gdb调试的简单操作总结
gdb是一个命令行下的、功能强大的调试器。
在学习 gdb 前,我们要知道几个最基本的 cmd 命令。
cmd
首先,对于 win10 系统,我们按 Windows + R 键,打开运行窗口,在里面输入 cmd,这样就可以打开 cmd 命令窗口了,是一个黑框。
接下来是一些最基本的命令。
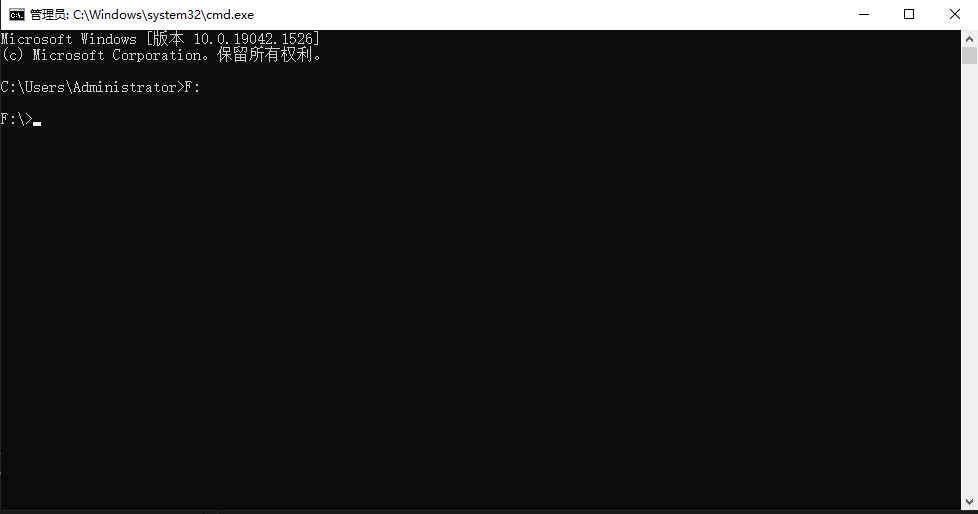
F: 打开 F 盘;E: 打开 E 盘,等等
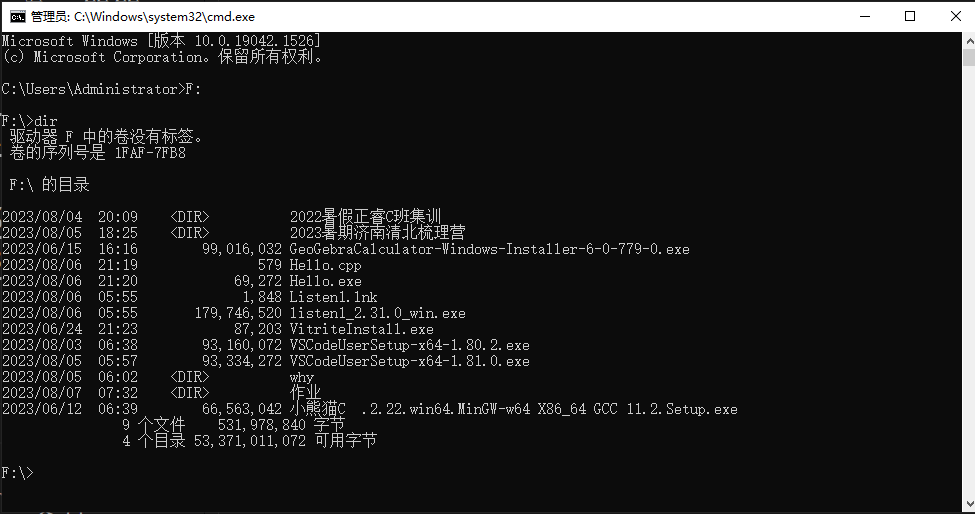
dir 查看文件夹中的文件
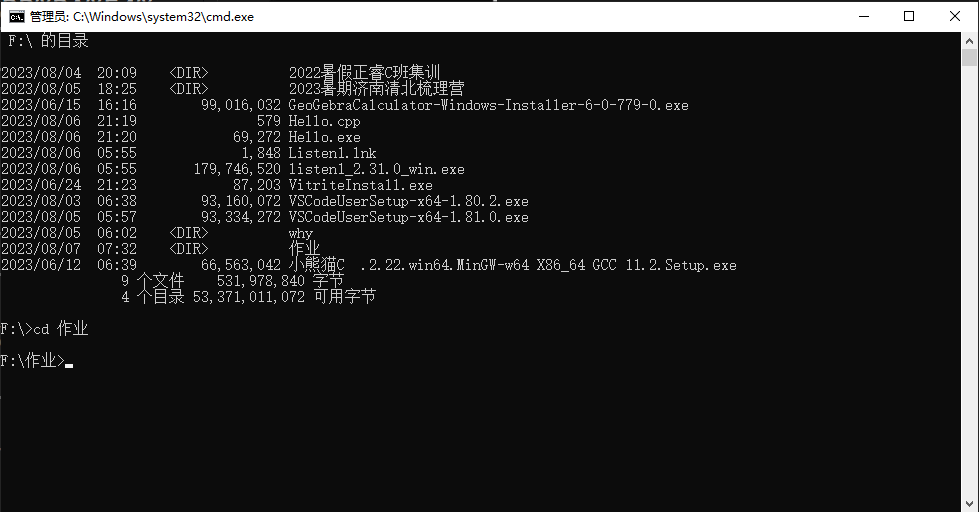
cd XXX.XXX 打开 XXX.XXX 文件
cd.. 返回上一级(文件夹)
cls 清屏(如果你觉得屏幕中的信息太多的话可以用这个命令)
ping [网址] 查看一个网站的信息(中括号不用打)
gdb 调试前的操作
在进行 gdb 调试之前,请先确保你安装了 gdb、g++、gcc 等。
首先,在 cmd 中进入到你的代码的文件夹页面,我的代码在 F 盘,如下图。
现在,我只要进入这个地址就行了。

要进行调试的文件是 ceshi.cpp,我们先在 cmd 中输入 g++ -g ceshi.cpp -o ceshi.exe 命令,然后等待一会,文件夹中就会出现一个名为 ceshi.exe 的文件。
之后输入 gdb 命令,会变成这样。
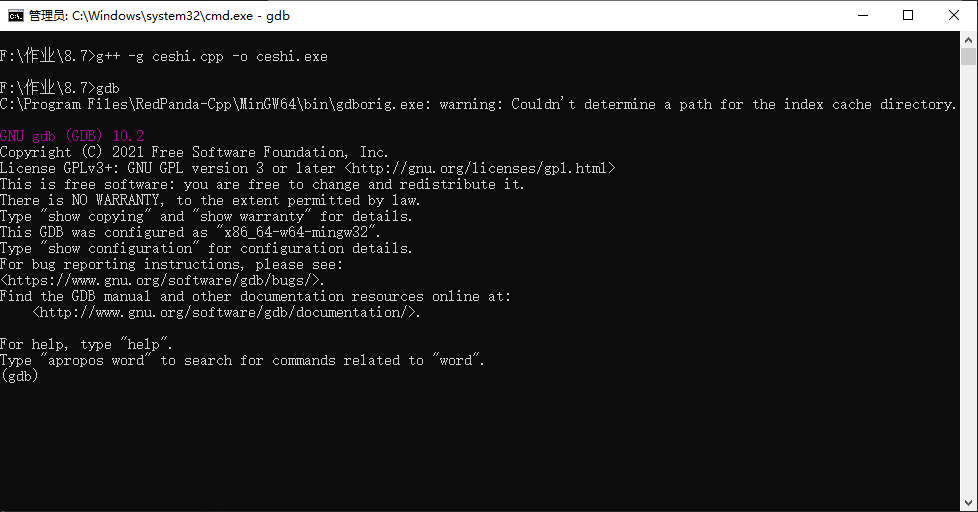
现在,我们用 file 命令来将刚才生成的 .exe 文件载入 gdb 调试器中,输入 file ceshi.exe(这里的 ceshi.exe 是刚才生成的 .exe 文件,你也可以起别的名字),如果出现下面的情况,就说明你成功了。

现在,我们就可以对这份代码进行调试了。
调试
这是 ceshi.cpp 里面的代码。
//The code was written by yifan, and yifan is neutral!!!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define bug puts("NOIP rp ++!");
template<typename T>
inline T read() {
T x = 0;
bool fg = 0;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
fg |= (ch == '-');
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return fg ? ~x + 1 : x;
}
int a[10];
vector<int> s;
void bre() {
int n = 10;
while (n --) {
puts("qwq");
}
}
int main() {
int n = read<int>(), m = read<int>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++ i) {
a[i] = i;
s.emplace_back(i);
}
puts("AK IOI!");
bre();
puts("end!");
return 0;
}我们要学会一些基础的命令。
r 运行代码,也就是我们平时的运行,你输入数据,它进行操作,最后输出。
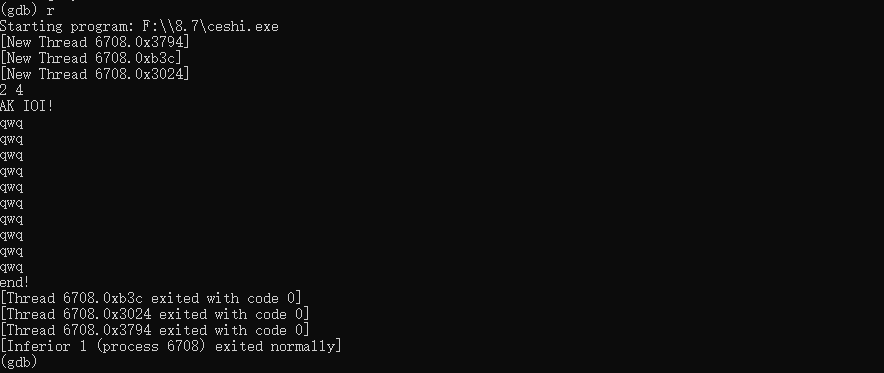
l 查看代码,l [数字] 查看第几行附近的代码(取决于你输入的数字)

b [数字或函数名] 在第几行设置断点或者在函数处设置断点,代码运行到这一行时就会停下,函数名要带小括号,例如 main 函数就是 main()
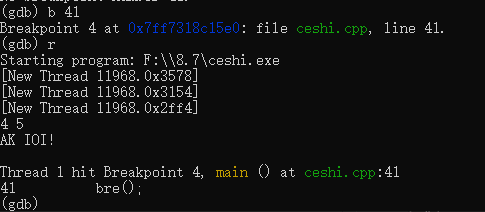
c 从断点处继续运行至下一断点处或者程序结束处。

p [变量、数组名或者 STL 容器名] 查看变量、数组或者 STL 容器中的元素,如果数组或者 STL 中的元素过多,则只会显示大小。
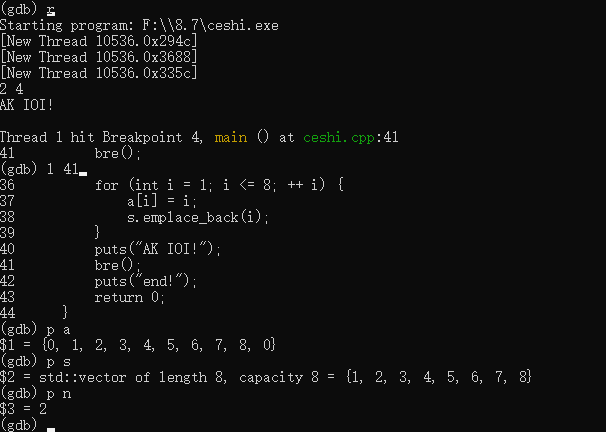
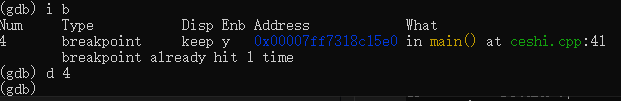
d 断点编号 删除断点,i b 查看所有断点。
watch [变量或数组] 观测某个变量或数组,当这个变量或者数组中的元素出现变化时,程序就暂停,并给你显示变化,在程序运行后才可以使用。
(gdb) r // 运行
Starting program: F:\\8.7\ceshi.exe
[New Thread 10196.0x1b74]
[New Thread 10196.0x173c]
[New Thread 10196.0xe84]
Thread 1 hit Breakpoint 1, main () at ceshi.cpp:36
36 n = read<int>(), m = read<int>(); // 碰到断点
(gdb) watch n // 添加监测变量 n
Hardware watchpoint 2: n
(gdb) c // 继续运行
Continuing.
2 3
Thread 1 hit Hardware watchpoint 2: n // n 的变化
Old value = 0
New value = 2
main () at ceshi.cpp:36
36 n = read<int>(), m = read<int>();
(gdb) watch a // 添加监测数组 a
Watchpoint 3: a
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Watchpoint 2 deleted because the program has left the block
in which its expression is valid.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a // a 的变化
Old value = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a
Old value = {0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a
Old value = {0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a
Old value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a
Old value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a
Old value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 0, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a
Old value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Thread 1 hit Watchpoint 3: a
Old value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0}
New value = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 0}
main () at ceshi.cpp:39
39 s.emplace_back(i);
(gdb) c
Continuing.
AK IOI!
qwq
qwq
qwq
qwq
qwq
qwq
qwq
qwq
qwq
qwq
end!
[Thread 10196.0xe84 exited with code 0]
[Thread 10196.0x173c exited with code 0]
[Thread 10196.0x1b74 exited with code 0]
[Inferior 1 (process 10196) exited normally]
(gdb)info watch查看所有监测。info locals显示局部变量。info f显示当前栈的情况。finish完成函数。call [函数名]调用子函数。n从断点处开始,下一行,不进入子函数。s从断点处开始,下一行,进入子函数(包括快读、STL 的输入函数等等)。return忽略程序未完成的语句,强行返回。whatis [变量名]返回变量的数据类型。set var [变量 = 数值]强行给变量赋值。q退出。
到此这篇关于gdb调试的简单操作总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关gdb调试内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

C语言中的strdup()函数和其与strcpy()函数的区别
这篇文章主要介绍了C语言中的strdup()函数和其与strcpy()函数的区别,同样用于拷贝字符串的两个函数的异同值得注意,需要的朋友可以参考下2015-08-08












最新评论