C语言中的搜索算法详细解读
一、分析
有大量的信息(关键字:描述),需要在大量的信息当中搜索想要的信息:
(1)如果用全部检索(遍历)方法搜索关键字,无疑会浪费时间和资源;
(2)如果用树构建一个搜索树,层层搜索关键字(的一个字母),搜索到后就是需要的描述,就会节约很多时间。
二、算法思想
创建一个结构体,有关于关键字指针的数组,还有信息对应的描述。
typedef struct search_tree_node { //定义搜索树节点
struct search_tree_node* ch[CHAR_SIZE]; //分类
char desc[DESC_SIZE]; //描述
}STNode;
1、文字介绍
指针数组大小为 CHAR_SIZE = 26(默认全部是小写),每一个节点只存储关键字的一个字母,层层递进,当关键字存储完后,最后一个节点里的描述信息就是从根节点到当前节点构成关键字对应的描述。(所以默认关键字不能重复)
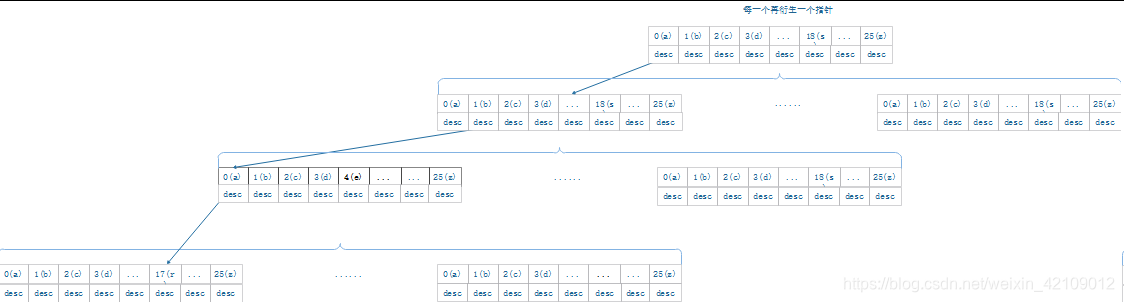
2、图例
从每一层读取一个字母,找到最后一个字母下面就是描述。(bear)
三、算法实现
1、代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define CHAR_SIZE 26 //字母大小(26小写)
#define KEY_SIZE 256 //关键字大小
#define DESC_SIZE 256 //描述区大小
#define BUFF_SIZE 512 //缓冲区大小
#define FILE_NAME "test.txt" //文件路径
typedef struct search_tree_node { //定义搜索树节点
struct search_tree_node* ch[CHAR_SIZE]; //分类
char desc[DESC_SIZE]; //描述
}STNode;
int get_word(FILE* fp, char* key, char* desc); //分离文本信息
STNode* new_node(); //新建节点
int insert_st_tree(STNode** st_tree, char* key, char* desc); //插入信息
char* find(STNode* st_tree, char* key); //查找分类
int main() {
char key[KEY_SIZE];
char desc[DESC_SIZE];
STNode* st_tree = NULL;
char* data;
FILE* fp = fopen(FILE_NAME, "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "fopen error!\n");
return -1;
}
while (1) {
int res = get_word(fp, key, desc);
if (res != -1) {
printf("%s\n", key);
printf("%s\n", desc);
}
else {
break;
}
insert_st_tree(&st_tree, key, desc);
}
data = find(st_tree, (char*)"ant");
if (data != NULL) {
printf("\nFind description: %s", data);
}
else {
printf("\nCan not find!\n");
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
/*****************************************************************************
* @data : 2020/4/19
* @brief : 读取文件,分离关键字和描述信息
* @input :
* fp : 文件指针
* key : 关键字(返回)
* desc: 描述信息(返回)
* @output:
* -1 : 失败
* 0 : 成功
*****************************************************************************/
int get_word(FILE* fp, char* key, char* desc) {
int i, j;
char buff[BUFF_SIZE];
char* res = fgets(buff, BUFF_SIZE, fp); //逐行读取(包括换行符)
if (res == NULL) {
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < KEY_SIZE - 1 && buff[i] != ':'; i++) { //预留结束符,分割标志
key[i] = buff[i];
}
key[i] = '\0';
i++;
for (j = 0; j < DESC_SIZE - 1 && buff[i] != '\0'; j++, i++) { //预留结束符,结束标志
desc[j] = buff[i];
}
desc[j] = '\0';
return 0;
}
/*****************************************************************************
* @data : 2020/4/19
* @brief : 创建新搜索树结点
* @input :
* none : none
* @output:
* node : 初始化的新结点
*****************************************************************************/
STNode* new_node() {
STNode* node;
node = (STNode*)malloc(sizeof(STNode)); //分配一个空间
if (node == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
for (int i = 0; i < CHAR_SIZE; i++) { //初始化
node->ch[i] = NULL;
}
node->desc[0] = '\0';
return node;
}
/*****************************************************************************
* @data : 2020/4/19
* @brief : 创建搜索树
* @input :
* st_tree : 二级指针创建搜索树
* key : 关键字
* desc : 描述信息
* @output:
* -1 : 失败
* 0 : 成功
*****************************************************************************/
int insert_st_tree(STNode** st_tree, char* key, char* desc) {
if (*st_tree == NULL) {
*st_tree = new_node();
if (*st_tree == NULL) {
return -1;
}
}
if (*key == '\0') {
strcpy((*st_tree)->desc, desc);
return 0;
}
//递归创建,因为以小写英文字母为例(26),ASCII码减去'a',得到指针相对地址(或数组下标)
return insert_st_tree((*st_tree)->ch + *key - 'a', key + 1, desc);
}
/*****************************************************************************
* @data : 2020/4/19
* @brief : 使用搜索树查询关键字描述(有返回,无)
* @input :
* st_tree : 搜索树
* key : 关键字
* @output:
* desc : 描述信息
* NULL : 空
*****************************************************************************/
char* find(STNode* st_tree, char* key) {
if (st_tree == NULL) { //为空,返回 NULL
return NULL;
}
if (*key == '\0') { //完全匹配,返回描述信息
if (st_tree->desc[0] == '\0') {
return NULL;
}
return st_tree->desc;
}
return find(st_tree->ch[*key - 'a'], key + 1); //递归查找
}
2、测试数据
ant:a small insect that lives in group
bee:an animal that can pick flowers and make honey
bear:the bear's body is thick and fat, and its hair is long and dense
beetle:an animal that feeds on pollen and a few nectar
dog:an animal which is loyal to human
dove:a flighty bird that feeds mainly on cereals
donkey:an animal with short legs and long ears
snake:a long and thin animal that lives in grass or other dark places
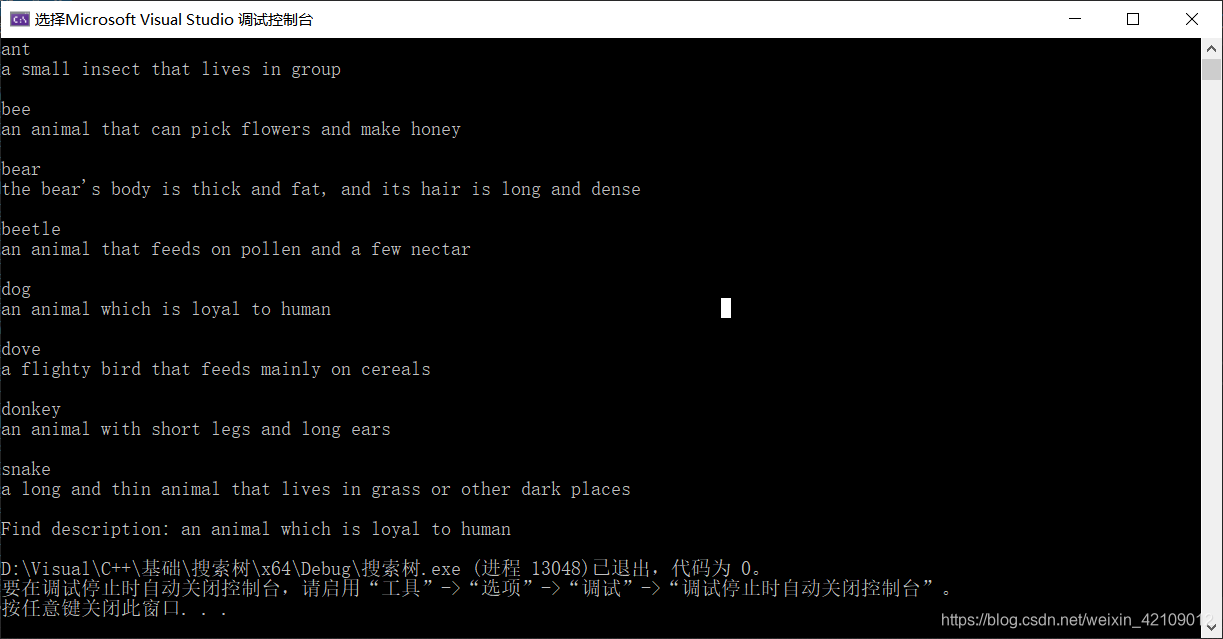
四、结果图
以找 dog 为例:
五、总结
要是能够实现加载下一层,是不是就相当于简化的搜索提示。
到此这篇关于C语言中的搜索算法详细解读的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C语言搜索算法内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!












最新评论