spring boot定时器实现定时同步数据的操作步骤
前言
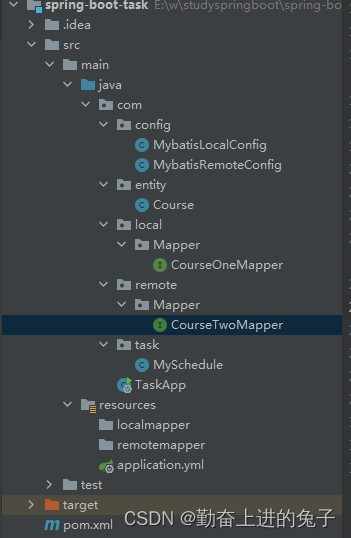
一、依赖和目录结构
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.3.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.49</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置文件
server:
port: 8089
spring:
datasource:
remote :
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.2/student?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 111
local :
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.1/student?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 111
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl #开启sql日志二、使用步骤
2.1 两个数据源的不同引用配置
package com.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
*
* @date :Created in 2023/12/2 19:51
* @description:本地数据源
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.local.Mapper", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate1")
public class MybatisLocalConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.local")
public DataSource dataSource1() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory1(@Qualifier("dataSource1") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 设置mapper.xml文件的位置
factoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:localmapper/*.xml"));
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate1(@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory1") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.remote.Mapper", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "sqlSessionTemplate2")
public class MybatisRemoteConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.remote")
public DataSource dataSource2() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory2(@Qualifier("dataSource2") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 设置mapper.xml文件的位置
factoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapper2/*.xml"));
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate2(@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory2") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}2.2 对应的mapper
public interface CourseOneMapper extends BaseMapper<Course> {
}public interface CourseTwoMapper extends BaseMapper<Course> {
/**
* 批量插入
* @param list
*/
@Insert("<script> " +
"INSERT INTO tbl_course (name, teacher) VALUES " +
"<foreach collection='list' item='item' separator=','> " +
"(#{item.name}, #{item.teacher})" +
"</foreach> " +
"</script>")
void batchInsert(@Param("list") List<Course> list);
}@TableName("tbl_course")
public class Course {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String teacher;
public Course() {
}
public Course(Integer id, String name, String teacher) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.teacher = teacher;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return id
*/
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param id
*/
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 获取
* @return teacher
*/
public String getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param teacher
*/
public void setTeacher(String teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Course{id = " + id + ", name = " + name + ", teacher = " + teacher + "}";
}
}2.3 定时任务处理
@EnableScheduling //开启定时
@Component
public class MySchedule {
@Resource
private CourseOneMapper courseOneMapper;
@Resource
private CourseTwoMapper courseTwoMapper;
/**
* 每隔10秒执行一次
*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000000)
public void test(){
//查询到要同步的数据
List<Course> coursesOne = courseOneMapper.selectList(null);
//批量插入
courseTwoMapper.batchInsert(coursesOne);
}
}总结
在Java中,@Scheduled注解是用于指定定时任务的执行规则的。它可以应用于方法或者类上面。
如果应用于方法上,该方法将被视为一个定时任务,并按照指定的时间规则进行调度执行。
如果应用于类上,该类中所有带有@Scheduled注解的方法都会被视为定时任务。
@Scheduled注解的参数可以用来指定任务的执行规则,包括以下几个方面:
fixedDelay:指定任务开始执行之后的延迟时间(毫秒数),任务执行完成后,再经过指定的延迟时间再次执行。例如:@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000)表示任务开始执行后,等待5秒后再次执行。
fixedRate:指定任务开始执行之后的间隔时间(毫秒数),任务执行完成后,立即开始下一次执行。例如:@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000)表示任务开始执行后,每隔5秒执行一次。
initialDelay:指定任务首次执行的延迟时间(毫秒数)。例如:@Scheduled(initialDelay = 5000)表示任务首次执行延迟5秒。
cron:使用Cron表达式指定复杂的任务执行规则。Cron表达式由6个部分组成,分别表示秒、分钟、小时、日期、月份和星期几。例如:@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 12 * * ?")表示每天中午12点执行任务。
除了以上参数,@Scheduled注解还支持fixedDelayString、fixedRateString和zone等属性,可以使用字符串形式的时间间隔和指定时区。
需要注意的是,@Scheduled注解需要与@EnableScheduling注解一起使用,以启用定时任务的功能。
到此这篇关于spring boot定时器实现定时同步数据的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关spring boot定时器同步数据内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

Spring boot route Controller接收参数常用方法解析
这篇文章主要介绍了Spring boot route Controller接收参数常用方法解析,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2020-10-10












最新评论