用Firefox来Hacking Web 2.0程序(图)
互联网 发布时间:2008-10-08 19:37:54 作者:佚名  我要评论
我要评论
Introduction //简介
AJAX and interactive web services form the backbone of “web 2.0” applications. This technological transformation brings about new challenges for security professionals.
This article looks at some of the methods, tools and tric
Figure 7. Debugging with Firebug.
All JavaScript dependencies of this particular page can be viewed. Calls are made to the ajaxlib.js and validation.js scripts. These two scripts must have several functions. It can be deduced that the login process utilizes some of these functions. We can use a “breakpoint” to step through the entire application. Once a breakpoint is set, we can input credential information, click the “Submit” button and control the execution process. In our example, we have set a breakpoint in the “auth” function as shown in Figure 8.
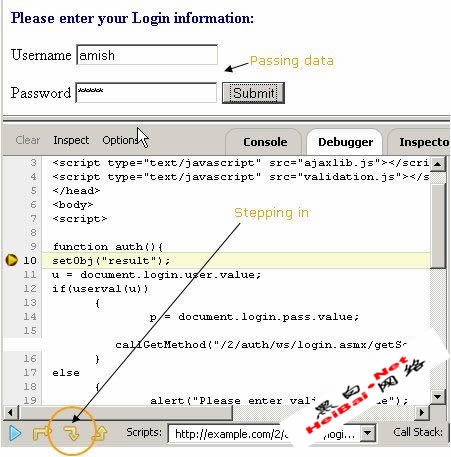
Figure 8. Setting a breakpoint and controlling execution process.
We now step through the debugging process by clicking the “step in” button, which was highlighted in Figure 8. JavaScript execution moves to another function, userval, residing in the file validation.js as shown in Figure 9.
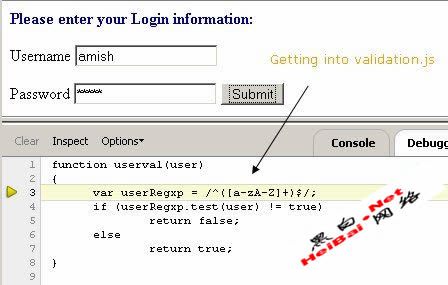
Figure 9. Moving to validation.js script page.
The preceding screenshot shows the regular expression pattern used to validate the username field. Once validation is done execution moves to another function callGetMethod as shown in Figure 10.

Finally, at the end of the execution sequence, we can observe the call to backend web services as being made by the XHR object. This is shown in Figure 11.
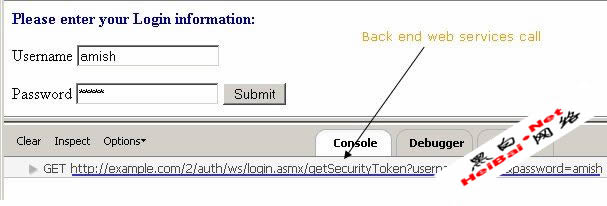
Figure 11. Web services call on the Firebug console.
Here we have identified the resource location for the backend web services:
http://example.com/2/auth/ws/login.asmx/getSecurityToken?username=amish&password=amish
The preceding resource is clearly some web services running under the .NET framework. This entire dissection process has thrown up an interesting detail: we've found a user validation routine that can be bypassed very easily. It is a potential security threat to the web application.
Taking our assessment further, we can now access the web service and its endpoints by using a WSDL file and directly bruteforce the service. We can launch several different injection attacks - SQL or XPATH - with tools such as wsChess [ref 7].
In this particular case, the application is vulnerable to an XPATH injection. The methodology for web services assessment overall is different and is outside the scope of this article. However this walkthrough technique helps identify several client-side attacks such as XSS, DOM manipulation attacks, client-side security control bypassing, malicious Ajax code execution, and so on.
Conclusion
Service-oriented architecture (SOA), Ajax, Rich Internet Applications (RIA) and web services are critical components to next generation web applications. To keep pace with these technologies and combat next-generation application security challenges, one needs to design and develop different methodologies and tools. One of the efficient methodologies of assessing applications is by effectively using a browser.
In this article we have seen three techniques to assess web 2.0 applications. By using these methodologies it is possible to identify and isolate several Ajax-related vulnerabilities. Browser automation scripting can assist us in web asset profiling and discovery, that in turn can help in identifying vulnerable server-side resources.
Next generation applications use JavaScript extensively. Smooth debugging tools are our knights in shining armor. The overall techniques covered in this article is a good starting point for web 2.0 assessments using Firefox.
References
[ref 1] Ajax security,
http://www.securityfocus.com/infocus/1868
[ref 2] XHR Object specification, http://www.w3.org/TR/XMLHttpRequest/
[ref 3] Firebug download, https://addons.mozilla.org/firefox/1843/; Firebug usage, http://www.joehewitt.com/software/firebug/docs.php
[ref 4] Chickenfoot quick start, http://groups.csail.mit.edu/uid/chickenfoot/quickstart.html
[ref 5] Chickenfoot API reference - http://groups.csail.mit.edu/uid/chickenfoot/api.html
[ref 6] Venkman walkthrough, http://www.mozilla.org/projects/venkman/venkman-walkthrough.html
[ref 7] wsChess, http://net-square.com/wschess
About the author
Shreeraj Shah, BE, MSCS, MBA, is the founder of Net Square and leads Net Square’s consulting, training and R&D activities. He previously worked with Foundstone, Chase Manhattan Bank and IBM. He is also the author of Hacking Web Services (Thomson) and co-author of Web Hacking: Attacks and Defense (Addison-Wesley). In addition, he has published several advisories, tools, and whitepapers, and has presented at numerous conferences including RSA, AusCERT, InfosecWorld (Misti), HackInTheBox, Blackhat, OSCON, Bellua, Syscan, etc. You can read his blog at http://shreeraj.blogspot.com/.
All JavaScript dependencies of this particular page can be viewed. Calls are made to the ajaxlib.js and validation.js scripts. These two scripts must have several functions. It can be deduced that the login process utilizes some of these functions. We can use a “breakpoint” to step through the entire application. Once a breakpoint is set, we can input credential information, click the “Submit” button and control the execution process. In our example, we have set a breakpoint in the “auth” function as shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8. Setting a breakpoint and controlling execution process.
We now step through the debugging process by clicking the “step in” button, which was highlighted in Figure 8. JavaScript execution moves to another function, userval, residing in the file validation.js as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9. Moving to validation.js script page.
The preceding screenshot shows the regular expression pattern used to validate the username field. Once validation is done execution moves to another function callGetMethod as shown in Figure 10.

Finally, at the end of the execution sequence, we can observe the call to backend web services as being made by the XHR object. This is shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11. Web services call on the Firebug console.
Here we have identified the resource location for the backend web services:
http://example.com/2/auth/ws/login.asmx/getSecurityToken?username=amish&password=amish
The preceding resource is clearly some web services running under the .NET framework. This entire dissection process has thrown up an interesting detail: we've found a user validation routine that can be bypassed very easily. It is a potential security threat to the web application.
Taking our assessment further, we can now access the web service and its endpoints by using a WSDL file and directly bruteforce the service. We can launch several different injection attacks - SQL or XPATH - with tools such as wsChess [ref 7].
In this particular case, the application is vulnerable to an XPATH injection. The methodology for web services assessment overall is different and is outside the scope of this article. However this walkthrough technique helps identify several client-side attacks such as XSS, DOM manipulation attacks, client-side security control bypassing, malicious Ajax code execution, and so on.
Conclusion
Service-oriented architecture (SOA), Ajax, Rich Internet Applications (RIA) and web services are critical components to next generation web applications. To keep pace with these technologies and combat next-generation application security challenges, one needs to design and develop different methodologies and tools. One of the efficient methodologies of assessing applications is by effectively using a browser.
In this article we have seen three techniques to assess web 2.0 applications. By using these methodologies it is possible to identify and isolate several Ajax-related vulnerabilities. Browser automation scripting can assist us in web asset profiling and discovery, that in turn can help in identifying vulnerable server-side resources.
Next generation applications use JavaScript extensively. Smooth debugging tools are our knights in shining armor. The overall techniques covered in this article is a good starting point for web 2.0 assessments using Firefox.
References
[ref 1] Ajax security,
http://www.securityfocus.com/infocus/1868
[ref 2] XHR Object specification, http://www.w3.org/TR/XMLHttpRequest/
[ref 3] Firebug download, https://addons.mozilla.org/firefox/1843/; Firebug usage, http://www.joehewitt.com/software/firebug/docs.php
[ref 4] Chickenfoot quick start, http://groups.csail.mit.edu/uid/chickenfoot/quickstart.html
[ref 5] Chickenfoot API reference - http://groups.csail.mit.edu/uid/chickenfoot/api.html
[ref 6] Venkman walkthrough, http://www.mozilla.org/projects/venkman/venkman-walkthrough.html
[ref 7] wsChess, http://net-square.com/wschess
About the author
Shreeraj Shah, BE, MSCS, MBA, is the founder of Net Square and leads Net Square’s consulting, training and R&D activities. He previously worked with Foundstone, Chase Manhattan Bank and IBM. He is also the author of Hacking Web Services (Thomson) and co-author of Web Hacking: Attacks and Defense (Addison-Wesley). In addition, he has published several advisories, tools, and whitepapers, and has presented at numerous conferences including RSA, AusCERT, InfosecWorld (Misti), HackInTheBox, Blackhat, OSCON, Bellua, Syscan, etc. You can read his blog at http://shreeraj.blogspot.com/.
相关文章
 CC主要是用来攻击页面的,大家都有这样的经历,就是在访问论坛时,如果这个论坛比较大,访问的人比较多,打开页面的速度会比较慢,对不?!一般来说,访问的人越多,论坛的页2024-01-06
CC主要是用来攻击页面的,大家都有这样的经历,就是在访问论坛时,如果这个论坛比较大,访问的人比较多,打开页面的速度会比较慢,对不?!一般来说,访问的人越多,论坛的页2024-01-06 入侵者主要通过Potato程序攻击拥有SYSTEM权限的端口伪造网络身份认证过程,利用NTLM重放机制骗取SYSTEM身份令牌,最终取得系统权限,该安全风险微软并不认为存在漏洞,所以2021-04-15
入侵者主要通过Potato程序攻击拥有SYSTEM权限的端口伪造网络身份认证过程,利用NTLM重放机制骗取SYSTEM身份令牌,最终取得系统权限,该安全风险微软并不认为存在漏洞,所以2021-04-15 这篇文章主要介绍了文件上传漏洞全面渗透分析小结,这里主要为大家分享一下防御方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2021-03-21
这篇文章主要介绍了文件上传漏洞全面渗透分析小结,这里主要为大家分享一下防御方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2021-03-21- 这篇文章主要介绍了sql手工注入语句&SQL手工注入大全,需要的朋友可以参考下2017-09-06
- 这篇文章主要介绍了详解Filezilla server 提权,需要的朋友可以参考下2017-05-13
FileZilla Server 2008 x64 提权与防御方法
这篇文章主要介绍了FileZilla Server 2008 x64 提权与防御方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2017-05-13- 不久之前我们说过关于http和https的区别,对于加密的https,我们一直认为它是相对安全的,可今天要讲的是,一种绕过HTTPS加密得到明文信息的web攻击方式,不知道这消息对你2016-08-10
iPhone和Mac也会被黑 一条iMessage密码可能就被盗了
一直以来苹果系统的安全性都是比安卓要高的,但是再安全的系统也免不了漏洞,苹果也一样。最近爆出的新漏洞,只需要接收一条多媒体信息或者iMessage就会导致用户信息泄露。2016-07-27- 国家正在修正关于黑客方面的法律法规,有一条震惊黑客圈的“世纪佳缘”起诉白帽黑客事件,深深的伤害了广大黑客们的心,加上扎克伯格和特拉维斯·卡兰尼克账号被盗,于是黑2016-07-11
如何逆向破解HawkEye keylogger键盘记录器进入攻击者邮箱
面对恶意邮件攻击,我们就只能默默忍受被他攻击,连自我保护能力都没有谈什么反抗?让人痛快的是,如今有了解决办法,逆向破解键盘记录器,进入攻击者邮箱2016-07-06



最新评论