0.1
# 端口,默认为6379
port: 6379
# 密码
password: 123456
# 连接超时时间
timeout: 10000#MyBatis-Plus相关配置
mybatis-plus:
#指定Mapper.xml路径,如果与Mapper路径相同的话,可省略
mapper-locations: classpath:org/wujiangbo/mapper/*Mapper.xml
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #开启驼峰大小写自动转换
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #开启控制台sql输出
4.8、使用
Controller中写两个接口分别测试一下缓存的新增和删除
package org.wujiangbo.controller;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.wujiangbo.annotation.CheckPermission;
import org.wujiangbo.annotation.MyCache;
import org.wujiangbo.annotation.MyCacheEvict;
import org.wujiangbo.result.JSONResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @desc 测试接口类
*/
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class TestController {
//测试删除缓存
@GetMapping("/deleteCache")
@MyCacheEvict(cacheNames = "cacheTest", key = "userData")
public JSONResult deleteCache(){
System.out.println("deleteCache success");
return JSONResult.success("deleteCache success");
}
//测试新增缓存
@GetMapping("/addCache")
@MyCache(cacheNames = "cacheTest", key = "userData")
public JSONResult addCache(){
System.out.println("addCache success");
return JSONResult.success("addCache success");
}
}4.9、测试
浏览器先访问:http://localhost:8001/addCache
然后再通过工具查看Redis中是不是添加了缓存数据,正确情况应该是缓存添加进去了
然后再访问:http://localhost:8001/deleteCache
再通过工具查看Redis,缓存应该是被删除了,没有了
到此完全符合预期,测试成功
总结
本文主要是介绍了分布式缓存利用AOP+注解的方式处理,方便使用和扩展希望对大家有所帮助
最后本案例代码已全部提交到gitee中了,地址如下:
https://gitee.com/colinWu_java/spring-boot-base.git
本文新增的代码在【RedisDistributedCache】分支中
到此这篇关于Redis结合AOP与自定义注解实现分布式缓存流程详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Redis分布式缓存内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

spring-core组件详解——PropertyResolver属性解决器
这篇文章主要介绍了spring-core组件详解——PropertyResolver属性解决器,需要的朋友可以参考下2016-05-05












最新评论