用Firefox来Hacking Web 2.0程序(图)
互联网 发布时间:2008-10-08 19:37:54 作者:佚名  我要评论
我要评论
Introduction //简介
AJAX and interactive web services form the backbone of “web 2.0” applications. This technological transformation brings about new challenges for security professionals.
This article looks at some of the methods, tools and tric
Introduction //简介
AJAX and interactive web services form the backbone of “web 2.0” applications. This technological transformation brings about new challenges for security professionals.
This article looks at some of the methods, tools and tricks to dissect web 2.0 applications (including Ajax) and discover security holes using Firefox and its plugins. The key learning objectives of this article are to understand the:
* web 2.0 application architecture and its security concerns.
* hacking challenges such as discovering hidden calls, crawling issues, and Ajax side logic discovery.
* discovery of XHR calls with the Firebug tool.
* simulation of browser event automation with the Chickenfoot plugin.
* debugging of applications from a security standpoint, using the Firebug debugger.
* methodical approach to vulnerability detection.
Web 2.0 application overview
The newly coined term “web 2.0” refers to the next generation of web applications that have logically evolved with the adoption of new technological vectors. XML-driven web services that are running on SOAP, XML-RPC and REST are empowering server-side components. New applications offer powerful end-user interfaces by utilizing Ajax and rich internet application (Flash) components.
This technological shift has an impact on the overall architecture of web applications and the communication mechanism between client and server. At the same time, this shift has opened up new security concerns [ref 1] and challenges.
New worms such as Yamanner, Samy and Spaceflash are exploiting “client-side” AJAX frameworks, providing new avenues of attack and compromising confidential information.
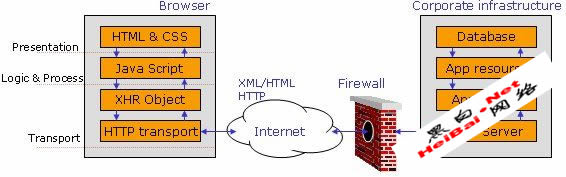
Figure 1. Web 2.0 architecture layout.
As shown in Figure 1, the browser processes on the left can be divided into the following layers:
* Presentation layer - HTML/CSS provides the overall appearance to the application in the browser window.
* Logic & Process - JavaScript running in the browser empowers applications to execute business and communication logic. AJAX-driven components reside in this layer.
* Transport - XMLHttpRequest (XHR) [ref 2]. This object empowers asynchronous communication capabilities and XML exchange mechanism between client and server over HTTP(S).
The server-side components on the right of Figure 1 that typically reside in the corporate infrastructure behind a firewall may include deployed web services along with traditional web application resources. An Ajax resource running on the browser can directly talk to XML-based web services and exchange information without refreshing the page. This entire communication is hidden from the end-user, in other words the end-user would not “feel” any redirects. The use of a “Refresh” and “Redirects” were an integral part of the first generation of web application logic. In the web 2.0 framework they are reduced substantially by implementing Ajax.
Web 2.0 assessment challenges
In this asynchronous framework, the application does not have many “Refreshes” and “Redirects”. As a result, many interesting server-side resources that can be exploited by an attacker are hidden. The following are three important challenges for security people trying to understand web 2.0 applications:
1. Discovering hidden calls - It is imperative that one identify XHR-driven calls generated by the loaded page in the browser. It uses JavaScript over HTTP(S) to make these calls to the backend servers.
2. Crawling challenges - Traditional crawler applications fail on two key fronts: one, to replicate browser behavior and two, to identify key server-side resources in the process. If a resource is accessed by an XHR object via JavaScript, then it is more than likely that the crawling application may not pick it up at all.
3. Logic discovery - Web applications today are loaded with JavaScript and it is difficult to isolate the logic for a particular event. Each HTML page may load three or four JavaScript resources from the server. Each of these files may have many functions, but the event may be using only a very small part of all these files for its execution logic.
We need to investigate and identify the methodology and tools to overcome these hurdles during a web application assessment. For the purpose of this article, we will use Firefox as our browser and try to leverage some of its plugins to combat the above challenges.
Discovering hidden calls
Web 2.0 applications may load a single page from the server but may make several XHR object calls when constructing the final page. These calls may pull content or JavaScript from the server asynchronously. In such a scenario, the challenge is to determine all XHR calls and resources pulled from the server. This is information that could help in identifying all possible resources and associated vulnerabilities. Let's start with a simple example.
Suppose we can get today’s business news by visiting a simple news portal located at:
http://example.com/news.aspx
The page in the browser would resemble the screenshot illustrated below in Figure 2.
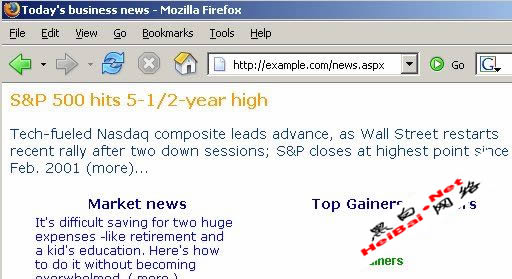
Being a web 2.0 application, Ajax calls are made to the server using an XHR object. We can determine these calls by using a tool known as Firebug [ref 3]. Firebug is a plug-in to the Firefox browser and has the ability to identify XHR object calls.
Prior to browsing a page with the plugin, ensure the option to intercept XHR calls is selected, as shown in Figure 3.
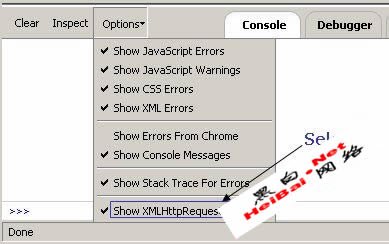
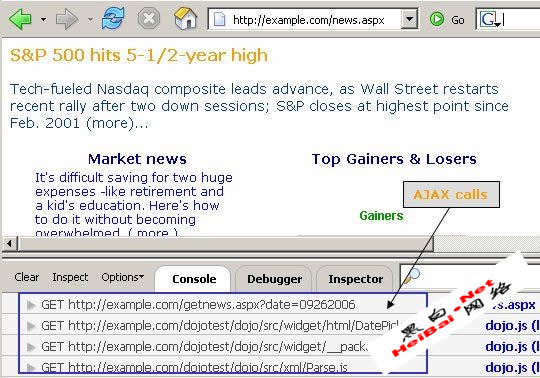
With the Firebug option to intercept XMLHttpRequest calls enabled, we browse the same page to discover all XHR object calls made by this particular page to the server. This exchange is shown in Figure 4.
AJAX and interactive web services form the backbone of “web 2.0” applications. This technological transformation brings about new challenges for security professionals.
This article looks at some of the methods, tools and tricks to dissect web 2.0 applications (including Ajax) and discover security holes using Firefox and its plugins. The key learning objectives of this article are to understand the:
* web 2.0 application architecture and its security concerns.
* hacking challenges such as discovering hidden calls, crawling issues, and Ajax side logic discovery.
* discovery of XHR calls with the Firebug tool.
* simulation of browser event automation with the Chickenfoot plugin.
* debugging of applications from a security standpoint, using the Firebug debugger.
* methodical approach to vulnerability detection.
Web 2.0 application overview
The newly coined term “web 2.0” refers to the next generation of web applications that have logically evolved with the adoption of new technological vectors. XML-driven web services that are running on SOAP, XML-RPC and REST are empowering server-side components. New applications offer powerful end-user interfaces by utilizing Ajax and rich internet application (Flash) components.
This technological shift has an impact on the overall architecture of web applications and the communication mechanism between client and server. At the same time, this shift has opened up new security concerns [ref 1] and challenges.
New worms such as Yamanner, Samy and Spaceflash are exploiting “client-side” AJAX frameworks, providing new avenues of attack and compromising confidential information.

Figure 1. Web 2.0 architecture layout.
As shown in Figure 1, the browser processes on the left can be divided into the following layers:
* Presentation layer - HTML/CSS provides the overall appearance to the application in the browser window.
* Logic & Process - JavaScript running in the browser empowers applications to execute business and communication logic. AJAX-driven components reside in this layer.
* Transport - XMLHttpRequest (XHR) [ref 2]. This object empowers asynchronous communication capabilities and XML exchange mechanism between client and server over HTTP(S).
The server-side components on the right of Figure 1 that typically reside in the corporate infrastructure behind a firewall may include deployed web services along with traditional web application resources. An Ajax resource running on the browser can directly talk to XML-based web services and exchange information without refreshing the page. This entire communication is hidden from the end-user, in other words the end-user would not “feel” any redirects. The use of a “Refresh” and “Redirects” were an integral part of the first generation of web application logic. In the web 2.0 framework they are reduced substantially by implementing Ajax.
Web 2.0 assessment challenges
In this asynchronous framework, the application does not have many “Refreshes” and “Redirects”. As a result, many interesting server-side resources that can be exploited by an attacker are hidden. The following are three important challenges for security people trying to understand web 2.0 applications:
1. Discovering hidden calls - It is imperative that one identify XHR-driven calls generated by the loaded page in the browser. It uses JavaScript over HTTP(S) to make these calls to the backend servers.
2. Crawling challenges - Traditional crawler applications fail on two key fronts: one, to replicate browser behavior and two, to identify key server-side resources in the process. If a resource is accessed by an XHR object via JavaScript, then it is more than likely that the crawling application may not pick it up at all.
3. Logic discovery - Web applications today are loaded with JavaScript and it is difficult to isolate the logic for a particular event. Each HTML page may load three or four JavaScript resources from the server. Each of these files may have many functions, but the event may be using only a very small part of all these files for its execution logic.
We need to investigate and identify the methodology and tools to overcome these hurdles during a web application assessment. For the purpose of this article, we will use Firefox as our browser and try to leverage some of its plugins to combat the above challenges.
Discovering hidden calls
Web 2.0 applications may load a single page from the server but may make several XHR object calls when constructing the final page. These calls may pull content or JavaScript from the server asynchronously. In such a scenario, the challenge is to determine all XHR calls and resources pulled from the server. This is information that could help in identifying all possible resources and associated vulnerabilities. Let's start with a simple example.
Suppose we can get today’s business news by visiting a simple news portal located at:
http://example.com/news.aspx
The page in the browser would resemble the screenshot illustrated below in Figure 2.

Being a web 2.0 application, Ajax calls are made to the server using an XHR object. We can determine these calls by using a tool known as Firebug [ref 3]. Firebug is a plug-in to the Firefox browser and has the ability to identify XHR object calls.
Prior to browsing a page with the plugin, ensure the option to intercept XHR calls is selected, as shown in Figure 3.

With the Firebug option to intercept XMLHttpRequest calls enabled, we browse the same page to discover all XHR object calls made by this particular page to the server. This exchange is shown in Figure 4.

相关文章
 CC主要是用来攻击页面的,大家都有这样的经历,就是在访问论坛时,如果这个论坛比较大,访问的人比较多,打开页面的速度会比较慢,对不?!一般来说,访问的人越多,论坛的页2024-01-06
CC主要是用来攻击页面的,大家都有这样的经历,就是在访问论坛时,如果这个论坛比较大,访问的人比较多,打开页面的速度会比较慢,对不?!一般来说,访问的人越多,论坛的页2024-01-06 入侵者主要通过Potato程序攻击拥有SYSTEM权限的端口伪造网络身份认证过程,利用NTLM重放机制骗取SYSTEM身份令牌,最终取得系统权限,该安全风险微软并不认为存在漏洞,所以2021-04-15
入侵者主要通过Potato程序攻击拥有SYSTEM权限的端口伪造网络身份认证过程,利用NTLM重放机制骗取SYSTEM身份令牌,最终取得系统权限,该安全风险微软并不认为存在漏洞,所以2021-04-15 这篇文章主要介绍了文件上传漏洞全面渗透分析小结,这里主要为大家分享一下防御方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2021-03-21
这篇文章主要介绍了文件上传漏洞全面渗透分析小结,这里主要为大家分享一下防御方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2021-03-21- 这篇文章主要介绍了sql手工注入语句&SQL手工注入大全,需要的朋友可以参考下2017-09-06
- 这篇文章主要介绍了详解Filezilla server 提权,需要的朋友可以参考下2017-05-13
FileZilla Server 2008 x64 提权与防御方法
这篇文章主要介绍了FileZilla Server 2008 x64 提权与防御方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2017-05-13- 不久之前我们说过关于http和https的区别,对于加密的https,我们一直认为它是相对安全的,可今天要讲的是,一种绕过HTTPS加密得到明文信息的web攻击方式,不知道这消息对你2016-08-10
iPhone和Mac也会被黑 一条iMessage密码可能就被盗了
一直以来苹果系统的安全性都是比安卓要高的,但是再安全的系统也免不了漏洞,苹果也一样。最近爆出的新漏洞,只需要接收一条多媒体信息或者iMessage就会导致用户信息泄露。2016-07-27- 国家正在修正关于黑客方面的法律法规,有一条震惊黑客圈的“世纪佳缘”起诉白帽黑客事件,深深的伤害了广大黑客们的心,加上扎克伯格和特拉维斯·卡兰尼克账号被盗,于是黑2016-07-11
如何逆向破解HawkEye keylogger键盘记录器进入攻击者邮箱
面对恶意邮件攻击,我们就只能默默忍受被他攻击,连自我保护能力都没有谈什么反抗?让人痛快的是,如今有了解决办法,逆向破解键盘记录器,进入攻击者邮箱2016-07-06



最新评论