PyTorch基础之torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss交叉熵损失
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss交叉熵损失
本文只考虑基本情况,未考虑加权。
torch.nnCrossEntropyLosss使用的公式
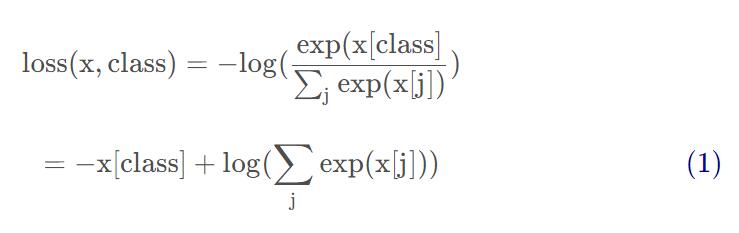
目标类别采用one-hot编码
其中,class表示当前样本类别在one-hot编码中对应的索引(从0开始),
x[j]表示预测函数的第j个输出
公式(1)表示先对预测函数使用softmax计算每个类别的概率,再使用log(以e为底)计算后的相反数表示当前类别的损失,只表示其中一个样本的损失计算方式,非全部样本。
每个样本使用one-hot编码表示所属类别时,只有一项为1,因此与基本的交叉熵损失函数相比,省略了其它值为0的项,只剩(1)所表示的项。
sample
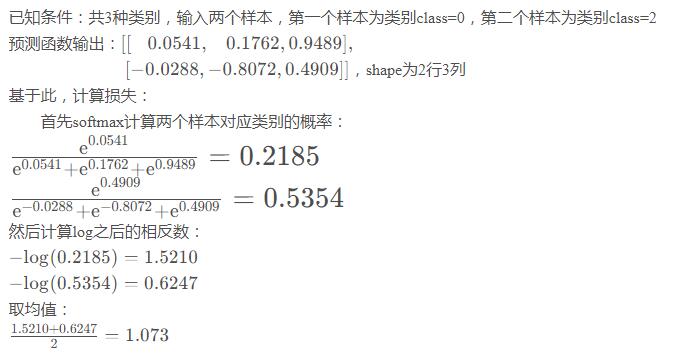
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss使用流程
torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss为一个类,并非单独一个函数,使用到的相关简单参数会在使用中说明,并非对所有参数进行说明。
首先创建类对象
In [1]: import torch In [2]: import torch.nn as nn In [3]: loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction="none")
参数reduction默认为"mean",表示对所有样本的loss取均值,最终返回只有一个值
参数reduction取"none",表示保留每一个样本的loss
计算损失
In [4]: pred = torch.tensor([[0.0541,0.1762,0.9489],[-0.0288,-0.8072,0.4909]], dtype=torch.float32) In [5]: class_index = torch.tensor([0, 2], dtype=torch.int64) In [6]: loss_value = loss_function(pred, class_index) In [7]: loss_value Out[7]: tensor([1.5210, 0.6247]) # 与上述【sample】计算一致
实际计算损失值调用函数时,传入pred预测值与class_index类别索引
在传入每个类别时,class_index应为一维,长度为样本个数,每个元素表示对应样本的类别索引,非one-hot编码方式传入
测试torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss的reduction参数为默认值"mean"
In [1]: import torch In [2]: import torch.nn as nn In [3]: loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction="mean") In [4]: pred = torch.tensor([[0.0541,0.1762,0.9489],[-0.0288,-0.8072,0.4909]], dtype=torch.float32) In [5]: class_index = torch.tensor([0, 2], dtype=torch.int64) In [6]: loss_value = loss_function(pred, class_index) In [7]: loss_value Out[7]: 1.073 # 与上述【sample】计算一致
交叉熵损失nn.CrossEntropyLoss()的真正计算过程
对于多分类损失函数Cross Entropy Loss,就不过多的解释,网上的博客不计其数。在这里,讲讲对于CE Loss的一些真正的理解。
首先大部分博客给出的公式如下:
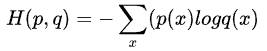
其中p为真实标签值,q为预测值。
在低维复现此公式,结果如下。在此强调一点,pytorch中CE Loss并不会将输入的target映射为one-hot编码格式,而是直接取下标进行计算。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
import numpy as np
#官方的实现
entroy=nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
input=torch.Tensor([[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],])
target = torch.tensor([0,1,2])
output = entroy(input, target)
print(output)
#输出 tensor(1.1142)
#自己实现
input=np.array(input)
target = np.array(target)
def cross_entorpy(input, target):
output = 0
length = len(target)
for i in range(length):
hou = 0
for j in input[i]:
hou += np.log(input[i][target[i]])
output += -hou
return np.around(output / length, 4)
print(cross_entorpy(input, target))
#输出 3.8162
我们按照官方给的CE Loss和根据公式得到的答案并不相同,说明公式是有问题的。
正确公式
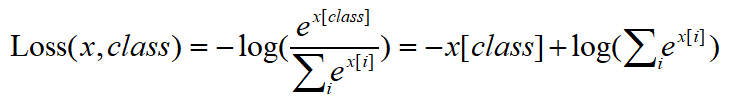
实现代码如下
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
import numpy as np
entroy=nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
input=torch.Tensor([[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],])
target = torch.tensor([0,1,2])
output = entroy(input, target)
print(output)
#输出 tensor(1.1142)
#%%
input=np.array(input)
target = np.array(target)
def cross_entorpy(input, target):
output = 0
length = len(target)
for i in range(length):
hou = 0
for j in input[i]:
hou += np.exp(j)
output += -input[i][target[i]] + np.log(hou)
return np.around(output / length, 4)
print(cross_entorpy(input, target))
#输出 1.1142
对比自己实现的公式和官方给出的结果,可以验证公式的正确性。
观察公式可以发现其实nn.CrossEntropyLoss()是nn.logSoftmax()和nn.NLLLoss()的整合版本。
nn.logSoftmax(),公式如下
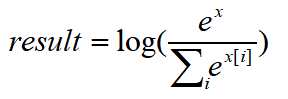
nn.NLLLoss(),公式如下
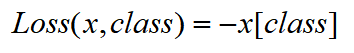
将nn.logSoftmax()作为变量带入nn.NLLLoss()可得
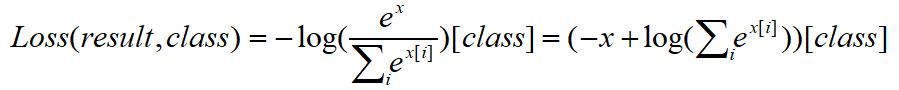
因为
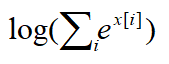
可看做一个常量,故上式可化简为:
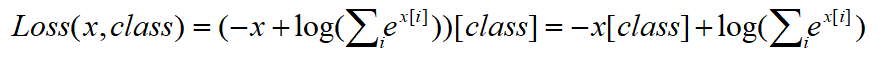
对比nn.Cross Entropy Loss公式,结果显而易见。
验证代码如下。
import torch import torch.nn as nn import math import numpy as np entroy=nn.CrossEntropyLoss() input=torch.Tensor([[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],[0.1234, 0.5555,0.3211],]) target = torch.tensor([0,1,2]) output = entroy(input, target) print(output) # 输出为tensor(1.1142) m = nn.LogSoftmax() loss = nn.NLLLoss() input=m(input) output = loss(input, target) print(output) # 输出为tensor(1.1142)
综上,可得两个结论
1.nn.Cross Entropy Loss的公式。
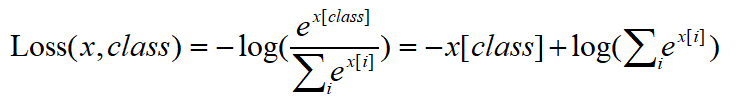
2.nn.Cross Entropy Loss为nn.logSoftmax()和nn.NLLLoss()的整合版本。
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
相关文章

Python 网络编程之TCP客户端/服务端功能示例【基于socket套接字】
这篇文章主要介绍了Python 网络编程之TCP客户端/服务端功能,结合实例形式分析了Python使用socket套接字实现TCP协议下的客户端与服务器端数据传输操作技巧,需要的朋友可以参考下2019-10-10












最新评论