RocketMQ中的消费者启动流程解读
RocketMQ消费者启动
问题
消费者启动的时候,去哪拿的消息呢?
问题答案
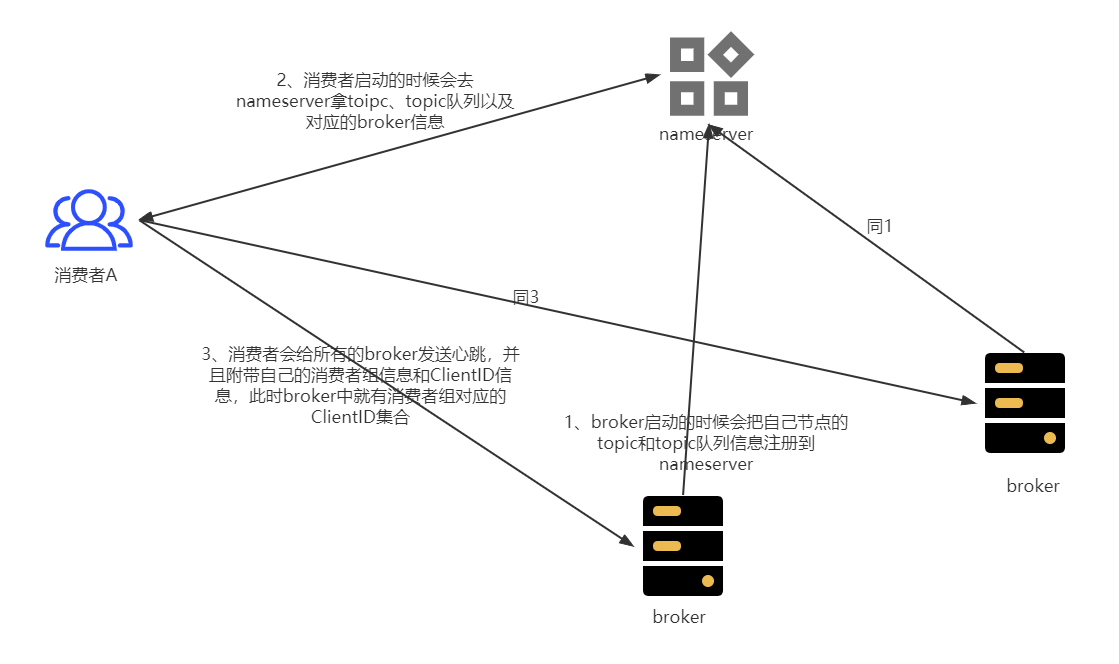
(1)当broker启动的时候,会把broker的地址端口、broker上的主题信息、主题队列信息发送到nameserver(如图中1)
(2)消费者Client启动的时候会去nameserver拿toipc、topic队列以及对应的broker信息,拿到以后把信息存储到本地(如图中2)
(3)消费者会给所有的broker发送心跳,并且附带自己的消费者组信息和ClientID信息,此时broker中就有消费者组对应的ClientID集合(如图中3)
(4)消费者启动后会reblance,有订阅的主题队列列表,并且通过broker可以拿到消费者组的ClientID集合,两个集合做rebalance,就可以拿到当前消费者对应消费的主题队列
(5) 消费者知道自己消费的主题队列,就可以根据队列信息通过Netty发送消息
跟源码
注意
本文是消费者启动流程,所以不去关注broker和nameserver的启动流程,这样关注点比较集中,因此步骤(1)本文不做描述。
消费者启动时怎么拿到toipc的信息
消费者启动的时候会调用 MQClientInstance###start()方法,start()方法里有会调用 MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()方法,里面的一段代码如下,会每隔一段时间更新一下topic路由信息
//MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer exception", e);
}
}
}, 10, this.clientConfig.getPollNameServerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);会把路由信息保存到本地的一个HashMap里,这样消费者就拿到了topic的信息并且会把broker的信息保存下来
//MQClientInstance###updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(final String topic, boolean isDefault,DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer) //根据主题从nameserver获取topic信息 topicRouteData = this.mQClientAPIImpl.getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, 1000 * 3);
//MQClientInstance###updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(final String topic, boolean isDefault,DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer)
//把主题和主题队列相关的broker保存下来
TopicRouteData cloneTopicRouteData = topicRouteData.cloneTopicRouteData();
for (BrokerData bd : topicRouteData.getBrokerDatas()) {
this.brokerAddrTable.put(bd.getBrokerName(), bd.getBrokerAddrs());
}总结:消费者拿到主题的队列列表和broker信息
消费者给broker发现心跳的作用
MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()方法,里面的一段代码如下,会每隔一段时间给所有的broker发送心跳消息
//MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.cleanOfflineBroker();
MQClientInstance.this.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask sendHeartbeatToAllBroker exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000, this.clientConfig.getHeartbeatBrokerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);那么发送的心跳包中携带什么信息呢?如代码中所示,携带clientID和组名称
//MQClientInstance###prepareHeartbeatData
private HeartbeatData prepareHeartbeatData() {
HeartbeatData heartbeatData = new HeartbeatData();
// clientID
//放入了当前消费者的clientID
//放入了当前消费者的clientID
//放入了当前消费者的clientID
heartbeatData.setClientID(this.clientId);
// Consumer
for (Map.Entry<String, MQConsumerInner> entry : this.consumerTable.entrySet()) {
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
ConsumerData consumerData = new ConsumerData();
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
consumerData.setGroupName(impl.groupName());
consumerData.setConsumeType(impl.consumeType());
consumerData.setMessageModel(impl.messageModel());
consumerData.setConsumeFromWhere(impl.consumeFromWhere());
consumerData.getSubscriptionDataSet().addAll(impl.subscriptions());
consumerData.setUnitMode(impl.isUnitMode());
heartbeatData.getConsumerDataSet().add(consumerData);
}
}
// Producer
for (Map.Entry<String/* group */, MQProducerInner> entry : this.producerTable.entrySet()) {
MQProducerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
ProducerData producerData = new ProducerData();
producerData.setGroupName(entry.getKey());
heartbeatData.getProducerDataSet().add(producerData);
}
}
return heartbeatData;
}此时broker拿到心跳消息怎么处理的呢?有一部分逻辑如下面代码所示,记录一下消费者信息
//ClientManageProcessor###heartBeat(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request)
```java
public RemotingCommand heartBeat(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request) {
//省略
for (ConsumerData data : heartbeatData.getConsumerDataSet()) {
//省略
boolean changed = this.brokerController.getConsumerManager().registerConsumer(
data.getGroupName(),
clientChannelInfo,
data.getConsumeType(),
data.getMessageModel(),
data.getConsumeFromWhere(),
data.getSubscriptionDataSet(),
isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable
);
//省略
}
//省略
}消费者怎么做reblance
MQClientInstance的start的方法里会开启一个rebalance的线程,如下面代码所示
//MQClientInstance###start()
public void start() throws MQClientException {
//省略
// Start rebalance service
this.rebalanceService.start();
//省略
}跟RebalanceService的run()方法一直跟下去最后跟到RebalanceImpl的rebalanceByTopic方法,如下面代码所示。根据主题队列列表和消费者组集合去做一个Rebalance,最后的返回结果是当前消费者需要消费的主题队列。
//RebalanceImpl##rebalanceByTopic
private void rebalanceByTopic(final String topic, final boolean isOrder) {
//获取订阅的主题的队列
//获取订阅的主题的队列
//获取订阅的主题的队列
Set<MessageQueue> mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
//获取同消费者组的ClientID集合
//获取同消费者组的ClientID集合
//获取同消费者组的ClientID集合
List<String> cidAll = this.mQClientFactory.findConsumerIdList(topic, consumerGroup);
if (mqSet != null && cidAll != null) {
List<MessageQueue> mqAll = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
mqAll.addAll(mqSet);
//排序
//排序
//排序
Collections.sort(mqAll);
Collections.sort(cidAll);
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy strategy = this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
List<MessageQueue> allocateResult = null;
try {
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
allocateResult = strategy.allocate(
this.consumerGroup,
this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(),
mqAll,
cidAll);
} catch (Throwable e) {
}
Set<MessageQueue> allocateResultSet = new HashSet<MessageQueue>();
if (allocateResult != null) {
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
allocateResultSet.addAll(allocateResult);
}
//此处看下面的消费者怎么去拉消息
//此处看下面的消费者怎么去拉消息
//此处看下面的消费者怎么去拉消息
boolean changed = this.updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(topic, allocateResultSet, isOrder);
}
}总结:消费者拿到主题的队列列表和消费者组中ClientID集合,通过在消费者这变做rebalance,从而确定被分配的主题队列集合
消费者怎么拉取消息
此处还是继续跟上面的代码,,然后执行到下面的代码,当消费者确定自己被分配的主题队列后,会把主题队列封装成PullRequest 并进行dispatch
//RebalanceImpl###updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance
private boolean updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(final String topic, final Set<MessageQueue> mqSet,
final boolean isOrder) {
//省列
List<PullRequest> pullRequestList = new ArrayList<PullRequest>();
for (MessageQueue mq : mqSet) {
//省略
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest();
pullRequest.setConsumerGroup(consumerGroup);
pullRequest.setNextOffset(nextOffset);
pullRequest.setMessageQueue(mq);
pullRequest.setProcessQueue(pq);
pullRequestList.add(pullRequest);
changed = true;
}
}
//省略
//派发请求任务
this.dispatchPullRequest(pullRequestList);
return changed;
}下面跟RebalanceImpl###dispatchPullRequest方法,最后跟到下面的代码,就是把PullRequest放入到一个阻塞队列里。
//PullMessageService###executePullRequestImmediately
public void executePullRequestImmediately(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
try {
this.pullRequestQueue.put(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("executePullRequestImmediately pullRequestQueue.put", e);
}
}那么谁取阻塞队列里的数据谁就是消费消息了? PullMessageService是一个线程,他的run方法里会取上面阻塞队列里的PullRequest,如下面代码所示
//PullMessageService###run()
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}从PullMessageService###pullMessage方法一直往下跟,就跟到下面的代码
//DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl###pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest)
public void pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
//省略
final long beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
};
//省略
try {
//发送数据并且执行回调方法,下面我们看一下回调方法的内容就好好了
//发送数据并且执行回调方法,下面我们看一下回调方法的内容就好好了
//发送数据并且执行回调方法,下面我们看一下回调方法的内容就好好了
this.pullAPIWrapper.pullKernelImpl(
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
subExpression,
subscriptionData.getExpressionType(),
subscriptionData.getSubVersion(),
pullRequest.getNextOffset(),
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullBatchSize(),
sysFlag,
commitOffsetValue,
BROKER_SUSPEND_MAX_TIME_MILLIS,
CONSUMER_TIMEOUT_MILLIS_WHEN_SUSPEND,
CommunicationMode.ASYNC,
pullCallback
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("pullKernelImpl exception", e);
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, pullTimeDelayMillsWhenException);
}
}那么回调方法是什么逻辑呢?代码如下所示,发现数据并且submitConsumeRequest
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(PullResult pullResult) {
if (pullResult != null) {
pullResult = DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.pullAPIWrapper.processPullResult(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), pullResult,
subscriptionData);
switch (pullResult.getPullStatus()) {
//发现数据
//发现数据
//发现数据
case FOUND:
long prevRequestOffset = pullRequest.getNextOffset();
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
long pullRT = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTimestamp;
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullRT(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup(),
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullRT);
long firstMsgOffset = Long.MAX_VALUE;
if (pullResult.getMsgFoundList() == null || pullResult.getMsgFoundList().isEmpty()) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
} else {
firstMsgOffset = pullResult.getMsgFoundList().get(0).getQueueOffset();
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullTPS(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup(),
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullResult.getMsgFoundList().size());
boolean dispatchToConsume = processQueue.putMessage(pullResult.getMsgFoundList());
//跟进去
//跟进去
//跟进去
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.consumeMessageService.submitConsumeRequest(
pullResult.getMsgFoundList(),
processQueue,
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
dispatchToConsume);
if (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval() > 0) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest,
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval());
} else {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
}
//省略
break;
case NO_NEW_MSG:
case NO_MATCHED_MSG:
//省略
}
}
}
};跟上面submitConsumeRequest方法的到下面的代码,封装成ConsumeRequest,其实ConsumerRequest是一个线程
//ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService###submitConsumeRequest
public void submitConsumeRequest(
final List<MessageExt> msgs,
final ProcessQueue processQueue,
final MessageQueue messageQueue,
final boolean dispatchToConsume) {
final int consumeBatchSize = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeMessageBatchMaxSize();
if (msgs.size() <= consumeBatchSize) {
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgs, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
} else {
//省略
}
}
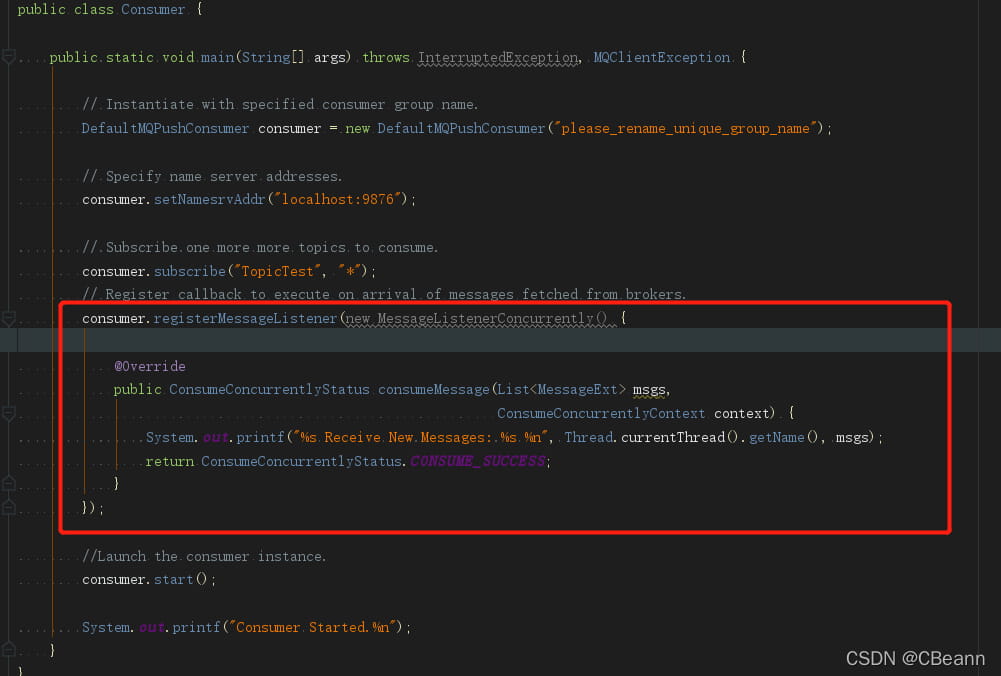
}ConsumeRequest的run方法就会执行我们注册的listener方法,此时就消费到数据
```java
@Override
public void run() {
//省略
status = listener.consumeMessage(Collections.unmodifiableList(msgs), context);
//省略
}
}
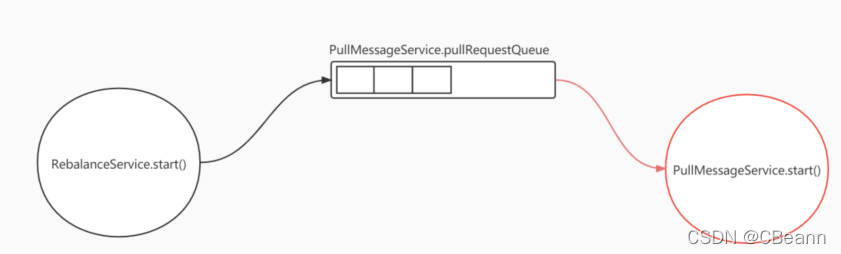
总结: 如下图所示,RebalanceService线程会根据情况把请求放在PullMessageService的pullRequestQueue阻塞队列队列里,队列的每一个节点就是拉请求;PullMessageService线程就是不断去pullRequestQueue里拿任务然后去看一下broker中有没有数据,如果有数据就消费。
总结
(1)忽然发现nameserver在整个过程中的作用感觉不是很大,其实我感觉这种设计还挺好的,因为把所有的压力都放在nameserver返回减少系统的健壮性。
(2)RocketMQ的rebalance是在消息消费者这边实现的,这样有一个很大的优势是减少nameserver和broker的压力。那消费者是怎么实现rebalance的呢?通过一个参数为当前消费者ID、主题队列、消费者组ClientID列表的匹配算法,每次只要保证算法的幂等性就可以了。
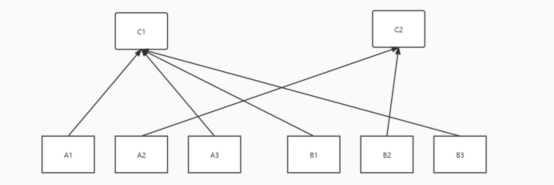
(3)RocketMQ的rebalance的rebalance是根据单个主题去实现的,这样的一个缺点是容易出现消费不平衡的问题。如下图所示。
(4)RocketMQ是AP的,因为他的很操作都是都是通过线程池的定时任务去做的。
到此这篇关于RocketMQ中的消费者启动流程解读的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关RocketMQ消费者启动内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

Spring Cloud Gateway全局通用异常处理的实现
这篇文章主要介绍了Spring Cloud Gateway全局通用异常处理的实现,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧2020-05-05












最新评论