Java中的Semaphore信号量使用解析
1、Semaphore 是什么
Semaphore 通常我们叫它信号量, 可以用来控制同时访问特定资源的线程数量,通过协调各个线程,以保证合理的使用资源。
可以把它简单的理解成我们停车场入口立着的那个显示屏,每有一辆车进入停车场显示屏就会显示剩余车位减1,每有一辆车从停车场出去,显示屏上显示的剩余车辆就会加1,当显示屏上的剩余车位为0时,停车场入口的栏杆就不会再打开,车辆就无法进入停车场了,直到有一辆车从停车场出去为止。
2、使用场景
主要用于那些资源有明确访问数量限制的场景,常用于限流 。
比如:数据库连接池,同时进行连接的线程有数量限制,连接不能超过一定的数量,当连接达到了限制数量后,后面的线程只能排队等前面的线程释放了数据库连接才能获得数据库连接。
public class TestPoolSemaphore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pool pool = new Pool(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
Connection conn = pool.borrow();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
pool.free(conn);
}).start();
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Pool")
class Pool {
// 1. 连接池大小
private final int poolSize;
// 2. 连接对象数组
private Connection[] connections;
// 3. 连接状态数组 0 表示空闲, 1 表示繁忙
private AtomicIntegerArray states;
private Semaphore semaphore;
// 4. 构造方法初始化
public Pool(int poolSize) {
this.poolSize = poolSize;
// 让许可数与资源数一致
this.semaphore = new Semaphore(poolSize);
this.connections = new Connection[poolSize];
this.states = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[poolSize]);
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
connections[i] = new MockConnection("连接" + (i+1));
}
}
// 5. 借连接
public Connection borrow() {// t1, t2, t3
// 获取许可
try {
semaphore.acquire(); // 没有许可的线程,在此等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
// 获取空闲连接
if(states.get(i) == 0) {
if (states.compareAndSet(i, 0, 1)) {
log.debug("borrow {}", connections[i]);
return connections[i];
}
}
}
// 不会执行到这里
return null;
}
// 6. 归还连接
public void free(Connection conn) {
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
if (connections[i] == conn) {
states.set(i, 0);
log.debug("free {}", conn);
semaphore.release();
break;
}
}
}
}
class MockConnection implements Connection {
private String name;
public MockConnection(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MockConnection{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Clob createClob() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {
}
@Override
public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public String getSchema() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}比如:停车场场景,车位数量有限,同时只能容纳多少台车,车位满了之后只有等里面的车离开停车场外面的车才可以进入。
/**
* @author WGR
* @create 2020/12/27 -- 22:19
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建 semaphore 对象
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
// 2. 10个线程同时运行
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int x = i;
new Thread(() -> {
// 3. 获取许可
try {
semaphore.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println(x +"占到车位。。。");
Thread.sleep(1);
System.out.println(x +"释放车位。。。");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4. 释放许可
semaphore.release();
}
}).start();
}
}
}3、Semaphore实现原理
(1)、Semaphore初始化
Semaphore semaphore=new Semaphore(3);
1、当调用new Semaphore(3) 方法时,默认会创建一个非公平的锁的同步阻塞队列。
2、把初始令牌数量赋值给同步队列的state状态,state的值就代表当前所剩余的令牌数量。
(2)获取令牌
semaphore.acquire();
1、当前线程会尝试去同步队列获取一个令牌,获取令牌的过程也就是使用原子的操作去修改同步队列的state ,获取一个令牌则修改为state=state-1。
2、 当计算出来的state<0,则代表令牌数量不足,此时会创建一个Node节点加入阻塞队列,挂起当前线程。
3、当计算出来的state>=0,则代表获取令牌成功。
源码:
/**
* 获取1个令牌
*/
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}/**
* 共享模式下获取令牌,获取成功则返回,失败则加入阻塞队列,挂起线程
* @param arg
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
//尝试获取令牌,arg为获取令牌个数,当可用令牌数减当前令牌数结果小于0,则创建一个节点加入阻塞队列,挂起当前线程。
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}/**
* 1、创建节点,加入阻塞队列,
* 2、重双向链表的head,tail节点关系,清空无效节点
* 3、挂起当前节点线程
* @param arg
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
//创建节点加入阻塞队列
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
//获得当前节点pre节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);//返回锁的state
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
//重组双向链表,清空无效节点,挂起当前线程
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}Semaphore 有点像一个停车场,permits 就好像停车位数量,当线程获得了 permits 就像是获得了停车位,然后停车场显示空余车位减一刚开始,permits(state)为 3,这时 5 个线程来获取资源
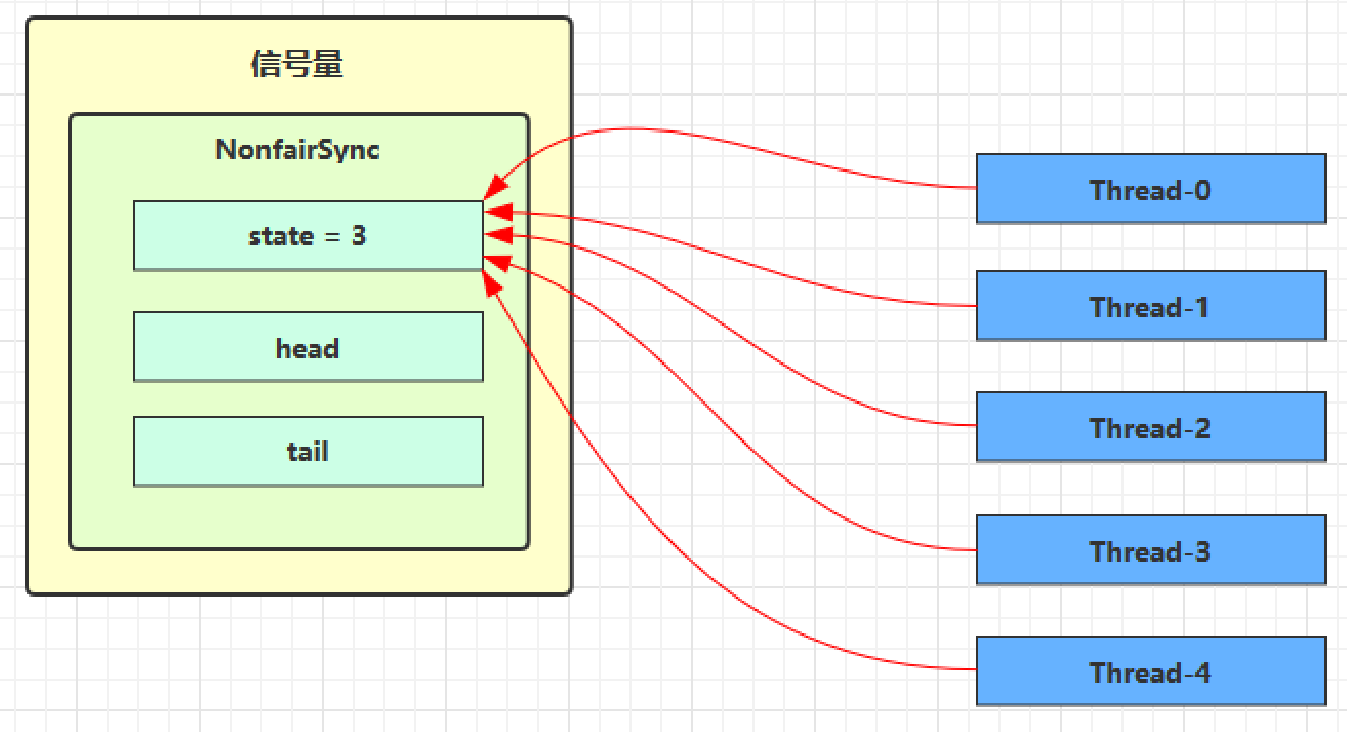
假设其中 Thread-1,Thread-2,Thread-4 cas 竞争成功,而 Thread-0 和 Thread-3 竞争失败,进入 AQS 队列park 阻塞
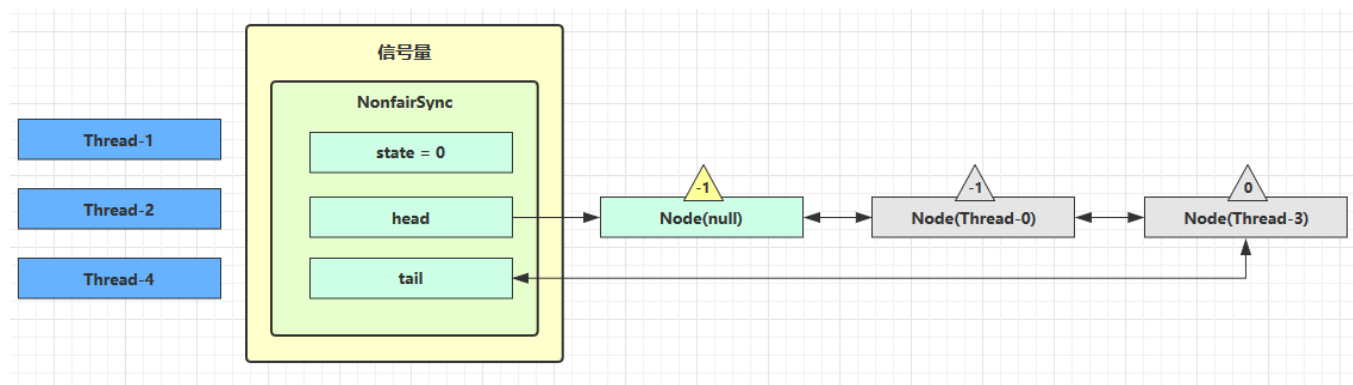
(3)、释放令牌
semaphore.release();
当调用semaphore.release() 方法时
1、线程会尝试释放一个令牌,释放令牌的过程也就是把同步队列的state修改为state=state+1的过程
2、释放令牌成功之后,同时会唤醒同步队列的所有阻塞节共享节点线程
3、被唤醒的节点会重新尝试去修改state=state-1 的操作,如果state>=0则获取令牌成功,否则重新进入阻塞队列,挂起线程。
源码:
/**
* 释放令牌
*/
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}/**
*释放共享锁,同时唤醒所有阻塞队列共享节点线程
* @param arg
* @return
*/
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
//释放共享锁
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
//唤醒所有共享节点线程
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}/**
* 唤醒所有共享节点线程
*/
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {//是否需要唤醒后继节点
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))//修改状态为初始0
continue;
unparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒h.nex节点线程
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE));
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}这时 Thread-4 释放了 permits,状态如下
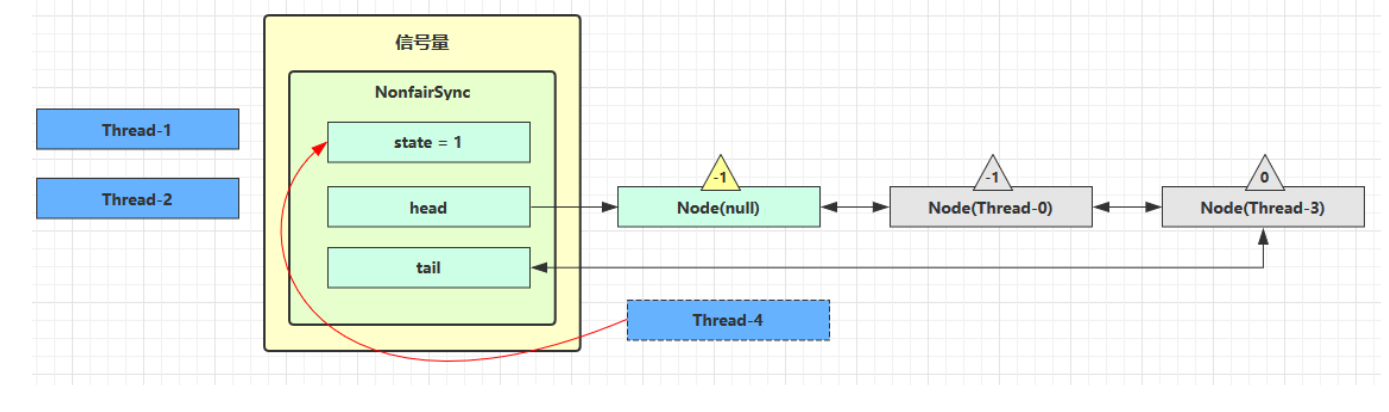
接下来 Thread-0 竞争成功,state 再次设置为 0,设置自己为 head 节点,断开原来的 head 节点,unpark 接下来的 Thread-3 节点,但由于 state 是 0,因此 Thread-3 在尝试不成功后再次进入 park 状态
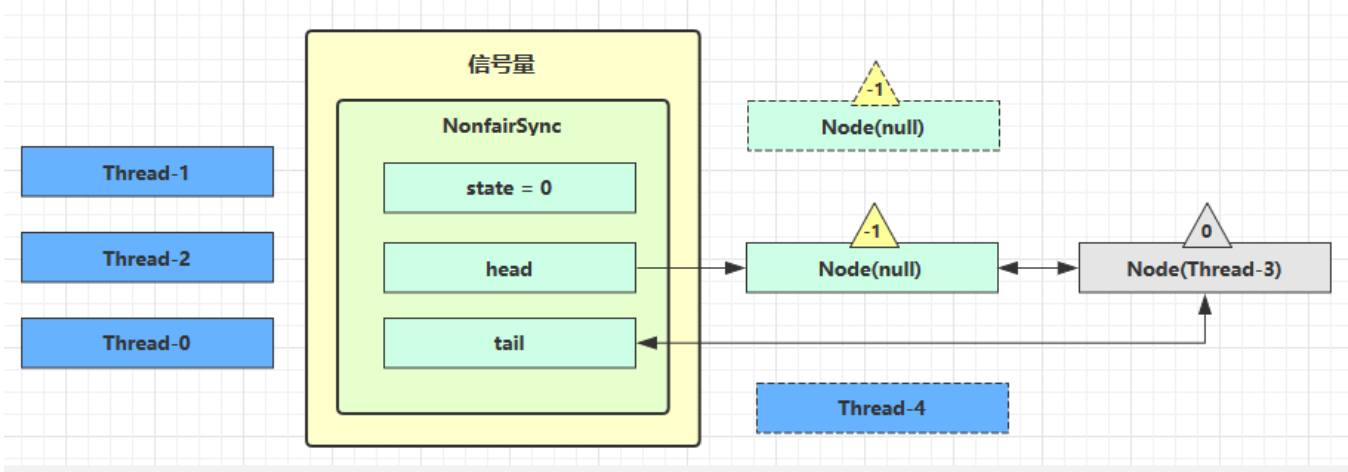
到此这篇关于Java中的Semaphore信号量使用解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Semaphore信号量内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

Spring Boot实战之netty-socketio实现简单聊天室(给指定用户推送消息)
本篇文章主要介绍了Spring Boot实战之netty-socketio实现简单聊天室(给指定用户推送消息),具有一定的参考价值,有兴趣的可以了解一下。2017-03-03
将springboot项目生成可依赖的jar并引入到项目中的方法
SpringBoot项目默认打包的是可运行jar包,也可以打包成不可运行的jar包,本文给大家介绍将springboot项目生成可依赖的jar并引入到项目中的方法,感兴趣的朋友一起看看吧2023-11-11
springboot配置多数据源的实例(MongoDB主从)
下面小编就为大家分享一篇springboot配置多数据源的实例(MongoDB主从),具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。一起跟随小编过来看看吧2017-12-12
Springboot+MDC+traceId日志中打印唯一traceId
本文主要介绍了Springboot+MDC+traceId日志中打印唯一traceId,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考一下2021-10-10
Maven中怎么手动添加jar包到本地仓库详解(repository)
这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于Maven中怎么手动添加jar包到本地仓库的相关资料,文中通过图文以及实例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2023-04-04
Spring系列中的beanFactory与ApplicationContext
这篇文章主要介绍了Spring系列中的beanFactory与ApplicationContext,文章围绕主题展开详细的内容介绍,具有一定的参考价值,需要的小伙伴可以参考一下2022-09-09












最新评论