Qt正则表达式使用举例
更新时间:2024年02月19日 15:16:49 作者:骆驼胡杨
这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于Qt正则表达式使用的相关资料,Qt中的正则表达式模式匹配功能由QRegExp类实现,它完全支持Unicode,并可以应用于字符串验证、搜索、查找替换和分割等场景,需要的朋友可以参考下
正则表达式
正则表达式即一个文本匹配字符串的一种模式,Qt中QRegExp类实现使用正则表达式进行模式匹配,且完全支持Unicode,主要应用:字符串验证、搜索、查找替换、分割。
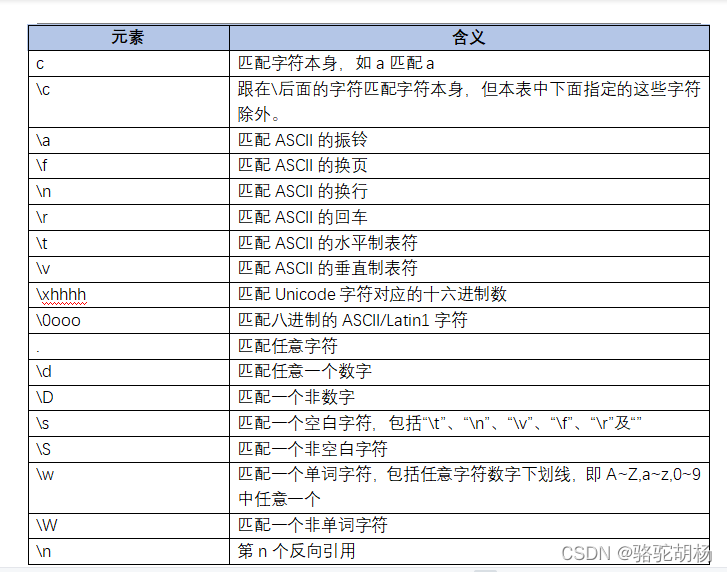
正则表达式中字符及字符集
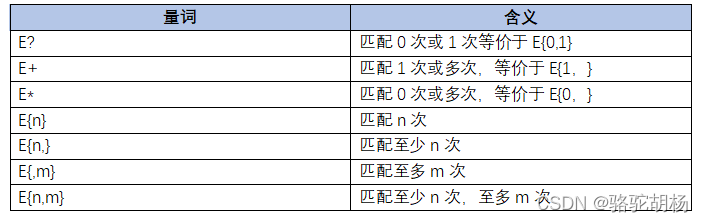
正则表达式中的量词
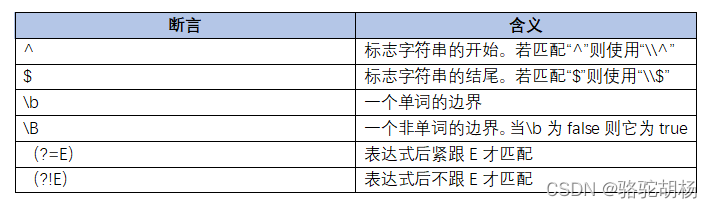
正则表达式中的断言
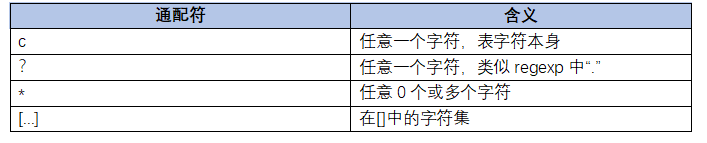
QRegExp同时支持通配符
新建控制台应用程序,项目名QRegExp
编辑main.cpp文件//匹配字符 QRegExp ret("a"); qDebug() << "是否匹配成功: " << ret.exactMatch("abc"); //false qDebug() << "是否匹配成功: " << ret.exactMatch("a"); //true //匹配数字 QRegExp retNum("(\\d*\\D{2})"); qDebug() << "是否匹配成功: " << retNum.exactMatch("120kg"); //true qDebug() << "是否匹配成功: " << retNum.exactMatch("180cm"); //true qDebug() << "是否匹配成功: " << retNum.exactMatch("3M"); //false //匹配通配符 QRegExp re("*.txt") ; re.setPatternSyntax(QRegExp::Wildcard); //支持通配符 qDebug() << "通配符匹配: " << re.exactMatch("a.txt"); //true qDebug() << "通配符匹配: " << re.exactMatch("a.txt.bak"); //false //匹配单词边界 QRegExp reg("\\b(hello|Hello)\\b"); qDebug() << "多个单词匹配: " << reg.indexIn("helloEveryone"); //-1表示失败 qDebug() << "多个单词匹配: " << reg.indexIn("Hmm Hello Everyone");//4 表示匹配到的字符位置 //匹配捕获的文本 //以 "(?:" 开始, 以 ")" 结束 QRegExp regHeight("(\\d+)(?:\\s*)(cm|inch)"); int res = regHeight.indexIn("zhangsan 170cm"); if(res > -1){ qDebug() << "regHeight(0):" << regHeight.cap(0); //170cm qDebug() << "regHeight(1):" << regHeight.cap(1); //170 qDebug() << "regHeight(2):" << regHeight.cap(2); //cm } //断言 (?!) 表示:不紧跟才能匹配 QRegExp regAssertFalse("面(?!包)"); QString str = "面包没了,只剩面条了"; str.replace(regAssertFalse, "龙虾鲍鱼"); qDebug() << str; //输出: "面包没了,只剩龙虾鲍鱼了" //断言 (?=) 表示:紧跟才匹配 QRegExp regAssertTrue("面(?=包)"); QString str1 = "面包没了,只剩面条了"; str1.replace(regAssertTrue, "草"); qDebug() << str1; //输出: "龙虾鲍鱼没了,只剩面条了"
qt5新类
//Qt5新类
QRegularExpression regExp("hello");
qDebug() << "QRegularExpression匹配字符: " <<regExp.match("hello world"); //输出(0, 5, "hello")
regExp.setPattern("([A-Z]{3,8})");
regExp.setPatternOptions(QRegularExpression::CaseInsensitiveOption); //大小写不敏感
qDebug() << "大小写不敏感匹配字符: " <<regExp.match("hello");
//新类捕获匹配
QRegularExpression regExp1("^(\\d\\d\\d\\d)/(\\d\\d)/(\\d\\d)$");
QRegularExpressionMatch match0 = regExp1.match("2022/04/04");
if(match0.isValid()){
QString strMatch0 = match0.captured(0);
QString year = match0.captured(1);
QString month = match0.captured(2);
QString day = match0.captured(3);
qDebug() << "日期: " << strMatch0;
qDebug() << "年: " << year;
qDebug() << "月: " << month;
qDebug() << "日: " << day;
}
QString sPattern;
sPattern = "^(Jan|Feb|Mar|Apr|May) \\d\\d \\d\\d\\d\\d$";
QRegularExpression regDate(sPattern);
QString ss("Feb 02 2022");
QRegularExpressionMatch dateMatch;
dateMatch = regDate.match(ss, 0,
QRegularExpression::PartialPreferCompleteMatch); //部分匹配
bool b_HasMatched = dateMatch.hasMatch(); //完整匹配的返回值
bool b_Partial = dateMatch.hasPartialMatch(); //部分匹配的返回值
qDebug() << b_HasMatched;
qDebug() << b_Partial;附正则表达式提取字符串中的数字方法 :
QString WndName("WndName1");
QRegExp rx("\\d+");
QString wndIndex;
rx.indexIn(WndName,0);
wndIndex=rx.cap(1);
qDebug()<<wndIndex;正则表达式从一个字符串里提取特定的字段或数据 例如从"a=100"里提取"a"和"100" :
QString pattern("(.*)=(.*)");
QRegExp rx(pattern);
QString str("a=100");
int pos = str.indexOf(rx); // 0, 第一个的位置
// 如果找不到str,则返回-1
// 你也可以使用rx.indexin(str)
qDebug() << pos;
if ( pos >= 0 )
{
qDebug() << rx.matchedLength(); // 5, 匹配字符串到最后的长度
// 或者-1如果没有匹配
qDebug() << rx.capturedTexts(); // QStringList("a=100", "a", "100"),
// 0: 文本匹配模式
// 1: 第一个()捕获的文本
// 2: 第二个文本的捕获
qDebug() << rx.cap(0); // a=100, 文本匹配模式
qDebug() << rx.cap(1); // a, 第n个()捕获的文本
qDebug() << rx.cap(2); // 100,
qDebug() << rx.pos(0); // 0, 第n个捕获文本的位置
qDebug() << rx.pos(1); // 0
qDebug() << rx.pos(2); // 2
}总结
到此这篇关于Qt正则表达式使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Qt正则表达式内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

C++ Boost MetaStateMachine定义状态机超详细讲解
Boost是为C++语言标准库提供扩展的一些C++程序库的总称。Boost库是一个可移植、提供源代码的C++库,作为标准库的后备,是C++标准化进程的开发引擎之一,是为C++语言标准库提供扩展的一些C++程序库的总称2022-12-12
















最新评论