C++ STL标准库之std::list使用介绍及用法详解
0. std::list 简介

头文件:
#include <list>
模板类list是一个容器,list是由双向链表来实现的,每个节点存储1个元素。list支持前后两种移动方向。
优势: 任何位置执行插入和删除动作都非常快
list与vector的区别:
- list不支持随机存取;
- 在list的任何位置执行插入和移除都非常快.插入和删除动作不影响指向其它元素的指针,引用,迭代器,不会造成失效;
- list不支持随机存取,不提供下标操作符和at()函数;
- list没有提供容量,空间重新分配等操作函数,每个元素都有自己的内存;
- list也提供了特殊成员函数,专门用于移动元素.
1 std::list 定义对象
list<A> listname; list<A> listname(size); list<A> listname(size,value); list<A> listname(elselist); list<A> listname(first, last);
2 std::list添加元素
void push_front(const T& x); // 头部添加 void push_back(const T& x); // 尾部添加
3 std::list删除元素
void pop_front(); // 头部删除 void pop_back(); // 尾部删除
4 std::list容器容量
size_type size() const; // 返回元素个数 size_type max_size() const; // 返回list对象最大允许容量 void resize(size_type n, T x=T()); // 调整list对象的大小
5 std::list迭代器
begin() // 返回指向容器中第一个元素的双向迭代器。 end() // 返回指向容器中最后一个元素所在位置的下一个位置的双向迭代器。 rbegin() // 返回指向最后一个元素的反向双向迭代器。 rend() // 返回指向第一个元素所在位置前一个位置的反向双向迭代器。 cbegin() // 和 begin() 功能相同,只不过在其基础上,增加了 const 属性,不能用于修改元素。 cend() // 和 end() 功能相同,只不过在其基础上,增加了 const 属性,不能用于修改元素。 crbegin() // 和 rbegin() 功能相同,只不过在其基础上,增加了 const 属性,不能用于修改元素。 crend() // 和 rend() 功能相同,只不过在其基础上,增加了 const 属性,不能用于修改元素。
程序示例:
#pragma warning(disable:4786)
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
//#include <iomanip.h>
using namespace std;
template <class T>void print(const T& Ele)
{
cout<<" "<<Ele<<";"<<endl;
}
// 格式化输出
void Print_D(double& Ele)
{
cout.width(5); // 宽度5
cout.precision(1); // 保留1位小数
cout<<std::fixed<<Ele<<", ";
}
void Print_I(int& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<", ";
}
void main()
{
//上定义双向队列
list<string>mylist_string;
list<double>mylist_double(6);
//---------初始化mylist_string
mylist_string.push_front("1: Jack");
mylist_string.push_front("2: Tom");
mylist_string.push_front("3: Mike");
//---------初始化mylist_double
mylist_double.push_front(10.0);
mylist_double.push_front(20.0);
mylist_double.push_front(30.0);
mylist_double.push_front(40.0);
mylist_double.push_front(50.0);
//下述是三种容器定义形式
list<int> mylist_int(6,0); // 6个0:0 0 0 0 0 0
list<double>mylist_double2(6,0.0); // 6个0.0:0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
list<int>elselist(mylist_int); // 以其它双向队列初始化
list<double>Iterlist(mylist_double.begin(),mylist_double.end()); // 以其他队列初始化
//----输出各个容器中的元素
cout<<"打印 mylist_string:"<<endl;
list<string>::iterator iter_String; // 迭代器
for(iter_String=mylist_string.begin();iter_String!=mylist_string.end();iter_String++)
{
string temp=*iter_String;
print(temp);
}
cout<<"打印 mylist_double:"<<endl;
for_each(mylist_double.begin(),mylist_double.end(),Print_D);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 mylist_double2:"<<endl;
for_each(mylist_double2.begin(),mylist_double2.end(),Print_D);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 Iterlist:"<<endl;
for_each(Iterlist.begin(),Iterlist.end(),Print_D);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 mylist_int:"<<endl;
for_each(mylist_int.begin(),mylist_int.end(),Print_I);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 elselist:"<<endl;
for_each(elselist.begin(),elselist.end(),Print_I);
cout<<endl;
//各容器的容量
int size=mylist_string.size();
int maxsize=mylist_string.size();
mylist_string.resize(5);
size=mylist_double.size();
maxsize=mylist_double.max_size();
mylist_double.resize(5);
size=mylist_double2.size();
maxsize=mylist_double2.max_size();
mylist_double2.resize(5);
size=Iterlist.size();
maxsize=Iterlist.max_size();
Iterlist.resize(5);
size=mylist_int.size();
maxsize=mylist_int.max_size();
mylist_int.resize(5);
size=elselist.size();
maxsize=elselist.max_size();
elselist.resize(5);
//----再次输出各个容器中的元素
cout<<"打印 mylist_string:"<<endl;
for(iter_String=mylist_string.begin();iter_String!=mylist_string.end();iter_String++)
{
string temp=*iter_String;
print(temp);
}
cout<<"打印 mylist_double:"<<endl;
for_each(mylist_double.begin(),mylist_double.end(),Print_D);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 mylist_double2:"<<endl;
for_each(mylist_double2.begin(),mylist_double2.end(),Print_D);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 Iterlist:"<<endl;
for_each(Iterlist.begin(),Iterlist.end(),Print_D);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 mylist_int:"<<endl;
for_each(mylist_int.begin(),mylist_int.end(),Print_I);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 elselist:"<<endl;
for_each(elselist.begin(),elselist.end(),Print_I);
cout<<endl;
//使用迭代器相关的函数
list<double>::iterator Iter_D;
list<double>::reverse_iterator Iter_rD;
cout<<"打印 mylist_double 所有元素:"<<endl;
for_each(mylist_double.begin(),mylist_double.end(),Print_D);
cout<<endl;
double tmp=0.0;
Iter_D=mylist_double.begin();
tmp=*Iter_D;
cout<<"打印 mylist_double 的 begin:"<<endl;
cout<<tmp<<endl;
Iter_rD=mylist_double.rbegin();
tmp=*Iter_rD;
cout<<"\r\n打印 mylist_double 的 rbegin:"<<endl;
cout<<tmp<<endl;
Iter_D=mylist_double.end();
Iter_D--; // 必须--,end为指向最后一个元素所在位置后一个位置
tmp=*Iter_D;
cout<<"打印 mylist_double 的 end:"<<endl;
cout<<tmp<<endl;
Iter_rD=mylist_double.rend();
Iter_rD--; // 必须--,rend为指向第一个元素所在位置前一个位置
tmp=*Iter_rD;
cout<<"打印 mylist_double 的 rend:"<<endl;
cout<<tmp<<endl;
tmp=mylist_double.front();
cout<<"打印 mylist_double 的 front:"<<endl;
cout<<tmp<<endl; //
//cout<<mylist_double.front()<<endl;
tmp=mylist_double.back();
cout<<"打印 mylist_double 的 back:"<<endl;
cout<<tmp<<endl;
}

6 std::list判断是否为空
bool empty() const;
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
list<double>mylist;
mylist.push_back(10.2);
bool empty=0;
if(mylist.empty())
cout<<"The list is empty!"<<endl;
else
{
empty=mylist.empty();
cout<<mylist.front()<<", "<<empty<<endl;
}
}

7 std::list元素的存取和访问
list型容器不提供成员函数at()和操作符operator[],可以使用迭代器进行元素的访问.
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(double& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<" ,";
}
void main()
{
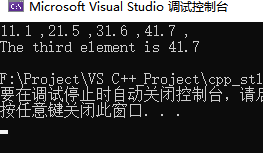
// 初始化list
list<double>mylist;
mylist.push_back(11.1);
mylist.push_back(21.5);
mylist.push_back(31.6);
mylist.push_back(41.7);
int count=mylist.size(); // 获取大小
for_each(mylist.begin(),mylist.end(),print); // 遍历打印
cout<<endl;
list<double>::iterator Iter_S;
Iter_S=mylist.begin();
cout<<"The third element is "<<*(++(++(++Iter_S)))<<endl;
}
8 std::list元素重置
list型容器提供了可以重置元素值的成员函数assign(),原型如下:
void assign(const_iterator first, const_iterator last); void assign(size_type n, const T& x=T());
使用方法:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// 打印队列所有元素
void print(list<double>& mylist)
{
list<double>::iterator Iter;
mylist.reverse();
for(Iter=mylist.begin();Iter!=mylist.end();Iter++)
{
cout<<*Iter<<", ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void main()
{
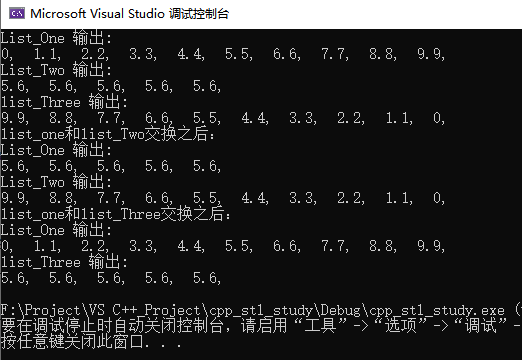
list<double> list_One,list_Two, list_Three;
// 初始化 list_One
double Ele=0.0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Ele=i+i/10.0;
list_One.push_front(Ele);
}
print(list_One);
// 初始化 list_Two
list_Two.assign(5,5.6);
print(list_Two);
// 初始化 list_Three
list_Three.assign(list_One.begin(),list_One.end());
print(list_Three);
}

9 std::list 交换两个容器的内容
list提供了成员函数swap().
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void print(list<double>& mylist)
{
list<double>::iterator Iter;
mylist.reverse();
for (Iter = mylist.begin(); Iter != mylist.end(); Iter++)
{
cout << *Iter << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void main()
{
list<double> list_One, list_Two, list_Three;
double Ele = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Ele = i + i / 10.0;
list_One.push_front(Ele);
}
cout << "List_One 输出:" << endl;
print(list_One);
list_Two.assign(5, 5.6);
cout << "List_Two 输出:" << endl;
print(list_Two);
list_Three.assign(list_One.begin(), list_One.end());
cout << "list_Three 输出:" << endl;
print(list_Three);
/******** list_One与list_Two交换 **********/
list_One.swap(list_Two);
cout << "list_one和list_Two交换之后:" << endl;
cout << "List_One 输出:" << endl;
print(list_One);
cout << "List_Two 输出:" << endl;
print(list_Two);
/******** list_One与list_Three交换 **********/
swap(list_One, list_Three);
cout << "list_one和list_Three交换之后:" << endl;
cout << "List_One 输出:" << endl;
print(list_One);
cout << "list_Three 输出:" << endl;
print(list_Three);
}
10 std::list元素的插入和删除
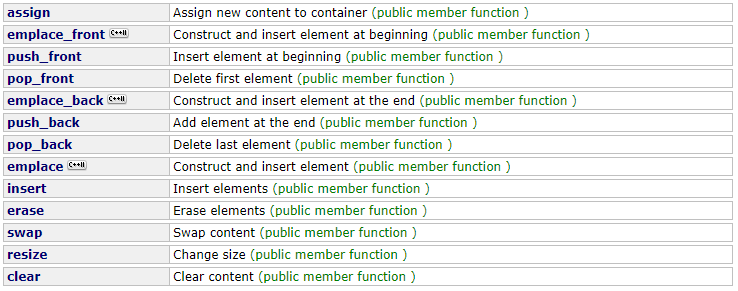
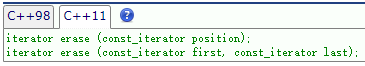
insert()的原型:
erase()的原型:
使用示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void OutToScreen(int& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<", ";
}
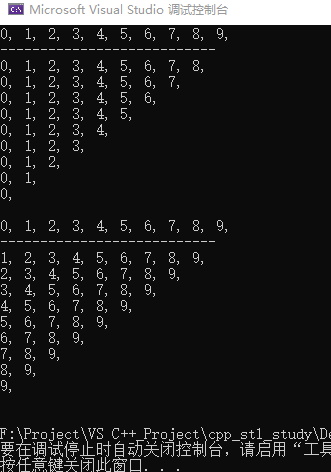
void main()
{
// 初始化mylt
list<int> mylt;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
mylt.push_back(i);
// 打印
for_each(mylt.begin(),mylt.end(),OutToScreen);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"---------------------------"<<endl;
// 从尾部删除:
while(!mylt.empty())
{
mylt.pop_back();
for_each(mylt.begin(),mylt.end(),OutToScreen);
cout<<endl;
}
// 重新初始化
mylt.clear();
for(int j=0;j<10;j++)
mylt.push_back(j);
// 打印
for_each(mylt.begin(),mylt.end(),OutToScreen);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"---------------------------"<<endl;
// 从头部删除
while(!mylt.empty())
{
mylt.erase(mylt.begin());
for_each(mylt.begin(),mylt.end(),OutToScreen);
cout<<endl;
}
}
11 std::list运算符函数
- operator ==:判断两个list是否相等
- operator <:判断两个list容器是否"前者小于后者"
- operator !=:判断两个list容器是否不相等
- operator <=:判断两个list容器是否"前者小于或等于后者"
- operator >:依次类推
- operator >=:依次类推
使用示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(int& Ele)
{
cout <<Ele<<" ";
}
void main()
{
// 初始化L1,L2
list<int> L1,L2;
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(2);
L2.assign(L1.begin(),L1.end());
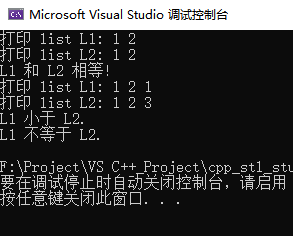
cout<<"打印 list L1: ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 list L2: ";
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
// 判断是否相等
if(L1==L2)
cout<<"L1 和 L2 相等!"<<endl;
L2.push_back(3);
L1.push_back(1);
cout<<"打印 list L1: ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"打印 list L2: ";
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
// 判断大小
if(L1<L2)
cout<<"L1 小于 L2."<<endl;
else if(L1>L2)
cout<<"L1 大于 L2."<<endl;
if(L1!=L2)
cout<<"L1 不等于 L2."<<endl;
}
12 std::list merge()和sort()
void merge(list& x); void merge(list& x, greater<T> pr); void sort(); void sort(greater<T>pr);
使用示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(int& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<" ";
}
void main()
{
// 初始化L1,L2,L3
list<int> L1,L2,L3;
list<int>::iterator I1,I2,I3;
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(5);
L2.push_back(2);
L2.push_back(3);
L3.push_back(7);
L3.push_back(8);
// 打印 L1,L2,L3
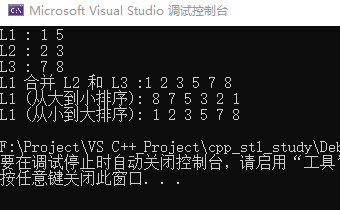
cout<<"L1 : ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L2 : ";
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L3 : ";
for_each(L3.begin(),L3.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L1 合并 L2 和 L3 :";
L1.merge(L2);
L1.merge(L3);
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print); //可知,在list合并之后,所有元素自动按从小到大排序
cout<<endl;
L1.sort(greater<int>()); //所有元素自动按从大到小排序
cout<<"L1 (从大到小排序): ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
L1.sort(); //默认按从小到大排序
cout<<"L1 (从小到大排序): ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print); //所有元素自动按从大到小排序
cout<<endl;
}
13 std::list remove() 和 remove_if()
void remove(const Type& _Val); template <class Pred> void remove_if(Pred pr);
使用示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(int& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<", ";
}
// 判断是否为偶数
bool is_Even(int & Ele)
{
return (Ele%2==1);
}
// 初始化列表
void Origin(list<int>& L, int num)
{
int temp;
L.clear();
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
temp=i+1;
L.push_back(temp);
}
for_each(L.begin(),L.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
}
void main()
{
list<int> L1;
Origin(L1,9); // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
// 添加一个9
int temp;
temp=9;
L1.push_back(temp);
// 添加一个8
temp=8;
L1.push_back(temp);
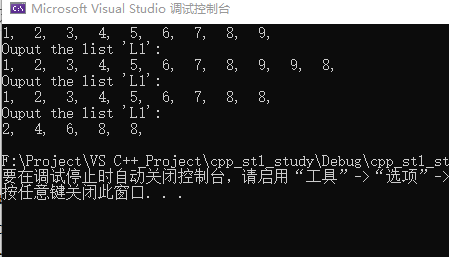
cout<<"Ouput the list \'L1\':"<<endl;
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
// 删除9
L1.remove(9);
cout<<"Ouput the list \'L1\':"<<endl;
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
// 删除非偶数
L1.remove_if(is_Even);
cout<<"Ouput the list \'L1\':"<<endl;
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
}
14 std::list splice()
// entire list (1)
void splice (const_iterator position, list& x);
void splice (const_iterator position, list&& x);
// single element (2)
void splice (const_iterator position, list& x, const_iterator i);
void splice (const_iterator position, list&& x, const_iterator i);
// element range (3)
void splice (const_iterator position, list& x,
const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
void splice (const_iterator position, list&& x,
const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(int& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<" ";
}
void main()
{
// 初始化L1,L2,L3,L0
list<int> L1,L2,L3,L0;
//list<int>::iterator I1,I2,I3;
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(5);
L2.push_back(2);
L2.push_back(3);
L3.push_back(7);
L3.push_back(8);
L0.push_back(9);
L0.push_back(-1);
// 打印 L1,L2,L3,L0
cout<<"L1 : ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L2 : ";
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L3 : ";
for_each(L3.begin(),L3.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L0 : ";
for_each(L0.begin(),L0.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L1 合并 L2:";
L1.splice(L1.end(),L2);
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L2 : ";
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L1 合并 L0 :";
L1.splice(L1.end(),L0,(++L0.begin()));
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L0 : ";
for_each(L0.begin(),L0.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L1 合并 L3 :";
L1.splice(L1.end(),L3,L3.begin(),L3.end());
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print); //可知,在list合并之后,所有元素自动按从小到大排序
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L3 : ";
for_each(L3.begin(),L3.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
L1.sort(greater<int>()); //所有元素自动按从大到小排序
cout<<"L1 (从大到小排序): ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
L1.sort(); //默认按从小到大排序
cout<<"L1 (从小到大排序): ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print); //所有元素自动按从大到小排序
cout<<endl;
}

15 std::list uniqe()
移除相邻重复元素
void uniqe();
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void Print(int& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<" ";
}
void main()
{
// 初始化L1,L2
list<int>L1,L2;
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(2);
L1.push_back(3);
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(2);
L1.push_back(3);
L1.push_back(5);
L1.push_back(7);
L2.assign(L1.begin(),L1.end());
// 打印 L1,L2
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),Print);
cout<<endl;
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),Print);
cout<<endl;
// 对L1进行排序,然后去重
L1.sort();
L1.unique();
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),Print);
cout<<endl;
// 对L2进行排序,对满足Pred条件的进行删除
L2.sort();
not_equal_to<int> Pred;
L2.unique(Pred);
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),Print);
cout<<endl;
}

16 std::list reverse()
实现将容器中所有元素用原来相反的顺序进行排列;
void reverse();
再次注意:list没有提供[]和at()
总结
到此这篇关于C++ STL标准库之std::list使用介绍及用法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ STL标准库std::list用法内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!












最新评论