Python使用Matplotlib实现创建动态图形
动态图形是使可视化更具吸引力和用户吸引力的好方法。它帮助我们以有意义的方式展示数据可视化。Python帮助我们使用现有强大的Python库创建动态图形可视化。Matplotlib是一个非常流行的数据可视化库,通常用于数据的图形表示,也用于使用内置函数的动态图形。
使用Matplotlib创建动态图形有两种方法:
- 使用pause()函数
- 使用FuncAnimation()函数
方法1:使用pause()函数
matplotlib库的pyplot模块中的pause()函数用于暂停参数中提到的间隔秒。考虑下面的例子,我们将使用matplotlib创建一个简单的线性图,并在其中显示Animation:
- 创建两个数组,X和Y,并存储从1到100的值。
- 使用plot()函数绘制X和Y。
- 添加pause()函数,并设置适当的时间间隔
- 运行程序,你会看到动态图形。
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt x = [] y = [] for i in range(100): x.append(i) y.append(i) # Mention x and y limits to define their range plt.xlim(0, 100) plt.ylim(0, 100) # Plotting graph plt.plot(x, y, color = 'green') plt.pause(0.01) plt.show()
方法2:使用FuncAnimation()函数
这个FuncAnimation()函数本身并不创建动画,而是从我们传递的一系列图形中创建动画。
语法: FuncAnimation(figure, animation_function, frames=None, init_func=None, fargs=None, save_count=None, *, cache_frame_data=True, **kwargs)
现在,您可以使用FuncAnimation函数制作多种类型的动画:
动态线性图形
在这个例子中,我们正在创建一个简单的线性图,它将显示一条直线的动画。同样,使用FuncAnimation,我们可以创建许多类型的动画视觉表示。我们只需要在一个函数中定义我们的动画,然后用合适的参数将其传递给FuncAnimation。
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation import numpy as np x = [] y = [] figure, ax = plt.subplots() # Setting limits for x and y axis ax.set_xlim(0, 100) ax.set_ylim(0, 12) # Since plotting a single graph line, = ax.plot(0, 0) def animation_function(i): x.append(i * 15) y.append(i) line.set_xdata(x) line.set_ydata(y) return line, animation = FuncAnimation(figure, func = animation_function, frames = np.arange(0, 10, 0.1), interval = 10) plt.show()
动态条形图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation, writers
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (7,5))
axes = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
axes.set_ylim(0, 300)
palette = ['blue', 'red', 'green',
'darkorange', 'maroon', 'black']
y1, y2, y3, y4, y5, y6 = [], [], [], [], [], []
def animation_function(i):
y1 = i
y2 = 5 * i
y3 = 3 * i
y4 = 2 * i
y5 = 6 * i
y6 = 3 * i
plt.xlabel("Country")
plt.ylabel("GDP of Country")
plt.bar(["India", "China", "Germany",
"USA", "Canada", "UK"],
[y1, y2, y3, y4, y5, y6],
color = palette)
plt.title("Bar Chart Animation")
animation = FuncAnimation(fig, animation_function,
interval = 50)
plt.show()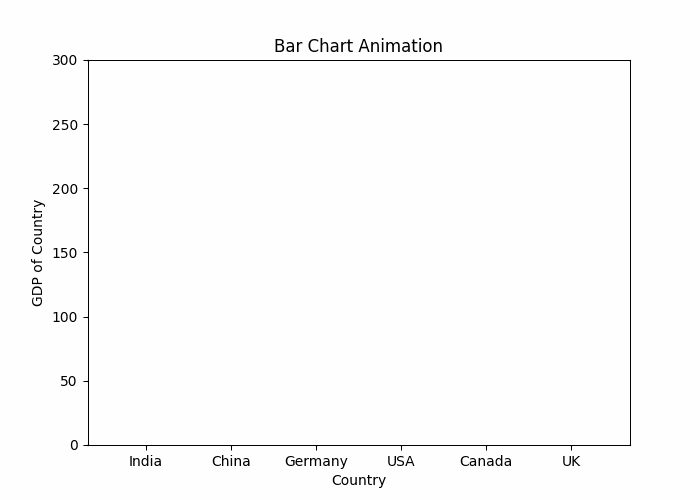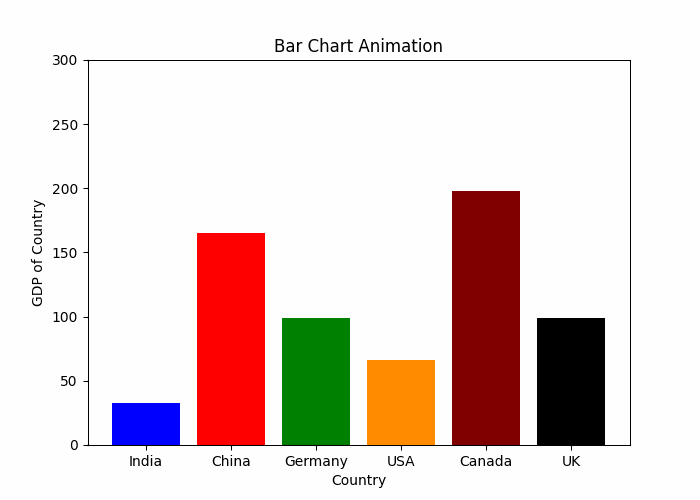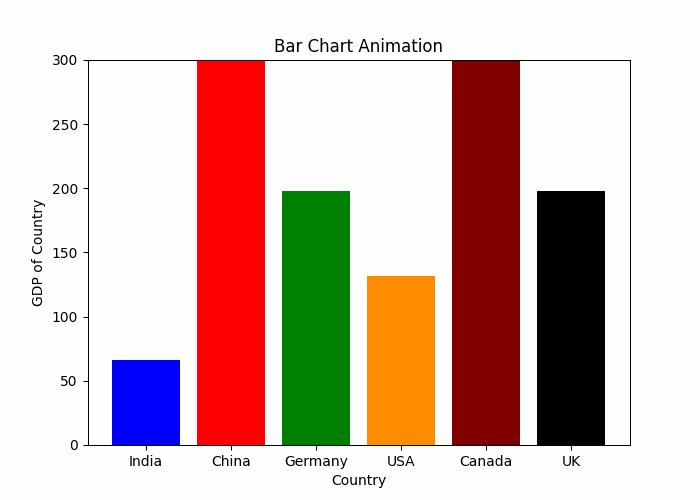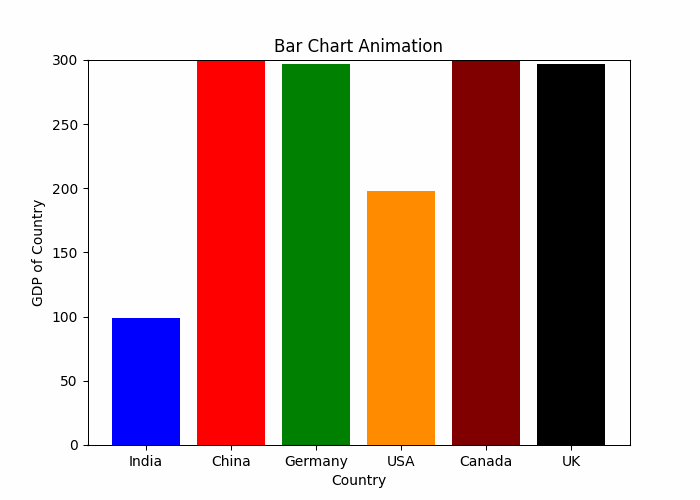
动态散点图
在这个例子中,我们将在python中使用random函数动态散点图。我们将迭代animation_func,在迭代的同时,我们将绘制x轴和y轴的随机值。
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation import random import numpy as np x = [] y = [] colors = [] fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7,5)) def animation_func(i): x.append(random.randint(0,100)) y.append(random.randint(0,100)) colors.append(np.random.rand(1)) area = random.randint(0,30) * random.randint(0,30) plt.xlim(0,100) plt.ylim(0,100) plt.scatter(x, y, c = colors, s = area, alpha = 0.5) animation = FuncAnimation(fig, animation_func, interval = 100) plt.show()
动态水平条形图
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
df = pd.read_csv('city_populations.csv',
usecols=['name', 'group', 'year', 'value'])
colors = dict(zip(['India','Europe','Asia',
'Latin America','Middle East',
'North America','Africa'],
['#adb0ff', '#ffb3ff', '#90d595',
'#e48381', '#aafbff', '#f7bb5f',
'#eafb50']))
group_lk = df.set_index('name')['group'].to_dict()
def draw_barchart(year):
dff = df[df['year'].eq(year)].sort_values(by='value',
ascending=True).tail(10)
ax.clear()
ax.barh(dff['name'], dff['value'],
color=[colors[group_lk[x]] for x in dff['name']])
dx = dff['value'].max() / 200
for i, (value, name) in enumerate(zip(dff['value'],
dff['name'])):
ax.text(value-dx, i, name,
size=14, weight=600,
ha='right', va='bottom')
ax.text(value-dx, i-.25, group_lk[name],
size=10, color='#444444',
ha='right', va='baseline')
ax.text(value+dx, i, f'{value:,.0f}',
size=14, ha='left', va='center')
# polished styles
ax.text(1, 0.4, year, transform=ax.transAxes,
color='#777777', size=46, ha='right',
weight=800)
ax.text(0, 1.06, 'Population (thousands)',
transform=ax.transAxes, size=12,
color='#777777')
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.StrMethodFormatter('{x:,.0f}'))
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', colors='#777777', labelsize=12)
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.margins(0, 0.01)
ax.grid(which='major', axis='x', linestyle='-')
ax.set_axisbelow(True)
ax.text(0, 1.12, 'The most populous cities in the world from 1500 to 2018',
transform=ax.transAxes, size=24, weight=600, ha='left')
ax.text(1, 0, 'by @pratapvardhan; credit @jburnmurdoch',
transform=ax.transAxes, ha='right', color='#777777',
bbox=dict(facecolor='white', alpha=0.8, edgecolor='white'))
plt.box(False)
plt.show()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15, 8))
animator = FuncAnimation(fig, draw_barchart,
frames = range(1990, 2019))
plt.show()
以上就是Python使用Matplotlib实现创建动态图形的详细内容,更多关于Python Matplotlib动态图形的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
相关文章

Python利用redis-py实现哈希数据类型的常用指令操作
这篇文章我们继续学习 “redis-py” 模块的一些关于 “哈希数据类型” 的相关指令用方法,比如利用 pyton 实现操作 “哈希表” 的数据、操作 “redis” 的事务等等2022-09-09












最新评论